Question: To be done in Python: 6. Pascal's Triangle The triangular array of numbers in Fig. 6.33 is called Pascal's triangle, in honor of the seventeenth
To be done in Python:
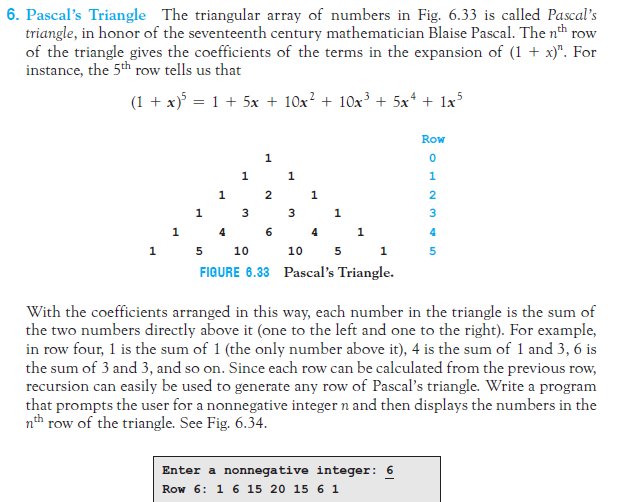
6. Pascal's Triangle The triangular array of numbers in Fig. 6.33 is called Pascal's triangle, in honor of the seventeenth century mathematician Blaise Pascal. The nt row of the triangle gives the coefficients of the terms in the expansion of (1 + x)". For instance, the 5th row tells us that (1 + x)5-1 + 5x + 10x2 + 10x3 5x4 1x5 1 2 5 10 10 5 FIQURE 6.33 Pascal's Triangle. With the coefficients arranged in this way, each number in the triangle is the sum of the two numbers directly above it (one to the left and one to the right). For example, in row four, 1 is the sum of 1 (the only number above it), 4 is the sum of and 3, 6 is the sum of 3 and 3, and so on. Since each row can be calculated from the previous row, recursion can easily be used to generate any row of Pascal's triangle. Write a program that prompts the user for a nonnegative integer n and then displays the numbers in the nth row of the triangle. See Fig, 6.34 Enter a nonnegative integer: 6 Row 6: 1 6 15 20 15 6 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


