Question: Three different objects, all with different masses, are initially at rest at the bottom of a set of steps. Each step is of uniform
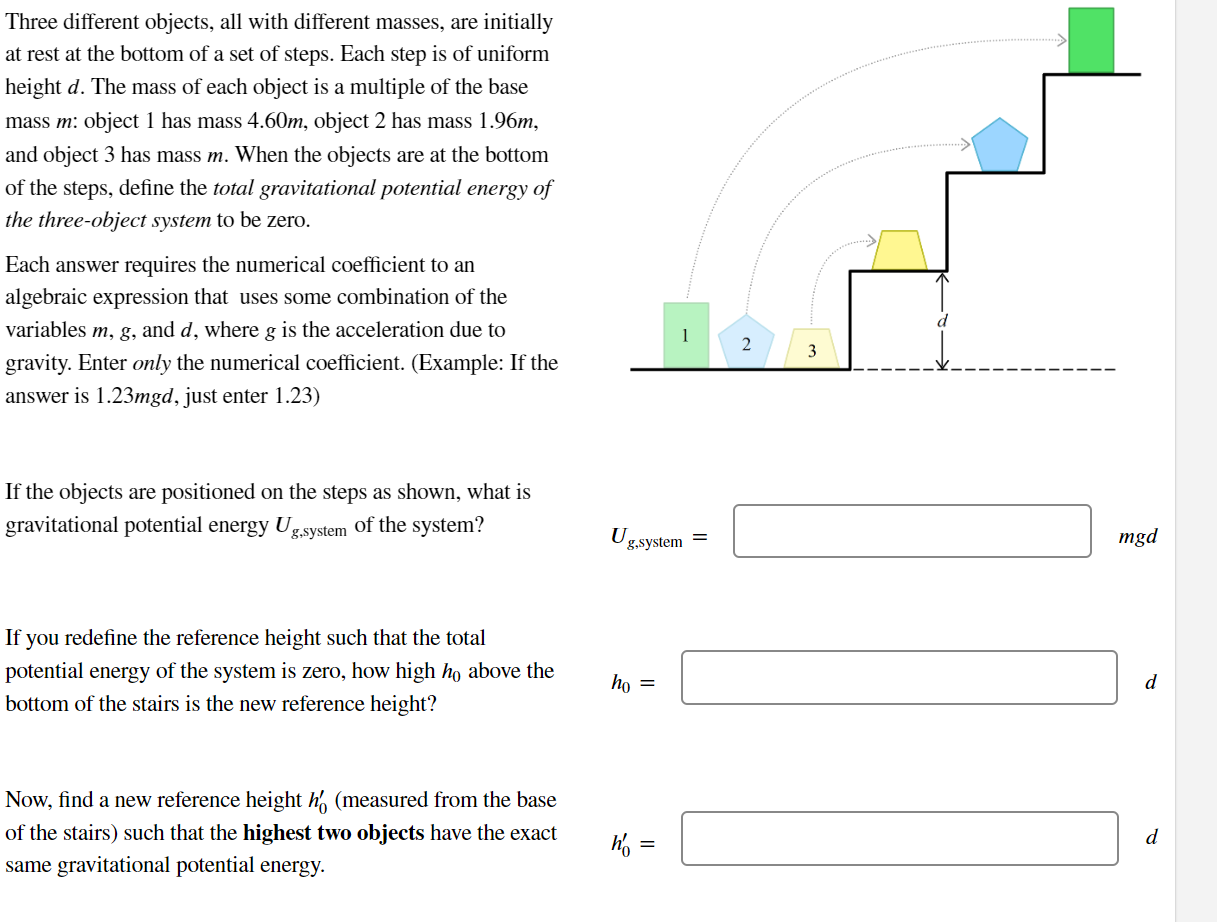
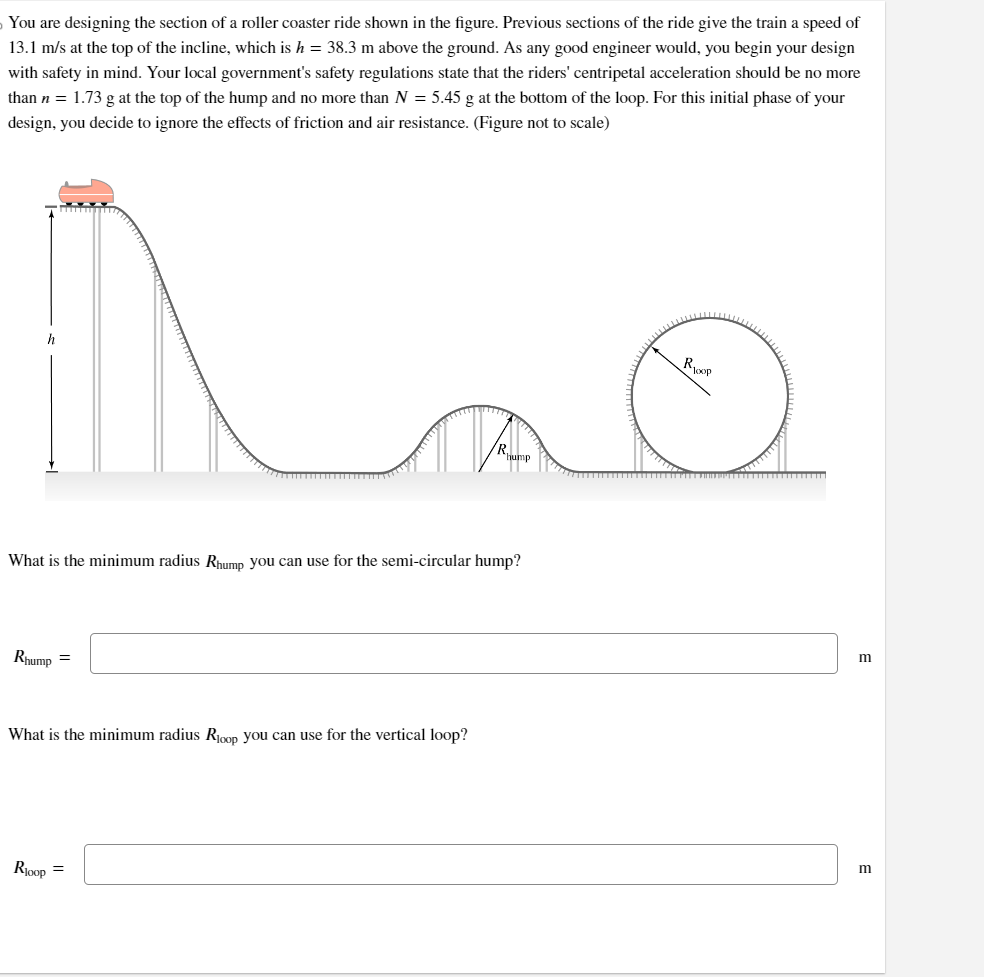
Three different objects, all with different masses, are initially at rest at the bottom of a set of steps. Each step is of uniform height d. The mass of each object is a multiple of the base mass m: object 1 has mass 4.60m, object 2 has mass 1.96m, and object 3 has mass m. When the objects are at the bottom of the steps, define the total gravitational potential energy of the three-object system to be zero. Each answer requires the numerical coefficient to an algebraic expression that uses some combination of the variables m, g, and d, where g is the acceleration due to gravity. Enter only the numerical coefficient. (Example: If the answer is 1.23mgd, just enter 1.23) If the objects are positioned on the steps as shown, what is gravitational potential energy Ug of the system? g.system Ug,system = 2 3 mgd If you redefine the reference height such that the total potential energy of the system is zero, how high ho above the bottom of the stairs is the new reference height? d ho = Now, find a new reference height ho (measured from the base of the stairs) such that the highest two objects have the exact same gravitational potential energy. h = d You are designing the section of a roller coaster ride shown in the figure. Previous sections of the ride give the train a speed of 13.1 m/s at the top of the incline, which is h = 38.3 m above the ground. As any good engineer would, you begin your design with safety in mind. Your local government's safety regulations state that the riders' centripetal acceleration should be no more than n = 1.73 g at the top of the hump and no more than N = 5.45 g at the bottom of the loop. For this initial phase of your design, you decide to ignore the effects of friction and air resistance. (Figure not to scale) h What is the minimum radius Rhump you can use for the semi-circular hump? Rhump What is the minimum radius Roop you can use for the vertical loop? Rloop = Roop m m
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


