Question: 2b. We consider a stock with current price S(0) = $62. The value at time t=0 of several European and American options with different strikes
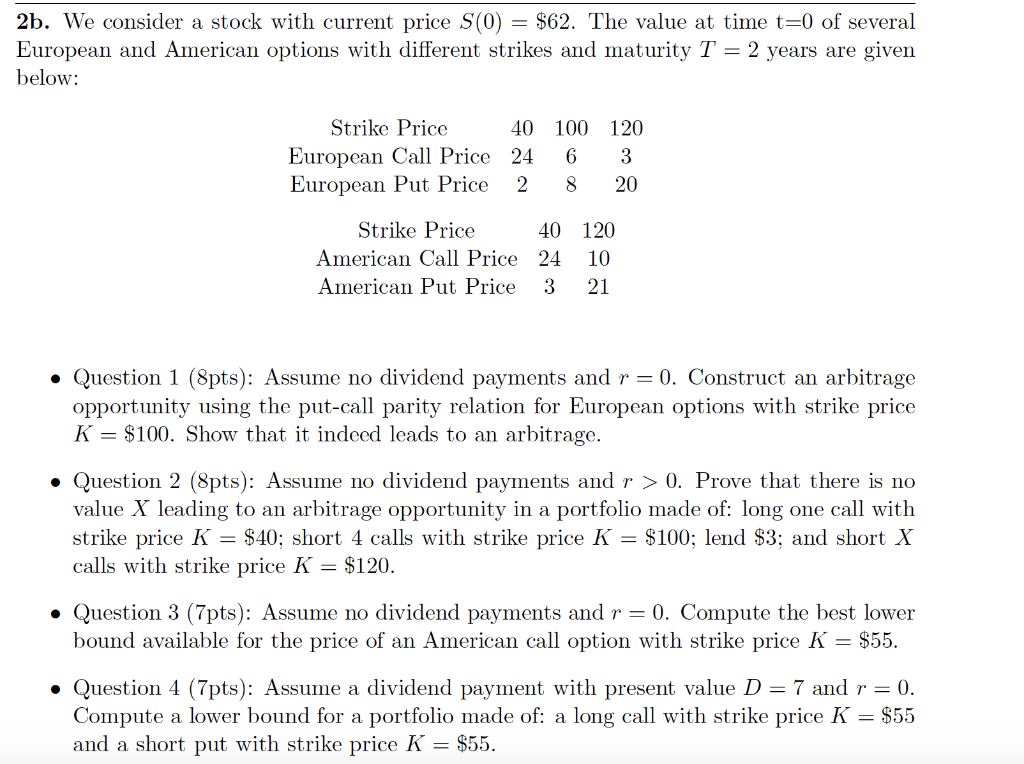
2b. We consider a stock with current price S(0) = $62. The value at time t=0 of several European and American options with different strikes and maturity T = 2 years are given below: Strike Price 40 100 120 European Call Price 24 6 3 European Put Price 2 8 20 Strike Price 40 American Call Price 24 American Put Price 3 120 10 21 Question 1 (8pts): Assume no dividend payments and r = 0. Construct an arbitrage opportunity using the put-call parity relation for European options with strike price K = $100. Show that it indeed leads to an arbitrage. Question 2 (8pts): Assume no dividend payments and r > 0. Prove that there is no value X leading to an arbitrage opportunity in a portfolio made of: long one call with strike price K = $40; short 4 calls with strike price K = $100; lend $3; and short X calls with strike price K = $120. Question 3 (7pts): Assume no dividend payments and r = 0. Compute the best lower bound available for the price of an American call option with strike price K = $55. Question 4 (7pts): Assume a dividend payment with present value D = 7 and r = 0. Compute a lower bound for a portfolio made of: a long call with strike price K = $55 and a short put with strike price K = $55. 2b. We consider a stock with current price S(0) = $62. The value at time t=0 of several European and American options with different strikes and maturity T = 2 years are given below: Strike Price 40 100 120 European Call Price 24 6 3 European Put Price 2 8 20 Strike Price 40 American Call Price 24 American Put Price 3 120 10 21 Question 1 (8pts): Assume no dividend payments and r = 0. Construct an arbitrage opportunity using the put-call parity relation for European options with strike price K = $100. Show that it indeed leads to an arbitrage. Question 2 (8pts): Assume no dividend payments and r > 0. Prove that there is no value X leading to an arbitrage opportunity in a portfolio made of: long one call with strike price K = $40; short 4 calls with strike price K = $100; lend $3; and short X calls with strike price K = $120. Question 3 (7pts): Assume no dividend payments and r = 0. Compute the best lower bound available for the price of an American call option with strike price K = $55. Question 4 (7pts): Assume a dividend payment with present value D = 7 and r = 0. Compute a lower bound for a portfolio made of: a long call with strike price K = $55 and a short put with strike price K = $55
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


