Question: Topic 2.1A Circular Flow Instructions: Below is a simplified version of the circular flow diagram. Identify economic actors, flows, and markets, then answer question 5.
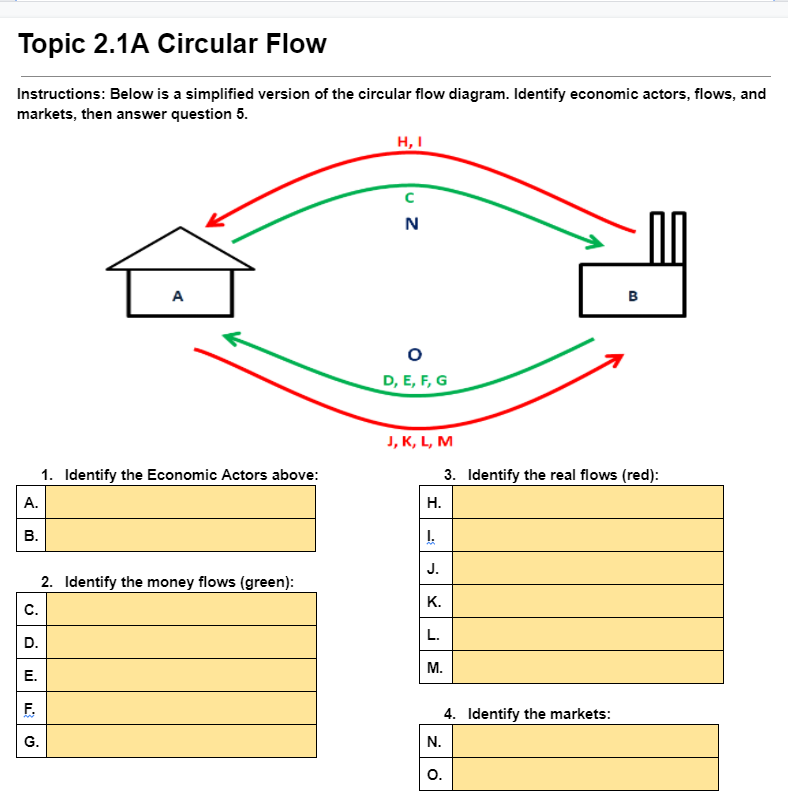
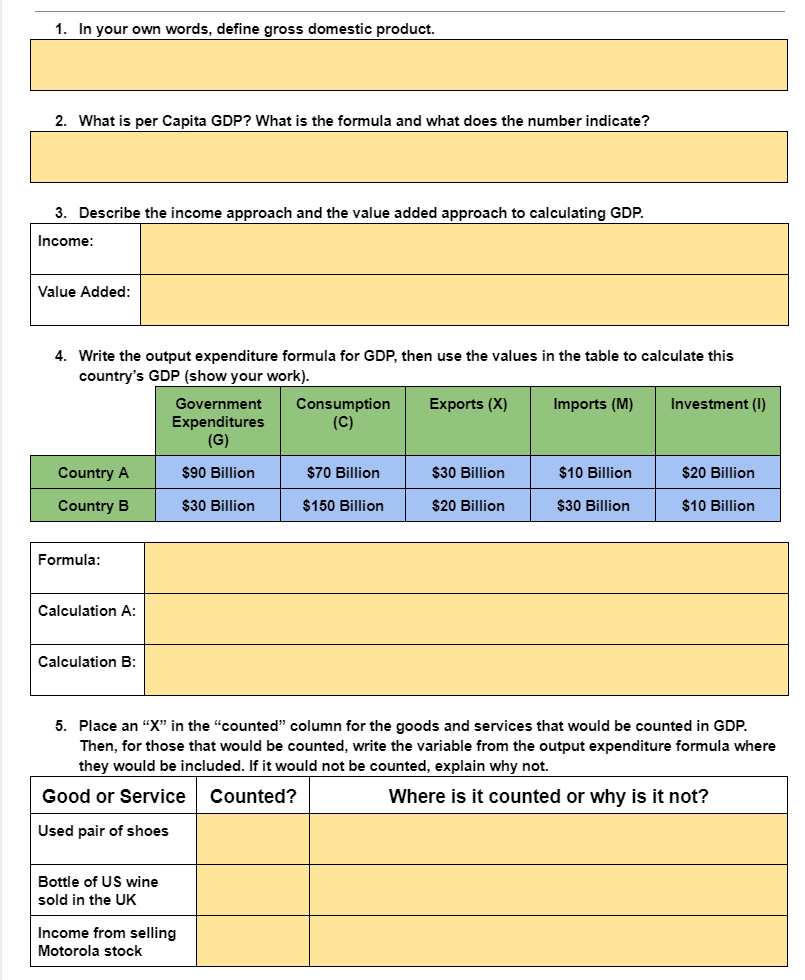
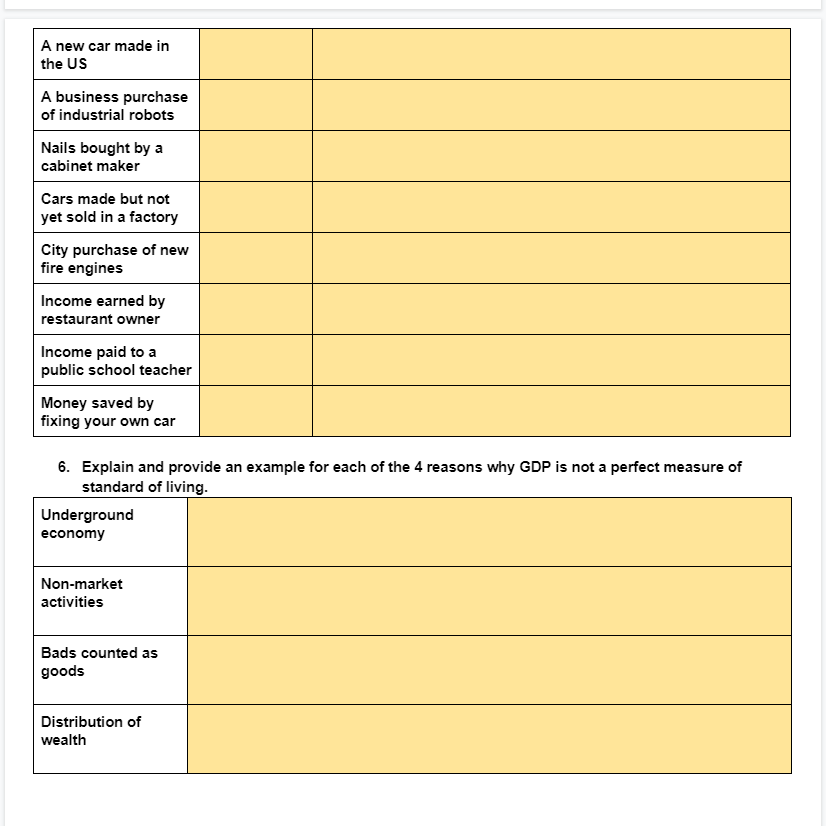
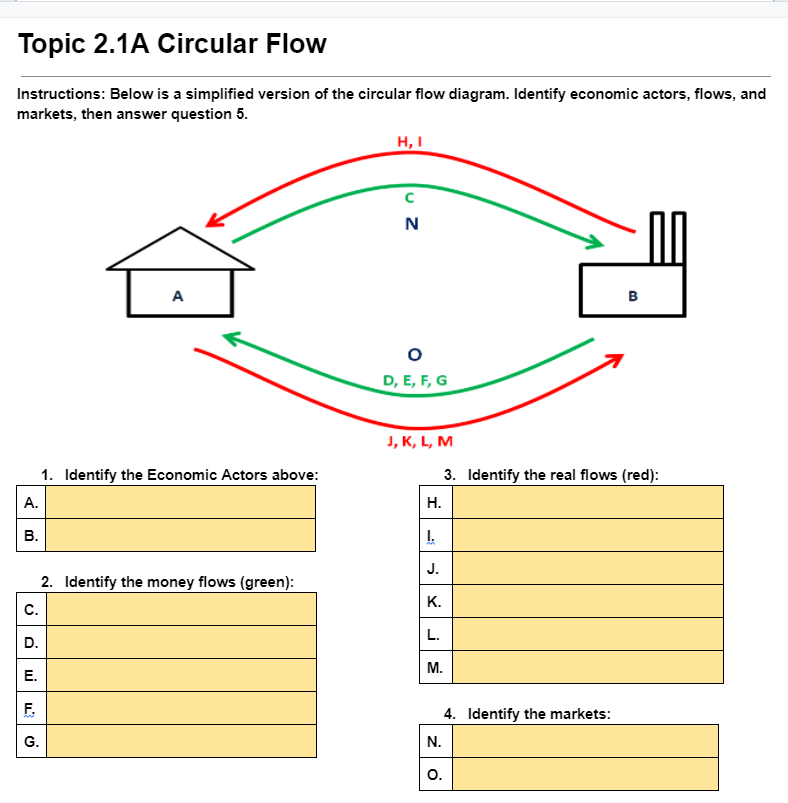
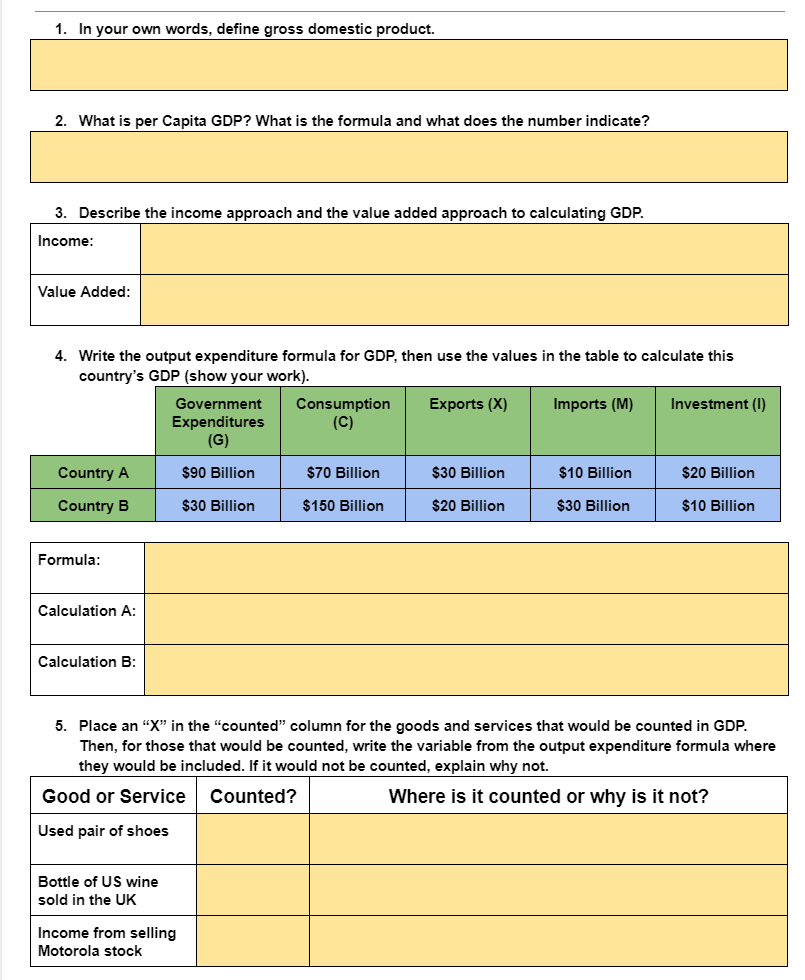
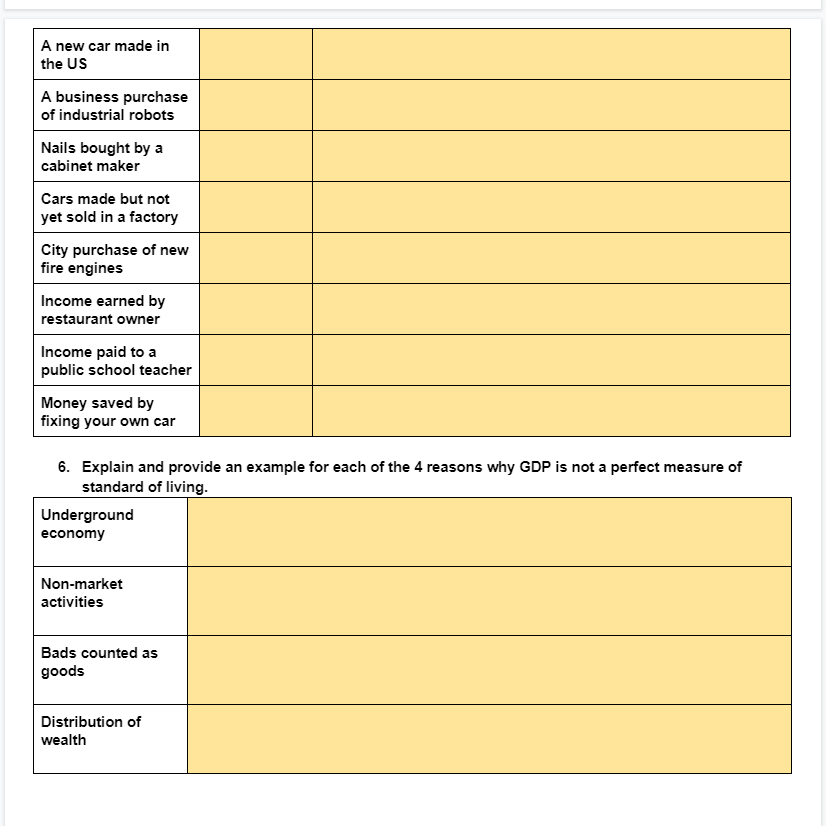
Topic 2.1A Circular Flow Instructions: Below is a simplified version of the circular flow diagram. Identify economic actors, flows, and markets, then answer question 5. H, I N A B O D, E, F, G J, K, L, M Identify the Economic Actors above: 3. Identify the real flows (red): A. H. 2. Identify the money flows (green): C. K. D M. F. 4. Identify the markets: G. N. O.1. In your own words, dene gross domestic product. 2. What is per Capita GDP? What: is the formula and what does the number indicate? : 3. Describe the income approach and the value added approach to calculating GDP. 4. Write the output expenditure formula for GDP, then use the values in the table to calculate this country's GDP [show your work]. Formula: Calculation A: Calculation El: 5. Place an \"I\" in the \"counted\" column for the goods and services that would be counted in GDP. Then. for those that would be counted, write the variable from the output expenditure formula where they would be included. If it would not be counted, explain why not. Good or Service Counted? Where is it counted or why is it not? Used pair of shoes Bottle of US wine sold in the UK Income from selling A new car made in the US A business purchase of industrial robots Nails bought by a cabinet maker Cars made but not yet sold in a factory City purchase of new fire engines Income earned by restaurant owner Income paid to a public school teacher Money saved by fixing your own car E. Explain and provide an example for each of the 4 reasons why GDP is not a perfect measure of standard of living. Underground economy Non-market activities Bads counted as goods Distribution of wealth
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


