Question: undefined In Java please Task Description: (8 pts) Task 1: Add three methods: union, intersection, and difference to the interface BagInterface for the ADT bag.

 undefined
undefined
In Java please
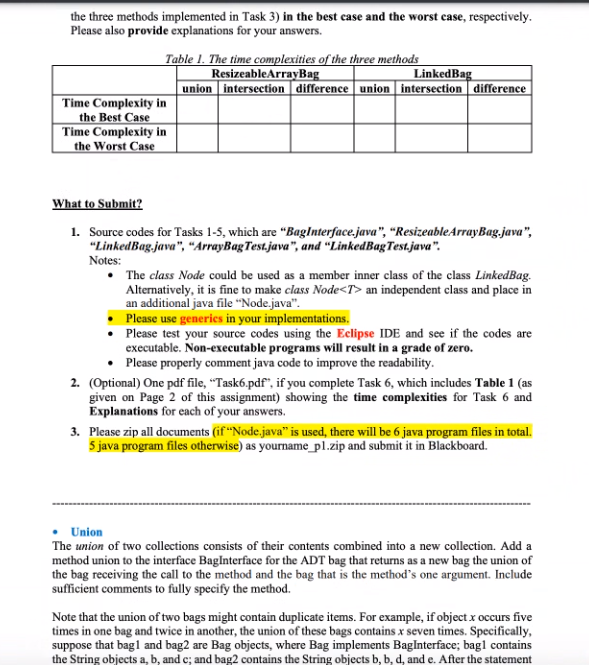
Task Description: (8 pts) Task 1: Add three methods: union, intersection, and difference to the interface BagInterface for the ADT bag. The detailed description of the three methods and how to call the three methods could be found on pages 2 and 3 of this assignment. Note: the three methods to implement are for Bags, not for Sets. (36 pts) Task 2: Implement the three methods, union, intersection, and difference, for the class ResizeableArrayBag. Note: the class ResizeableArrayBag presents an implementation of the ADT bag using a resizable array. Generies are needed! (36 pts) Task 3: Implement the three methods, union, intersection, and difference, for the class LinkedBag. Note: the class LinkedBag presents an implementation of the ADT bag using a linked chain. Generics are needed! (10 pts) Task 4: Write a client program, "ArrayBag Test.java, which contains a main method to test the three methods (union, intersection, and difference) you implemented for the class ResizeableArrayBag. Note that when you examine the method "difference", please test both bag2.differencebagl) and bagl.difference(bag), given two bags bag2 and bagl. (10 pts) Task 5: Write a client program, "LinkedBagTest.java", which contains a main method to test the three methods (union, intersection, and difference) you implemented for the class LinkedBag. Note that when you examine the method "difference", please test both bag2.difference bagl) and bagl.difference(bag), given two bags bag2 and bagl. Optional, Just for Extra Points: 10 pts) Task 6: Use Big O notations to indicate the time complexity of each method you implemented (the three methods implemented in Task 2 and the three methods implemented in Task 3) in the best case and the worst case, respectively. Please also provide explanations for your answers. Table 1. The time complexities of the three methods ResizeableArrayBag LinkedBag union intersection difference union intersection difference Time Complexity in the Best Case Time Complexity in the Worst Case What to Submit? 1. Source codes for Tasks 1-5, which are BagInterface.java", "ResizeableArrayBag.java", "LinkedBag.java", "ArrayBag Test.java", and "LinkedBag Test.java". Notes: The class Node could be used as a member inner class of the class LinkedBag. Alternatively, it is fine to make class Node an independent class and place in an additional java file "Node.java". Please use generies in your implementations. Please test your source codes using the Eclipse IDE and see if the codes are executable. Non-executable programs will result in a grade of zero. Please properly comment java code to improve the readability. 2. (Optional) One pdf file, "Task6.pdf", if you complete Task 6, which includes Table 1 (as given on Page 2 of this assignment) showing the time complexities for Task 6 and Explanations for each of your answers. 3. Please zip all documents (if Node.java is used, there will be 6 java program files in total. 5 java program files otherwise) as yourname_pl.zip and submit it in Blackboard. Union The union of two collections consists of their contents combined into a new collection. Add a method union to the interface BagInterface for the ADT bag that returns as a new bag the union of the bag receiving the call to the method and the bag that is the method's one argument. Include sufficient comments to fully specify the method. Note that the union of two bags might contain duplicate items. For example, if object x occurs five times in one bag and twice in another, the union of these bags contains x seven times. Specifically, suppose that bagi and bag2 are Bag objects, where Bag implements BagInterface; bagl contains the String objects a, b, and c; and bag2 contains the String objects b, b, d, and e. After the statement BagInterface everything - bagl.union(bag2); executes, the bag everything contains the strings a, b, b, b, c, d, and e. Note that union does not affect the contents of bagl and bag2, and the order of data items in the resulting bag everything doesn't matter. Intersection The intersection of two collections is a new collection of the entries that occur in both collections. That is, it contains the overlapping entries. Add a method intersection to the interface BagInterface for the ADT bag that returns as a new bag the intersection of the bag receiving the call to the method and the bag that is the method's one argument. Include sufficient comments to fully specify the method. Note that the intersection of two bags might contain duplicate items. For example, if object x occurs five times in one bag and twice in another, the intersection of these bags contains x twice. Specifically, suppose that bagl and bag2 are Bag objects, where Bag implements BagInterface; bagl contains the String objects a, b, and c; and bag2 contains the String objects b, b, d, and e. After the statement BagInterface commonItems = bagl.intersection(bag2); executes, the bag commonltems contains only the string b. If b had occurred in bagl twice, commonItems would have contained two occurrences of b, since bag2 also contains two occurrences of b. Note that intersection does not affect the contents of bagl and bag2. Difference The difference of two collections is a new collection of the entries that would be left in one collection after removing those that also occur in the second. Add a method difference to the interface BagInterface for the ADT bag that returns as a new bag the difference of the bag receiving the call to the method and the bag that is the method's one argument. Include sufficient comments to fully specify the method. Note that the difference of two bags might contain duplicate items. For example, if object x occurs five times in one bag and twice in another, the difference of these bags contains x three times. Specifically, suppose that bagi and bag2 are Bag objects, where Bag implements BagInterface; bagl contains the String objects a, b, and c; and bag2 contains the String objects b, b, d, and e. After the statement BagInterface leftover1 = bagl.difference/bag2); executes, the bag lehOverl contains the strings a and c. After the statement BagInterface leftover2 = bag2.differencebag]); executes, the bag leftover2 contains the strings b, d, and e. Note that difference does not affect the contents of bagl and bag2


 undefined
undefined


