Question: Tutorial Exercise A loaded ore car has a mass of 950 kg and rolls on rails with negligible friction. It starts from rest and is
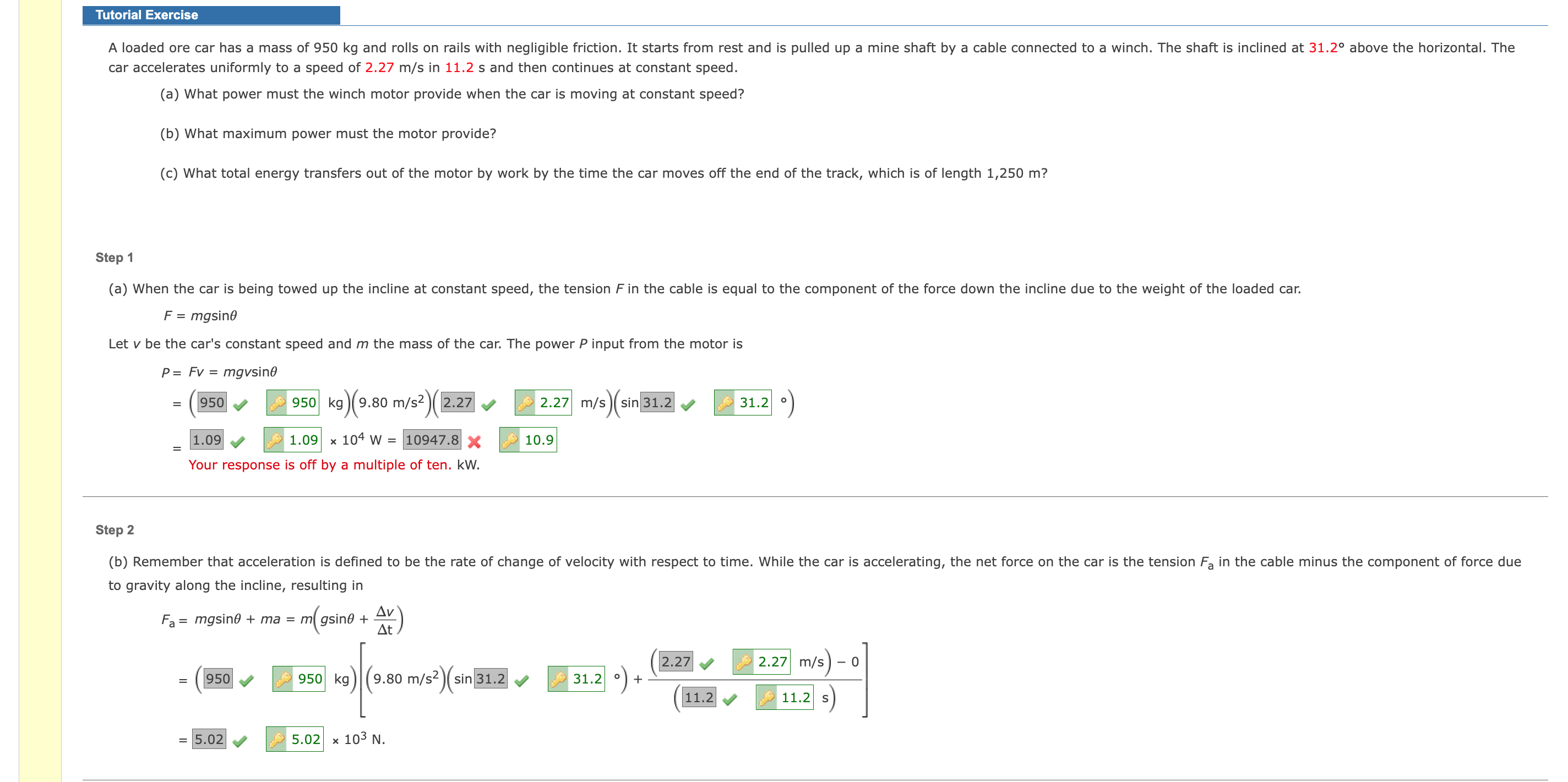
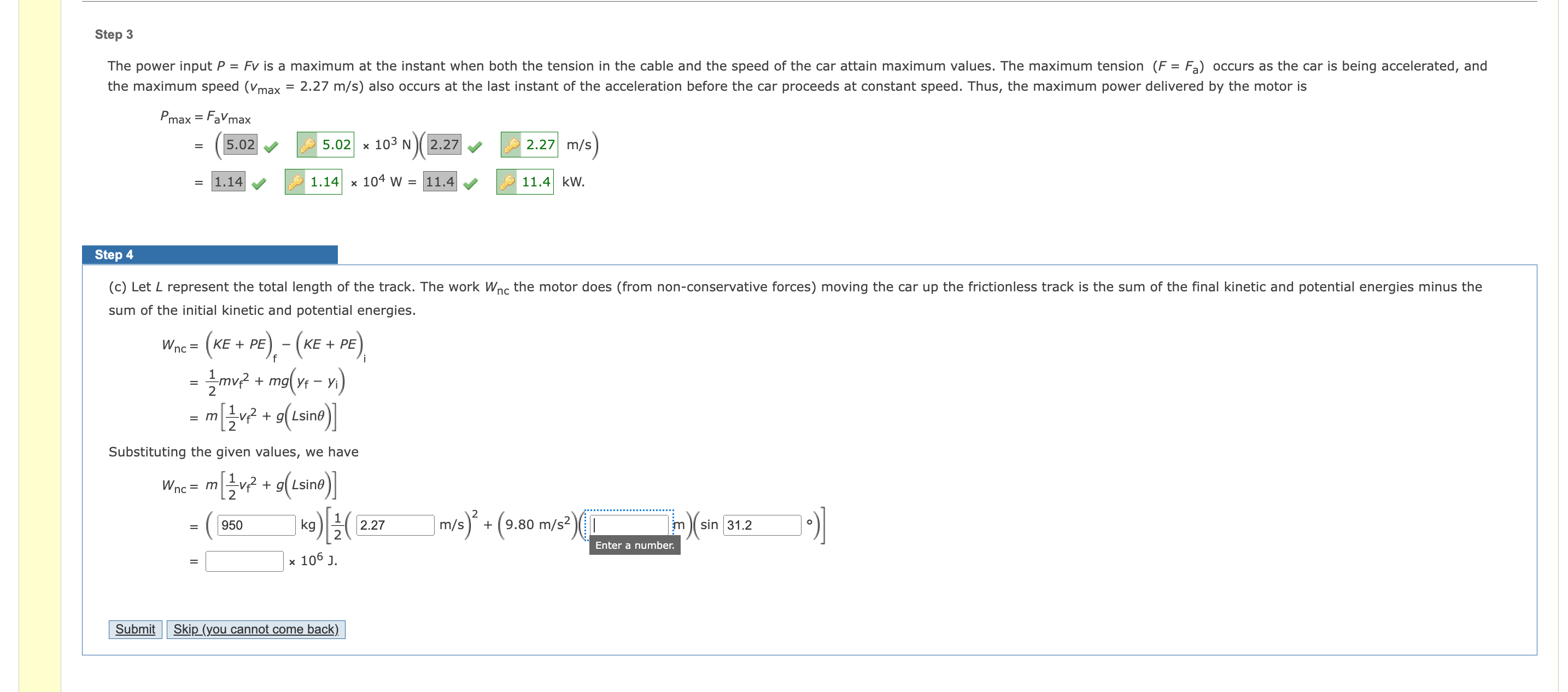
Tutorial Exercise A loaded ore car has a mass of 950 kg and rolls on rails with negligible friction. It starts from rest and is pulled up a mine shaft by a cable connected to a winch. The shaft is inclined at 31.2 above the horizontal. The car accelerates uniformly to a speed of 2.27 m/s in 11.2 s and then continues at constant speed. (a) What power must the winch motor provide when the car is moving at constant speed? (b) What maximum power must the motor provide? (c) What total energy transfers out of the motor by work by the time the car moves off the end of the track, which is of length 1,250 m? Step 1 (a) When the car is being towed up the incline at constant speed, the tension F in the cable is equal to the component of the force down the incline due to the weight of the loaded car. F = mgsin0 Let V be the car's constant speed and m the mass of the car. The power P input from the motor is P: Fv = mgvsinS = (950 v ,2 950 kg)(9.80 m/52)(2.z7 v ,2 2.27 m/s)(sin 31.2 v ,2 31.2 ) 1.09 '2 ,2 1.09 x 104w: 10947.8 x ,2 10.9 Your response is off by a multiple of ten. kw. Step 2 (b) Remember that acceleration is dened to be the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. While the car is accelerating, the net force on the car is the tension F3 in the cable minus the component of force due to gravity along the incline, resulting in FB = mgsin!) + ma = m(gsin0 + %) = (950 V2 ,2 950 kg) (9.80 m/sz)(sin 31.2 V ,2 31.2 ) + M (11.2 v ,2 11.2 s) = 5.02 w ,2 5.02 x 103 N. Step 3 The power input P = Fv is a maximum at the instant when both the tension in the cable and the speed of the car attain maximum values. The maximum tension (F = Fa) occurs as the car is being accelerated, and the maximum speed (Vmax = 2.27 m/s) also occurs at the last instant of the acceleration before the car proceeds at constant speed. Thus, the maximum power delivered by the motor is Pmax = FaVmax = 5.02 5.02 x 103 N 2.27 2.27 m/s) = 1.14 1.14 x 104 W = 11.4 11.4 KW. Step 4 (c) Let L represent the total length of the track. The work Wnc the motor does (from non-conservative forces) moving the car up the frictionless track is the sum of the final kinetic and potential energies minus the sum of the initial kinetic and potential energies. Wnc = (KE + PE) - (KE + PE) = 2mv2 + mg(yf- vi) 1v 2 + 9(Lsine) Substituting the given values, we have Wnc = m - v.2+ 9(Lsino) 950 kg ) 4 2.27 1m/s ) + (9.80 m /s2) [ m sin 31.2 10) Enter a number. x 106 J. Submit Skip (you cannot come back)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


