Question: Tree depth for carry-save reduction is analyzed in this problem. (a) How many 3-2 reduction levels are needed to reduce 16 summands to 2 using
Tree depth for carry-save reduction is analyzed in this problem. (a) How many 3-2 reduction levels are needed to reduce 16 summands to 2 using a pattern similar to that shown in Figure 9.19? (b) Repeat part (a) for reducing 32 summands to 2 to show that the claim of 8 levels in Section 9.5.3 is correct. (c) Compare the exact answers in parts (a) and (b) to the results obtained by using the approximation developed in Example 9.3 in Section 9.10.
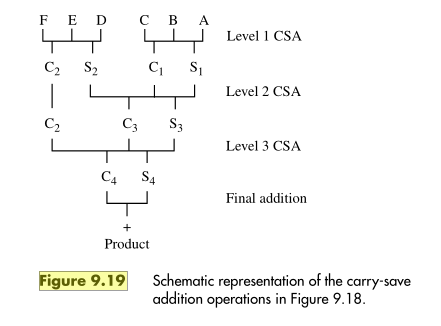

F E D 4 Level 1 CSA 1 C2 S2 Si Level 2 CSA C2 CZ Sz Level 3 CSA C4 S4 Final addition + + Product Figure 9.19 Schematic representation of the carry-save addition operations in Figure 9.18. Problem: How many levels of 4-2 reducers are needed to reduce k summands to 2 in a Example 9.3 reduction tree? How many levels are needed if 3-2 reducers are used? Solution: Let the number of levels be L. For 4-2 reducers, we have k(1/2) = 2 Take logarithms to the base 2 of each side of this equation to derive logak - L=1 or L = log2k - 1 For 3-2 reducers, we have k(2/3) = 2 As above, taking logarithms to the base 2, we derive log2k +L(log22 - log23) = log22 log2k +L(1 - 1.59) = 1 L = (1 logzk)/(-0.59) L = 1.7log2k 1.7 These expressions are only approximations unless the number of input summands to each level is a multiple of 4 in the case of 4-2 reduction, or is a multiple of 3 in the case of 3-2 reduction
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


