Question: To prepare for this assignment, review Figures 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.5, and 3.6 from Grant, R. M. (2019). Contemporary strategy analysis (10th ed.). Select a
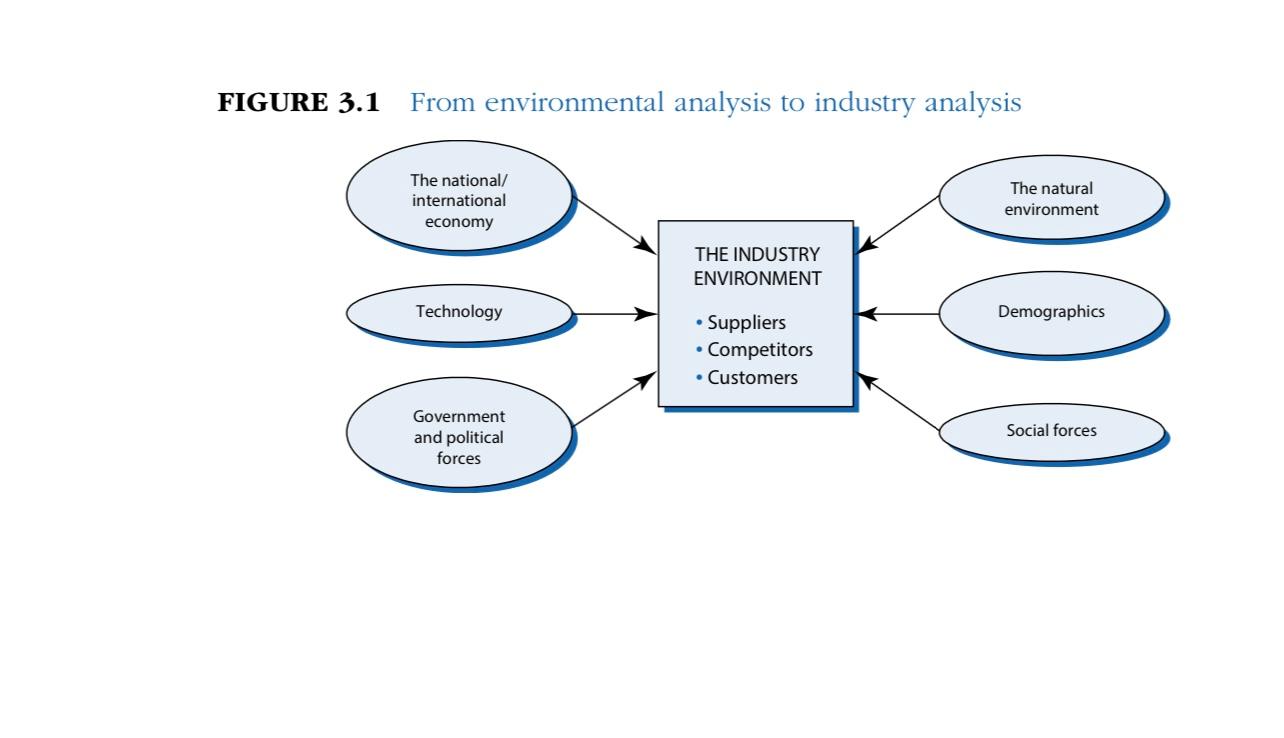
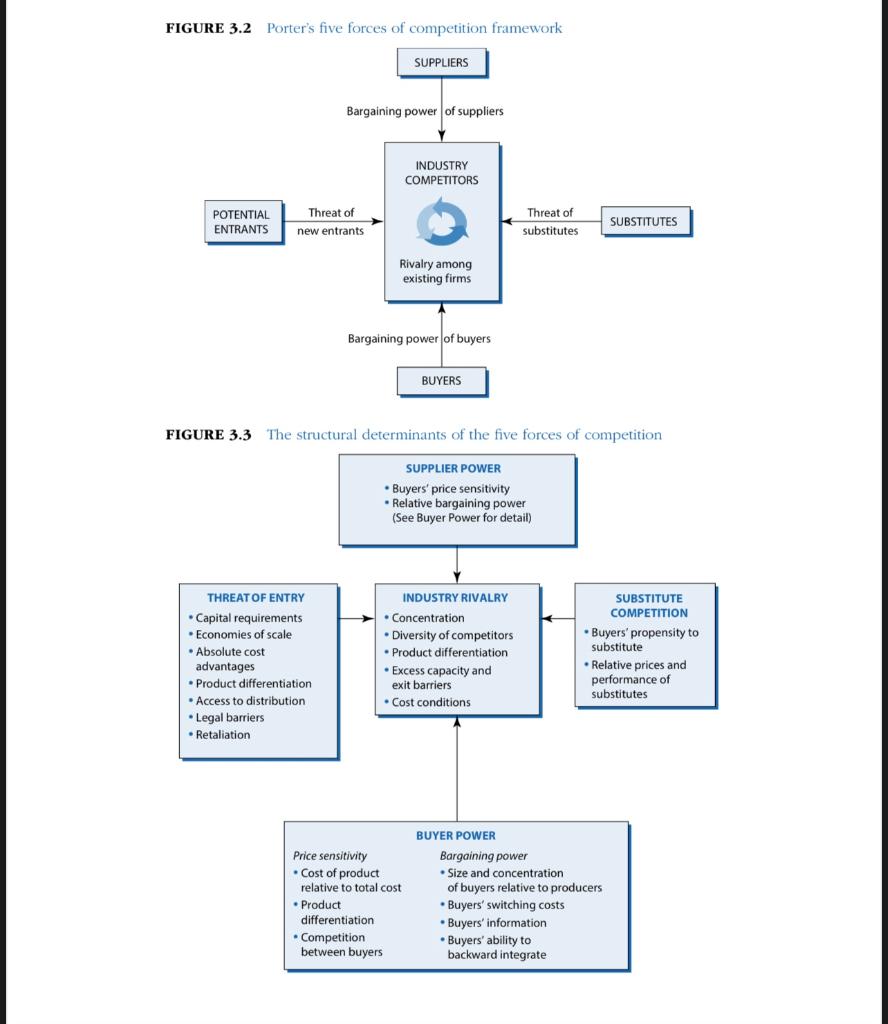
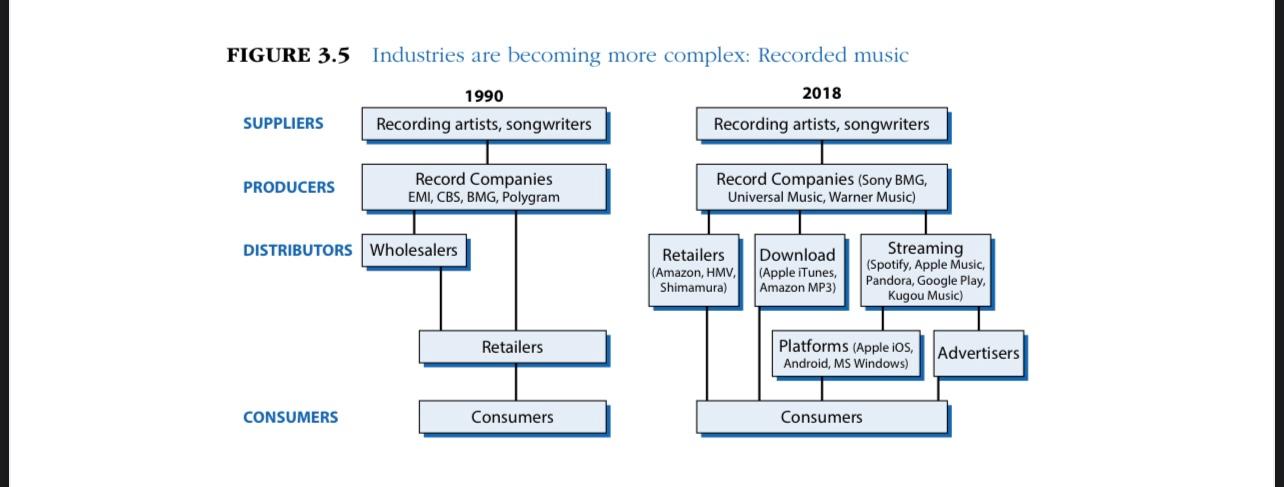
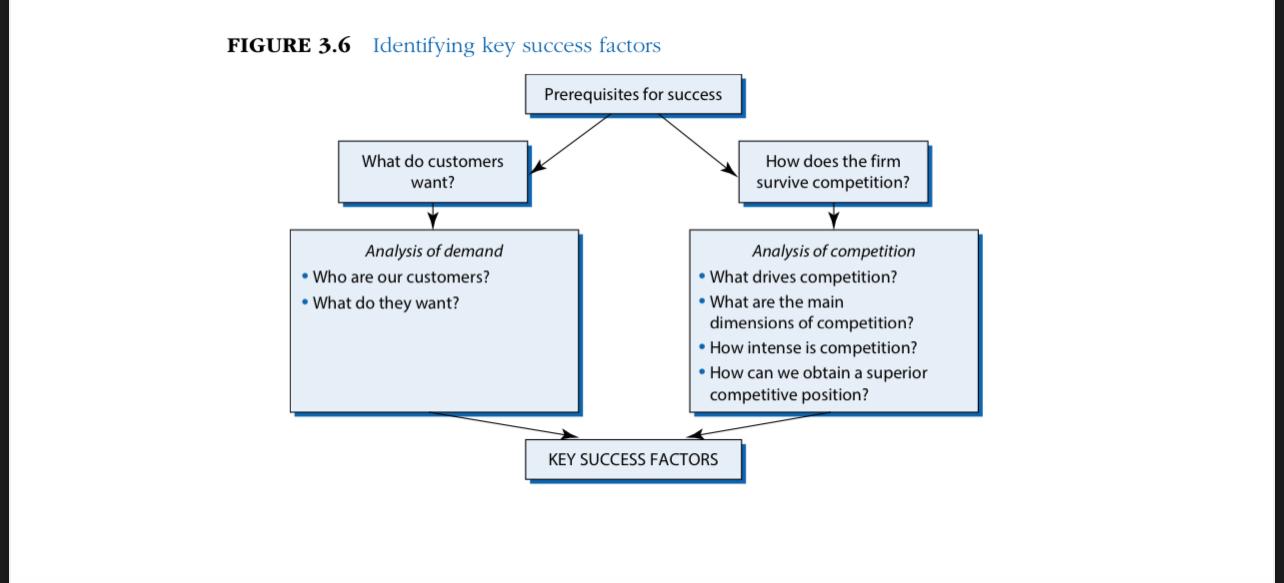
To prepare for this assignment, review Figures 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.5, and 3.6 from Grant, R. M. (2019). Contemporary strategy analysis (10th ed.). Select a Saudi Arabian company, identify the industry in which it competes, and identify its three main competitors. Complete an Industry Analysis by answering the following questions.
- Analyze and predict industry profitability:
- Apply a detailed Porters Five Forces framework with a graphic representation (Figure 3.3) and written explanation for your selected company in relation to the Five Forces.
- Given the Five Forces analysis outcomes, predict the level of industry profitability expressed as high, intermediate, or low.
- Implications for strategy:
- What strategies can the rival companies adopt to reduce competitive pressure and improve industry profitability?
- Which strategies do you recommend for your company to improve its competitiveness, position, and earnings?
- Identifying Key Success Factors (KSFs)What are the KSFs of your company?
- See Figure 3.6. Who are the customers and what do they want?
- See Figure 3.6. How does the company survive competition?
- Has your companys KSFs changed over time?
Your well-written paper should meet the following requirements:
- Be 6 to 7 pages in length,
FIGURE 3.1 From environmental analysis to industry analysis The national/ international economy The natural environment THE INDUSTRY ENVIRONMENT Technology Demographics Suppliers Competitors Customers Government and political forces Social forces FIGURE 3.2 Porter's five forces of competition framework SUPPLIERS Bargaining power of suppliers INDUSTRY COMPETITORS POTENTIAL ENTRANTS Threat of new entrants Threat of substitutes SUBSTITUTES Rivalry among existing firms Bargaining power of buyers BUYERS FIGURE 3.3 The structural determinants of the five forces of competition SUPPLIER POWER Buyers' price sensitivity . Relative bargaining power (See Buyer Power for detail) THREAT OF ENTRY Capital requirements Economies of scale Absolute cost advantages Product differentiation Access to distribution Legal barriers Retaliation INDUSTRY RIVALRY Concentration Diversity of competitors Product differentiation Excess capacity and exit barriers Cost conditions SUBSTITUTE COMPETITION Buyers' propensity to substitute Relative prices and performance of substitutes Price sensitivity Cost of product relative to total cost Product differentiation Competition between buyers BUYER POWER Bargaining power Size and concentration of buyers relative to producers Buyers' switching costs Buyers' information Buyers' ability to backward integrate FIGURE 3.5 Industries are becoming more complex: Recorded music 2018 1990 Recording artists, songwriters SUPPLIERS Recording artists, songwriters PRODUCERS Record Companies EMI, CBS, BMG, Polygram Record Companies (Sony BMG, Universal Music, Warner Music) DISTRIBUTORS Wholesalers Retailers (Amazon, HMV, Shimamura) Download (Apple iTunes, Amazon MP3) Streaming (Spotify, Apple Music Pandora, Google Play Kugou Music) Retailers Platforms (Apple iOS, Android, MS Windows) Advertisers CONSUMERS Consumers Consumers FIGURE 3.6 Identifying key success factors Prerequisites for success What do customers want? How does the firm survive competition? Analysis of demand Who are our customers? What do they want? Analysis of competition What drives competition? What are the main dimensions of competition? How intense is competition? How can we obtain a superior competitive position? KEY SUCCESS FACTORS FIGURE 3.1 From environmental analysis to industry analysis The national/ international economy The natural environment THE INDUSTRY ENVIRONMENT Technology Demographics Suppliers Competitors Customers Government and political forces Social forces FIGURE 3.2 Porter's five forces of competition framework SUPPLIERS Bargaining power of suppliers INDUSTRY COMPETITORS POTENTIAL ENTRANTS Threat of new entrants Threat of substitutes SUBSTITUTES Rivalry among existing firms Bargaining power of buyers BUYERS FIGURE 3.3 The structural determinants of the five forces of competition SUPPLIER POWER Buyers' price sensitivity . Relative bargaining power (See Buyer Power for detail) THREAT OF ENTRY Capital requirements Economies of scale Absolute cost advantages Product differentiation Access to distribution Legal barriers Retaliation INDUSTRY RIVALRY Concentration Diversity of competitors Product differentiation Excess capacity and exit barriers Cost conditions SUBSTITUTE COMPETITION Buyers' propensity to substitute Relative prices and performance of substitutes Price sensitivity Cost of product relative to total cost Product differentiation Competition between buyers BUYER POWER Bargaining power Size and concentration of buyers relative to producers Buyers' switching costs Buyers' information Buyers' ability to backward integrate FIGURE 3.5 Industries are becoming more complex: Recorded music 2018 1990 Recording artists, songwriters SUPPLIERS Recording artists, songwriters PRODUCERS Record Companies EMI, CBS, BMG, Polygram Record Companies (Sony BMG, Universal Music, Warner Music) DISTRIBUTORS Wholesalers Retailers (Amazon, HMV, Shimamura) Download (Apple iTunes, Amazon MP3) Streaming (Spotify, Apple Music Pandora, Google Play Kugou Music) Retailers Platforms (Apple iOS, Android, MS Windows) Advertisers CONSUMERS Consumers Consumers FIGURE 3.6 Identifying key success factors Prerequisites for success What do customers want? How does the firm survive competition? Analysis of demand Who are our customers? What do they want? Analysis of competition What drives competition? What are the main dimensions of competition? How intense is competition? How can we obtain a superior competitive position? KEY SUCCESS FACTORS








