Question: undefined EXERCISE 2.4 (Poisson parameter estimation. In this erample there are two hypotheses, H = 0 and H = 1, which occur with probabilities PHO)
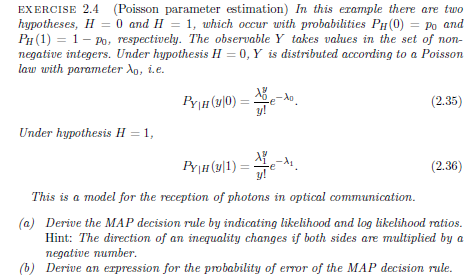 undefined
undefined
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


