Question: Transport problems and linear programming (VAM) e (MODI) 1 - Three warehouses, designated by 1, 2 and 3, must be suppressed with commodity from three
Transport problems and linear programming (VAM) e (MODI)
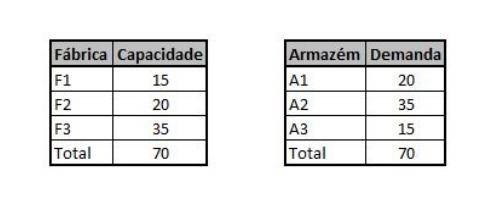
1 - Three warehouses, designated by 1, 2 and 3, must be suppressed with commodity from three factories, designated by 1, 2 and 3. THE capacity of each factory and the demand of each warehouse are given next:
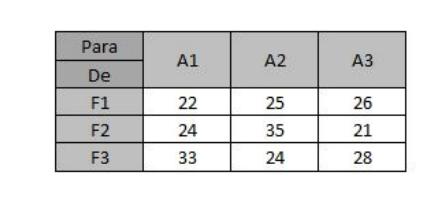
On the other hand, the unit costs of transporting the goods from each factory, for each warehouse, are the following (values in R$)
You want to minimize the total cost of transporting goods to the warehouses. Designating by the quantity of goods that you owe be shipped from factory to warehouse , formulate the model of linear programming corresponding to this transport problem.
2. Taking into account the previous exercise, determine: a) A solution based on intuition and trial and error, that is, how much will be shipped from each factory to each warehouse; b) The total cost of transport associated with the solution found; c) A solution approximated by the VAM (approximation method of Vogel); d) The total cost of transport associated with the approximate solution; compare it with the total cost found in item b)
3 - Taking into account exercise 1 and the approximate solution obtained by VAM in exercise 2, find the optimal solution using MODI (Modi Distribution Method).
4. Company industrial Paiva LTDA has two factories, A and B, that must supply three regional warehouses with a certain commodity, 1, 2 and 3. Due to the age and technology of the industrial plants, the factory A has a unit cost of production of R$ 50, while factory A factory B, more modern, can produce for 60% of this value (R$ 30). The production capacities of the goods are also different. on the agenda: while factory B manages to produce 40,000 units monthly, factory A produces only 25,000 units per month. the total produced is greater than would actually be necessary to meet the monthly demands from the three warehouses: 1 needs 25,000 units per month and 2 and 3 each need 15,000 monthly units. Finally, the transport costs associated with the goods are the following (in BRL):
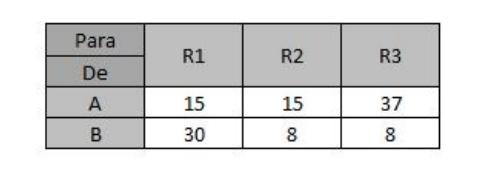
Taking into account manufacturing and shipping costs, determine how much should be shipped from each factory to each warehouse and cost total (manufacturing+transportation) associated. How much of the production of each factory is not used in this operation?
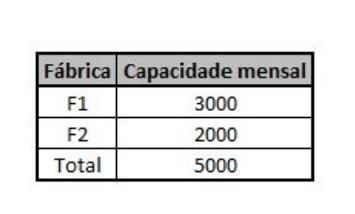
5 - The distributor MAJUVI LTDA wants to supply its four regional warehouses in the state of so paulo, designated by 1, 2, 3 and 4, with the following monthly demands:
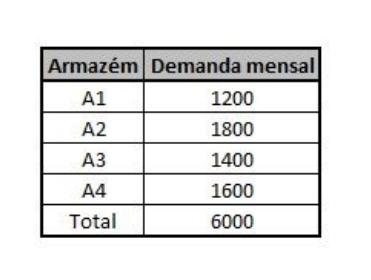
The distributor intends to buy as much as possible from the same manufacturer. sing, for negotiation reasons. The chosen manufacturer has the factories 1 and 2, with the following monthly production capacities:
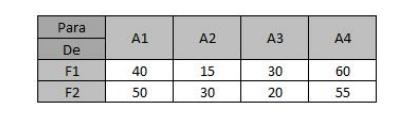
Unit transport costs from each factory to each warehouse are given in the following table, in R$:
a) Determine how much should be shipped from each factory to each warehouse and the associated total transport cost.
b) The distributor MAJUVI LTDA may or may not use another supplier to fully meet the demand of your warehouses? In if so, what quantities should the new supplier supply to each of the warehouses?
F1 Fbrica Capacidade 15 F2 20 F3 35 Total 70 Armazm Demanda A1 20 A2 35 A3 15 Total 70 Para A1 A2 A3 De F1 22 24 33 25 35 26 21 F2. F3 24 28 R1 R2 R3 Para De A 15 15 37 B 30 8 8 8 8 Armazm Demanda mensal A1 1200 A2 1800 A3 1400 A4 1600 Total 6000 Fbrica Capacidade mensal F1 3000 F2 2000 Total 5000 Para A1 A2 A4 De F1 F2 15 30 40 50 60 55 30 20
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


