Question: This will use almost all the knowledge about GUI we covered in this class. Particularly, we are going to write a program that draws a
This will use almost all the knowledge about GUI we covered in this class. Particularly, we are going to write a program that draws a Sudoku board with buttons, combobox on the side, and a text area at the bottom for output messages. The board itself is a 9 x 9 square, divided into 9 3x3 squares. Note that each smaller square is set off by a heavier border than the regular intersquare borders. Each square is a text field. So, the user is able to type an integer number (range from 0-9). On the side there are four buttons and a combobox. The four buttons allow you to solve, get a new puzzle, get a hint, or reset puzzle; the combobox lets you to choose difficulty level. We havent covered the combobox in details in the class. Thus, we will give a brief introduction here:
A JComboBox is a gadget that offers a set of predefined items of selection. To add items to the combobox, you can do one at a time, like:
JComboBox jCmb = new JComboBox();
jCmb.addItem(Novel);
Or do it in a batch mode when the object is created (three items are created), like:
String[] difficulties = { Easy, Medium, Hard };JComboBox difficultyBox = new JComboBox(difficulties);
To set a default item (make the item active (displayed)), you can use the setSelectedIndex() method. For example, the following segment of code will make Medium to be selected:
String[] difficulties = { Easy, Medium, Hard };//Create the combo box, select item at index 1.
//Indices start at 0, so 1 specifies Medium.
JComboBox difficultyBox = new JComboBox(difficulties);
difficultyBox.setSelectedIndex(1);
To get a selected item, you can use the following:
String s = (String)jCmb.getSelectedItem();
Note: you must use a cast before the assignment.
When a user selects one item from a combobox, it will generate two events:
ActionEvent (its corresponding method is actionPerformed()) and ItemEvent (its corresponding method is itemStateChanged()).
The JComboBox class has multiple constructors. Besides the one that takes one parameter, there is another one that takes no parameter.
To demonstrate the responses of our program, we use a text area as an output gadget. In this case, we use a titled border to single out the gadget. The caption text is Output Area as shown in Figure 1. The following segment of code shows how we can achieve this and use the text area to display the message Hi, world!.
JTextArea jtxtar = new JTextArea(30, 20);
Jtxtar.setBorder(BorderFactory.creatTitledBOrder(Output Area));
jtxtar.setText(Hi, world!);
Figure 1 shows the picture of the layout of the application:
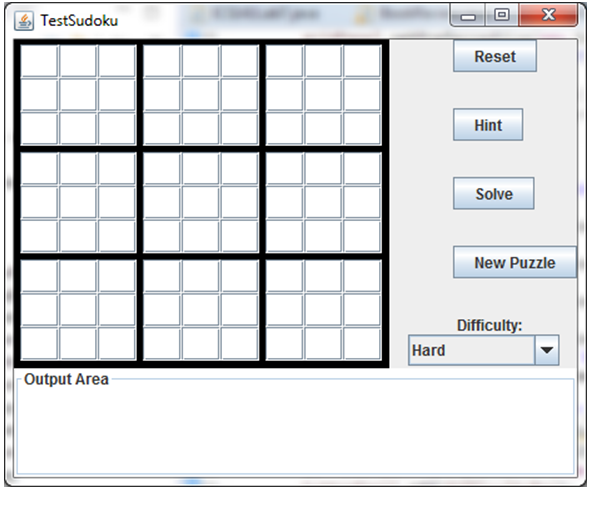
Requirements
This program has a lot of things to specify. Thus, I am going to divide the requirements into two areas: the layout requirements and the general requirements.
1)Layout Requirements
A. To make the GUI interface look nice, we need multiple layout managers to work together. Specifically, we ask you to use the requirements specified in Figure 2 as your layout design.
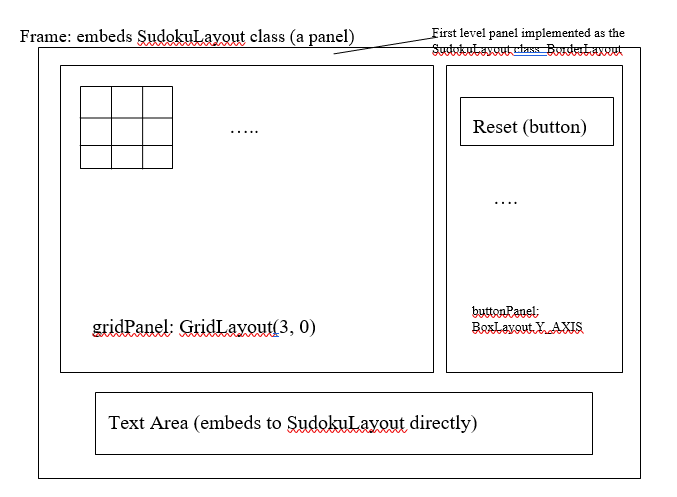
The SudokuLayout class (itself is a child of panel) is the first layer panel. Suggested dimension for this panel should be (450, 350). At the bottom of the Sudoku, there is a text area. This gadget has certain size. The following lines show how we can achieve this:
txtArea = new JTextArea(4, 20);
add(txtArea, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
As indicated in Figure 2, the frame embeds this panel as the first level organizer. The layout managers used by each panel should be the ones indicated by the above diagram. You should set borders for some containers as indicated in the above diagram.
Use two for loops to draw the text fields instead of brute-force of listing 81 text fields. You should do something like:
for (int k = 1; k
{
JPanel level2 = new JPanel();
.
for (int i = 1; i
{
JTextField text = new JTextField();
}
gridPanel.add(level2);
}
Note: the for-loops implementation saves you many lines of code but there is one shortcoming: cannot refer text field individually. Since we are focusing on the layout, the for-loop method is preferred.
For the Combobox, you should set Hard as its initial selected item (using program code).
2) General Requirements
A. To use two classes to implement the application: an application class named TestSudoku and a work class named SudokuLayout.
B. I do not expect you to implement every visual gadget. But I do expect you to implement some selected visual gadgets. Please implement the following visual gadgets and write listeners for them. These gadgets have the following behaviors:
Button Reset---when the button is clicked, the program will clear the text area, then output the string Reset button clicked! to the text area.
Button Hint---when the button is clicked, the program will clear the text area, then output the string Hint button clicked! to the text area.
Combobox Difficulty---when an item is selected, the program will clear the text area, then output the selected item name to the text area.
C. You should implement the listeners using loosely coupled methods (private listener class or private adapter class).
Notes
Dont worry about colors. If you want to play around with colors for text, textfields, buttons, etc., go right ahead. Have fun. But dont worry about it if you dont want to.
The borders around the game board, around the 3x3 sections, and around each individual square, are important. You should follow the requirement to get full credits.
2. Cut and paste your Java source code in the space below:
? TestSudoku Reset Solve New Puzzle Hard Output Area
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


