Question: Tutorial Sheet 1 1. Cardiac fluoroscopy is used to diagnose coronary artery disease by detecting whether 0, 1. 2 or 3 arteries are calcified. Defining
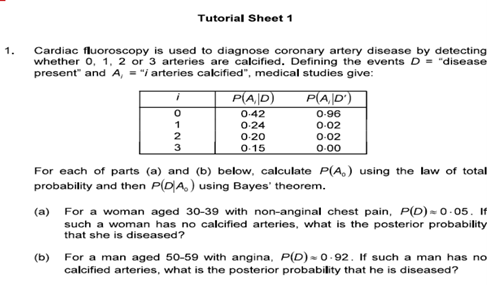
Tutorial Sheet 1 1. Cardiac fluoroscopy is used to diagnose coronary artery disease by detecting whether 0, 1. 2 or 3 arteries are calcified. Defining the events D = "disease present" and A, = "/ arteries calcified", medical studies give: P(A, D) P(A, D') 0.42 0-96 0.24 0-02 ON-O 0.20 0-02 0.15 0-00 For each of parts (a) and (b) below, calculate P(A, ) using the law of total probability and then P(D A, ) using Bayes' theorem. (a) For a woman aged 30-39 with non-anginal chest pain, P(D) = 0 .05. If such a woman has no calcified arteries, what is the posterior probability that she is diseased? (b) For a man aged 50-59 with angina, P(D) =0-92. If such a man has no calcified arteries, what is the posterior probability that he is diseased
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


