Question: Try to vectorize the code, not run it N times.In other words generate vectors of length N for the data, the noise, the received, the
Try to vectorize the code, not "run it N times."In other words generate vectors of length N for the data, the noise, the received, the decision.You compare B with B hat to determine if the decision is correct or not.Then count the number of errors and divide by N to determine the probability of error.
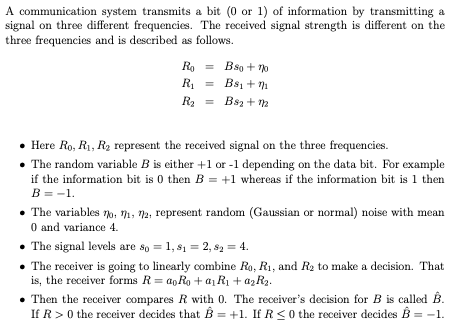

A communication system transmits a bit (0 or 1) of information by transmitting a signal on three different frequencies. The received signal strength is different on the three frequencies and is described as follows. Ro = Bao + 7 R1 = Bsi + m Ra = Baz + Th . Here Ro, Ri, Ry represent the received signal on the three frequencies. . The random variable B is either +1 or -1 depending on the data bit. For example if the information bit is 0 then B = +1 whereas if the information bit is 1 then B=-1. . The variables , m, 72, represent random (Gaussian or normal) noise with mean 0 and variance 4. . The signal levels are so = 1, $1 = 2, s, = 4. . The receiver is going to linearly combine Ro, Ri, and Re to make a decision. That is, the receiver forms R = apkg + a Ri + agRe. . Then the receiver compares R with 0. The receiver's decision for B is called B. If R > 0 the receiver decides that B = +1. If R 0)*(+1)+(ra0)*(+1)+(rb0)*(+1)+(rc
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


