Question: Use Python to solve 2 Airfoil Wake Drag Now that we understand a bit more about airfoil terminology, we can start to talk about what
Use Python to solve
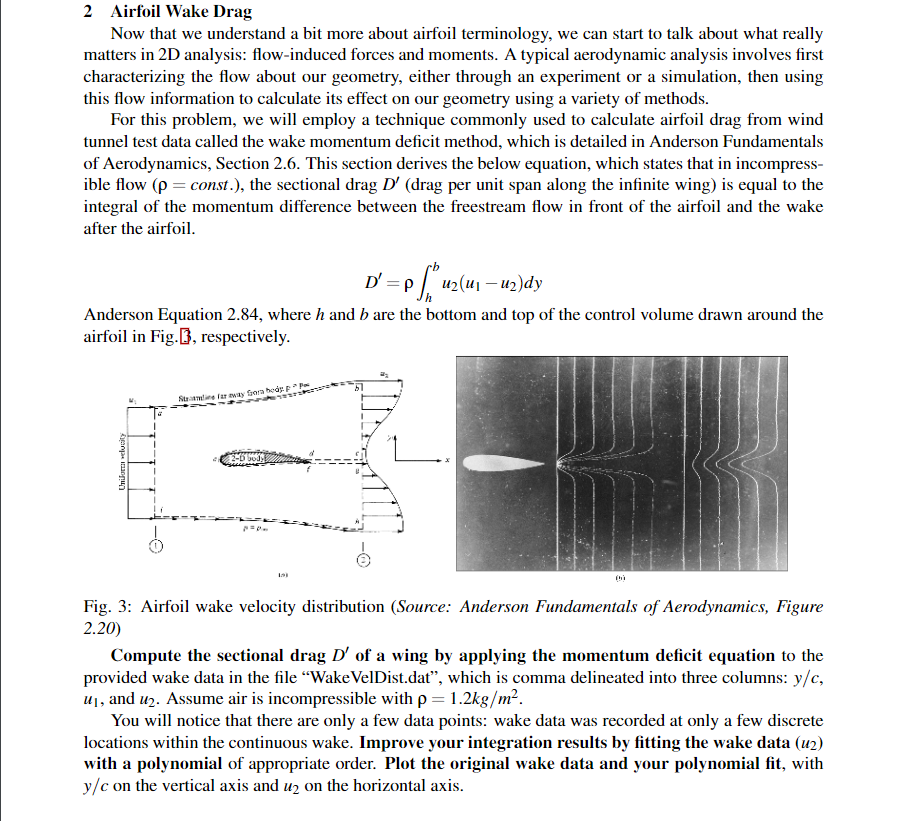
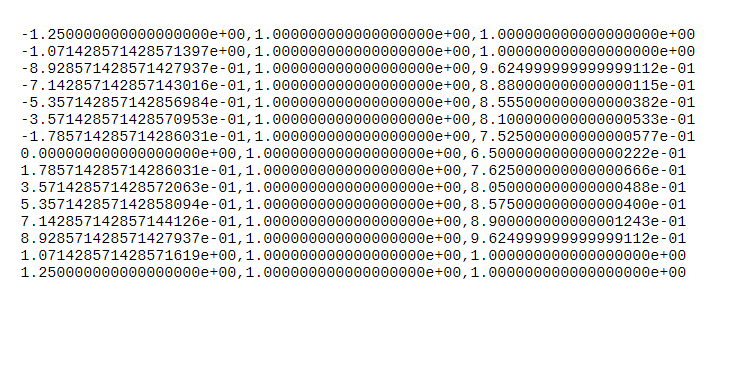
2 Airfoil Wake Drag Now that we understand a bit more about airfoil terminology, we can start to talk about what really matters in 2D analysis: flow-induced forces and moments. A typical aerodynamic analysis involves first characterizing the flow about our geometry, either through an experiment or a simulation, then using this flow information to calculate its effect on our geometry using a variety of methods. For this problem, we will employ a technique commonly used to calculate airfoil drag from wind tunnel test data called the wake momentum deficit method, which is detailed in Anderson Fundamentals of Aerodynamics, Section 2.6. This section derives the below equation, which states that in incompress- ible flow (p =const.), the sectional drag D' (drag per unit span along the infinite wing) is equal to the integral of the momentum difference between the freestream flow in front of the airfoil and the wake after the airfoil. ' = uz(uj - U2)dy Anderson Equation 2.84, where h and b are the bottom and top of the control volume drawn around the airfoil in Fig.B, respectively. Strinelar way Gorabeo.pl 2-6150 Unifordi velocity Fig. 3: Airfoil wake velocity distribution (Source: Anderson Fundamentals of Aerodynamics, Figure 2.20) Compute the sectional drag D' of a wing by applying the momentum deficit equation to the provided wake data in the file Wake VelDist.dat, which is comma delineated into three columns: y/c, u, and u2. Assume air is incompressible with p = 1.2kg/m. You will notice that there are only a few data points: wake data was recorded at only a few discrete locations within the continuous wake. Improve your integration results by fitting the wake data (uz) with a polynomial of appropriate order. Plot the original wake data and your polynomial fit, with y/c on the vertical axis and u2 on the horizontal axis. -1.250000000000000000e+00,1.000000000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000000000e+00 -1.071428571428571397e+00, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000000000e+00 -8.928571428571427937e-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 9.624999999999999112e-01 -7.142857142857143016e-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 8.880000000000000115e-01 -5.357142857142856984e-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 8.555000000000000382e-01 -3.571428571428570953e-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 8.100000000000000533e-01 -1.7857142857142860312-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 7.525000000000000577e-01 0.000000000000000000e+00,1.000000000000000000e+00, 6.500000000000000222e-01 1.7857142857142860312-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 7.625000000000000666e-01 3.571428571428572063e-01,1.000000000000000000e+00, 8.050000000000000488e-01 5.357142857142858094e-01,1.000000000000000000e+00, 8.575000000000000400e-01 7.142857142857144126e-01,1.000000000000000000e+00, 8.900000000000001243e-01 8.928571428571427937e-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 9.624999999999999112e-01 1.071428571428571619e+00, 1.000000000000000000e+00,1.000000000000000000e+00 1.250000000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000000000e+00,1.000000000000000000e+00 2 Airfoil Wake Drag Now that we understand a bit more about airfoil terminology, we can start to talk about what really matters in 2D analysis: flow-induced forces and moments. A typical aerodynamic analysis involves first characterizing the flow about our geometry, either through an experiment or a simulation, then using this flow information to calculate its effect on our geometry using a variety of methods. For this problem, we will employ a technique commonly used to calculate airfoil drag from wind tunnel test data called the wake momentum deficit method, which is detailed in Anderson Fundamentals of Aerodynamics, Section 2.6. This section derives the below equation, which states that in incompress- ible flow (p =const.), the sectional drag D' (drag per unit span along the infinite wing) is equal to the integral of the momentum difference between the freestream flow in front of the airfoil and the wake after the airfoil. ' = uz(uj - U2)dy Anderson Equation 2.84, where h and b are the bottom and top of the control volume drawn around the airfoil in Fig.B, respectively. Strinelar way Gorabeo.pl 2-6150 Unifordi velocity Fig. 3: Airfoil wake velocity distribution (Source: Anderson Fundamentals of Aerodynamics, Figure 2.20) Compute the sectional drag D' of a wing by applying the momentum deficit equation to the provided wake data in the file Wake VelDist.dat, which is comma delineated into three columns: y/c, u, and u2. Assume air is incompressible with p = 1.2kg/m. You will notice that there are only a few data points: wake data was recorded at only a few discrete locations within the continuous wake. Improve your integration results by fitting the wake data (uz) with a polynomial of appropriate order. Plot the original wake data and your polynomial fit, with y/c on the vertical axis and u2 on the horizontal axis. -1.250000000000000000e+00,1.000000000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000000000e+00 -1.071428571428571397e+00, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000000000e+00 -8.928571428571427937e-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 9.624999999999999112e-01 -7.142857142857143016e-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 8.880000000000000115e-01 -5.357142857142856984e-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 8.555000000000000382e-01 -3.571428571428570953e-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 8.100000000000000533e-01 -1.7857142857142860312-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 7.525000000000000577e-01 0.000000000000000000e+00,1.000000000000000000e+00, 6.500000000000000222e-01 1.7857142857142860312-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 7.625000000000000666e-01 3.571428571428572063e-01,1.000000000000000000e+00, 8.050000000000000488e-01 5.357142857142858094e-01,1.000000000000000000e+00, 8.575000000000000400e-01 7.142857142857144126e-01,1.000000000000000000e+00, 8.900000000000001243e-01 8.928571428571427937e-01, 1.000000000000000000e+00, 9.624999999999999112e-01 1.071428571428571619e+00, 1.000000000000000000e+00,1.000000000000000000e+00 1.250000000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000000000e+00,1.000000000000000000e+00
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


