Question: urgent please ACROSS: 2:gated channel opens in response to application of pressure 4: movement of membrane potential beyond resting value 7: finger-like extension that propagates

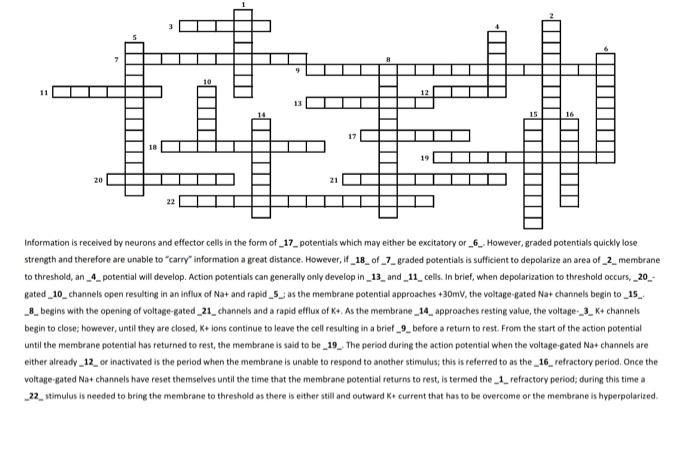
ACROSS: 2:gated channel opens in response to application of pressure 4: movement of membrane potential beyond resting value 7: finger-like extension that propagates an action potential between the axon and synaptic terminal 8: structural classification of most sensory neurons 9: open and close in response to changes in the membrane potential 12: site of information processing of a neuron 13: movement of the membrane potential from rest toward a positive value 14: determined by negatively charged intracellular materials, the Na+/+pump, and membrane permeability to K+ 15: structural classification of most neurons in the CNS 16: presynaptic decreases NT release from a presynaptic neuron 18: a neurotransmitter that alters the metabolic activity of a cell is known DOWN: 1: gated channel opens in response to binding of a neurotransmitter 3: site of intercellular communication may be electrical or chemical 5:action potential may be generated in response to suprathreshold stimulus 6: must reach threshold to develop this self-propagating electrical impulse 10: serve as 'receptors' of a neuron 11:Nagate activation and inactivation prevent another action potential from being developed during this period 17: the process by which a stimulus moves the membrane potential of a neuron closer to threshold 19: refers to the additive effect of postsynaptic potentials on the membrane as this 15 16 18 20 information is received by neurons and effector cells in the form of _17_potentials which may either be excitatory or _6...However, graded potentials quickly lose strength and therefore are unable to carry information a great distance. However, if _18_of_7_graded potentials is sufficient to depolarize an area of_2_membrane to threshold, an_4_potential will develop. Action potentials can generally only develop in_13_ and _11_ cells. In brief, when depolarization to threshold occurs, _20_ Rated_10_channels open resulting in an influx of Na+ and rapid _5.j as the membrane potential approaches +30mV, the voltage Rated Na+ channels begin to _15_ _8_begins with the opening of voltage-Rated_21_channels and a rapid efflux of K+. As the membrane_14_ approaches resting value, the voltage _3_K+ channels begin to close; however, until they are closed, K+ ions continue to leave the cell resulting in a brief_9_before a return to rest. From the start of the action potential until the membrane potential has returned to rest, the membrane is said to be _19_. The period during the action potential when the voltage-gated Na+ channels are either already_12_or inactivated is the period when the membrane is unable to respond to another stimulus; this is referred to as the _16_refractory period. Once the voltage-gated Na+ channels have reset themselves until the time that the membrane potential returns to rest, is termed the _1_refractory period; during this time a _22_ stimulus is needed to bring the membrane to threshold as there is either still and outward K+ current that has to be overcome or the membrane is hyperpolarized a ACROSS: 2:gated channel opens in response to application of pressure 4: movement of membrane potential beyond resting value 7: finger-like extension that propagates an action potential between the axon and synaptic terminal 8: structural classification of most sensory neurons 9: open and close in response to changes in the membrane potential 12: site of information processing of a neuron 13: movement of the membrane potential from rest toward a positive value 14: determined by negatively charged intracellular materials, the Na+/+pump, and membrane permeability to K+ 15: structural classification of most neurons in the CNS 16: presynaptic decreases NT release from a presynaptic neuron 18: a neurotransmitter that alters the metabolic activity of a cell is known DOWN: 1: gated channel opens in response to binding of a neurotransmitter 3: site of intercellular communication may be electrical or chemical 5:action potential may be generated in response to suprathreshold stimulus 6: must reach threshold to develop this self-propagating electrical impulse 10: serve as 'receptors' of a neuron 11:Nagate activation and inactivation prevent another action potential from being developed during this period 17: the process by which a stimulus moves the membrane potential of a neuron closer to threshold 19: refers to the additive effect of postsynaptic potentials on the membrane as this 15 16 18 20 information is received by neurons and effector cells in the form of _17_potentials which may either be excitatory or _6...However, graded potentials quickly lose strength and therefore are unable to carry information a great distance. However, if _18_of_7_graded potentials is sufficient to depolarize an area of_2_membrane to threshold, an_4_potential will develop. Action potentials can generally only develop in_13_ and _11_ cells. In brief, when depolarization to threshold occurs, _20_ Rated_10_channels open resulting in an influx of Na+ and rapid _5.j as the membrane potential approaches +30mV, the voltage Rated Na+ channels begin to _15_ _8_begins with the opening of voltage-Rated_21_channels and a rapid efflux of K+. As the membrane_14_ approaches resting value, the voltage _3_K+ channels begin to close; however, until they are closed, K+ ions continue to leave the cell resulting in a brief_9_before a return to rest. From the start of the action potential until the membrane potential has returned to rest, the membrane is said to be _19_. The period during the action potential when the voltage-gated Na+ channels are either already_12_or inactivated is the period when the membrane is unable to respond to another stimulus; this is referred to as the _16_refractory period. Once the voltage-gated Na+ channels have reset themselves until the time that the membrane potential returns to rest, is termed the _1_refractory period; during this time a _22_ stimulus is needed to bring the membrane to threshold as there is either still and outward K+ current that has to be overcome or the membrane is hyperpolarized a
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


