Question: u 5 + 1 G(S) = Q4. Consider the control system given on the right where nonlinearity NL is described NL (S-2)(s-B) by the following
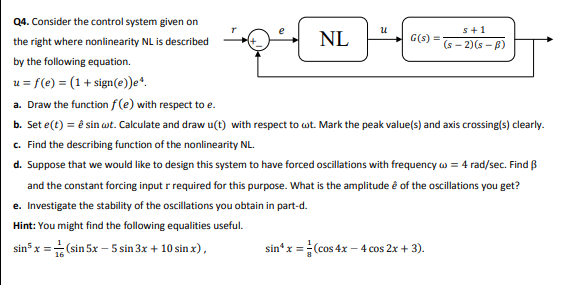
u 5 + 1 G(S) = Q4. Consider the control system given on the right where nonlinearity NL is described NL (S-2)(s-B) by the following equation u = f(e) = (1 + sign(e)) a. Draw the function f(e) with respect to e. b. Set e(t) = sin wt. Calculate and draw u(t) with respect to wt. Mark the peak value(s) and axis crossing(s) clearly. c. Find the describing function of the nonlinearity NL. d. Suppose that we would like to design this system to have forced oscillations with frequency w = 4 rad/sec. Find B and the constant forcing input r required for this purpose. What is the amplitude e of the oscillations you get? e. Investigate the stability of the oscillations you obtain in part-d. Hint: You might find the following equalities useful. sin> x = (sin 5x 5 sin 3x + 10 sin x), sin x = (cos 4x 4 cos 2x + 3). u 5 + 1 G(S) = Q4. Consider the control system given on the right where nonlinearity NL is described NL (S-2)(s-B) by the following equation u = f(e) = (1 + sign(e)) a. Draw the function f(e) with respect to e. b. Set e(t) = sin wt. Calculate and draw u(t) with respect to wt. Mark the peak value(s) and axis crossing(s) clearly. c. Find the describing function of the nonlinearity NL. d. Suppose that we would like to design this system to have forced oscillations with frequency w = 4 rad/sec. Find B and the constant forcing input r required for this purpose. What is the amplitude e of the oscillations you get? e. Investigate the stability of the oscillations you obtain in part-d. Hint: You might find the following equalities useful. sin> x = (sin 5x 5 sin 3x + 10 sin x), sin x = (cos 4x 4 cos 2x + 3)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


