Question: Use python to solve this problem. Follow this code please from Steam import steam class rankine(): def __init__(self, p_low, p_high, t_high=None, name='Rankine Cycle'): ''' Constructor
Use python to solve this problem. Follow this code please
from Steam import steam class rankine(): def __init__(self, p_low, p_high, t_high=None, name='Rankine Cycle'): ''' Constructor for the Rankine power cycle :param p_low: low pressure isobar (kPa) states 4&1 :param p_high: high pressure isobar (kPa) states 2&3 :param t_high: the highest temperature in the cycle (degrees C) state 1 :param name: a convenient name ''' #set the class property values self.p_low=p_low self.p_high=p_high self.t_high=t_high self.name=name #define more class properties self.efficiency=None self.turbine_work=0 self.pump_work=0 self.heat_added=0 self.state1=None #a steam object at t_high, p_high self.state2=None #a steam object at p_low, s_2 (s_2s) self.state3=None #a steam object at p_low, sat liq. self.state4=None #a steam object at p_high def calc_efficiency(self): #calculate the 4 states #state 1: turbine inlet (p_high, t_high) superheated or saturated vapor if(self.t_high==None): self.state1= #$MISSING CODE HERE$# #instantiate a steam object assuming saturated vapor at p_high, name='Turbine Inlet' else: #probably superheated self.state1= #$MISSING CODE HERE$# #instantiate a steam object at p_high, t_high, name='Turbine Inlet' #state 2: turbine exit (p_low, s=s_turbine inlet) two-phase self.state2=#$MISSING CODE HERE$# #instantiate a steam object #state 3: pump inlet (p_low, x=0) saturated liquid self.state3=#$MISSING CODE HERE$# #instantiate a steam object #state 4: pump exit (p_high,s=s_pump_inlet) typically sub-cooled, but estimate as saturated liquid self.state4= #Missing code here #instantiate a steam object #assume incompressible fluid, but h increases because of increase in p while v remains constant self.state4.h=self.state3.h+self.state3.v*(self.p_high-self.p_low) self.turbine_work= #$MISSING CODE HERE$# self.pump_work= #$MISSING CODE HERE$# self.heat_added= #$MISSING CODE HERE$# self.efficiency= #$MISSING CODE HERE$# return self.efficiency def print_summary(self): if self.efficiency==None: self.calc_efficiency() print('Cycle Summary for: ', self.name) print('\tEfficiency: {:0.3f}%'.format(self.efficiency)) print('\tTurbine Work: {:0.3f} kJ/kg'.format(self.turbine_work)) print('\tPump Work: {:0.3f} kJ/kg'.format(self.pump_work)) print('\tHeat Added: {:0.3f} kJ/kg'.format(self.heat_added)) self.state1.print() self.state2.print() self.state3.print() self.state4.print() def main(): rankine1=rankine(8,8000,t_high=500,name='Rankine Cycle - Superheated at turbine inlet') #t_high is specified #if t_high were not specified, then x_high = 1 is assumed eff=rankine1.calc_efficiency() print(eff) rankine1.state3.print() rankine1.print_summary() #hf=rankine1.state1.hf #hg=rankine1.state1.hg rankine2=rankine(8,8000, name='Rankine Cycle - Saturated at turbine inlet') eff2=rankine2.calc_efficiency() print(eff2) rankine2.print_summary() if __name__=="__main__": main()
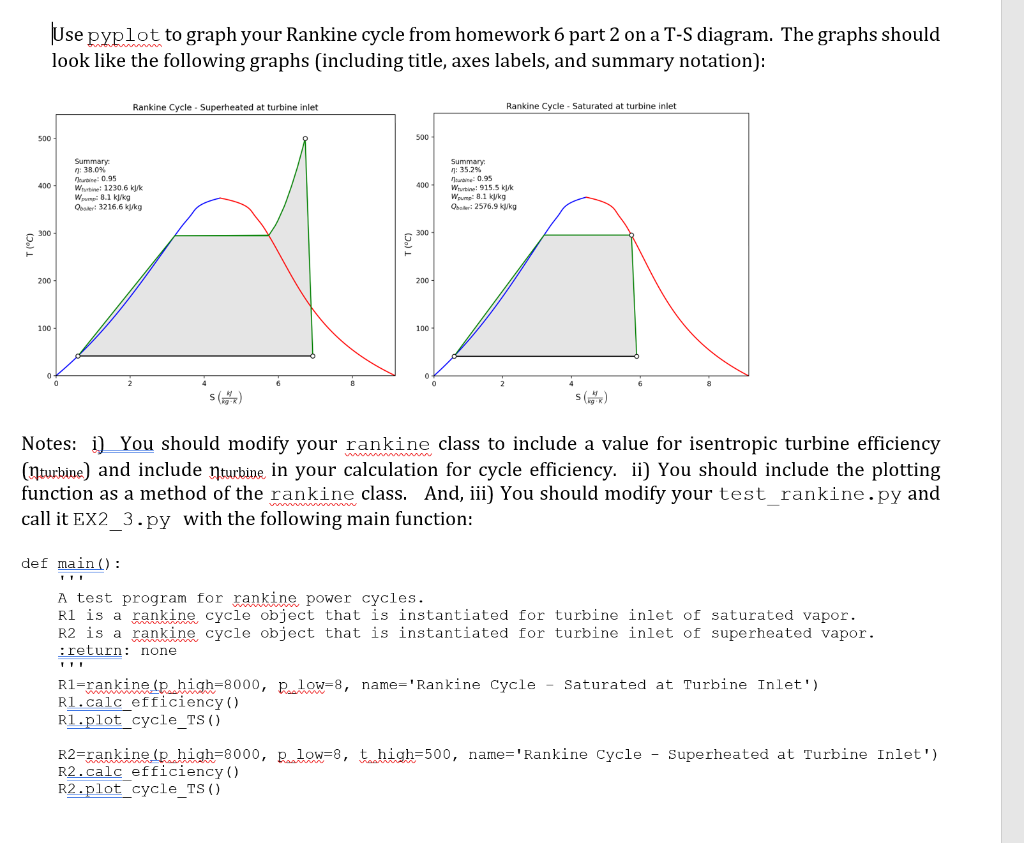
Use pyplot to graph your Rankine cycle from homework 6 part 2 on a T-S diagram. The graphs should look like the following graphs (including title, axes labels, and summary notation): Rankine Cycle - Superheated at turbine inlet Rankine Cycle - Saturated at turbine inlet 500 500 Summary Summary 400 7:38.0% 0.95 Wiwi: 1230.6 KJK Wpi 8.1 kl/kg Ooster: 3216.6 kg 400 7:35.2% ne:0.95 W 915.5 KK Wome 8.1 kykg Oster: 2576.9 kg 200 200 100 100 s() Notes: i) You should modify your rankine class to include a value for isentropic turbine efficiency (Iturbine) and include Nturbine in your calculation for cycle efficiency. ii) You should include the plotting function as a method of the rankine class. And, iii) You should modify your test_rankine.py and call it EX2_3.py with the following main function: def main(): A test program for rankine power cycles. R1 is a rankine cycle object that is instantiated for turbine inlet of saturated vapor. R2 is a rankine cycle object that is instantiated for turbine inlet of superheated vapor. :return: none Rl=rankine (p high=8000, Blow=8, name='Rankine Cycle - Saturated at Turbine Inlet') Rl.calc_efficiency) Rl.plot_cycle_TS() R2=rankine ( high=8000, Blow=8, thigh=500, name='Rankine Cycle - Superheated at Turbine Inlet') R2.calc efficiency ( ) R2.plot cycle_TS() Use pyplot to graph your Rankine cycle from homework 6 part 2 on a T-S diagram. The graphs should look like the following graphs (including title, axes labels, and summary notation): Rankine Cycle - Superheated at turbine inlet Rankine Cycle - Saturated at turbine inlet 500 500 Summary Summary 400 7:38.0% 0.95 Wiwi: 1230.6 KJK Wpi 8.1 kl/kg Ooster: 3216.6 kg 400 7:35.2% ne:0.95 W 915.5 KK Wome 8.1 kykg Oster: 2576.9 kg 200 200 100 100 s() Notes: i) You should modify your rankine class to include a value for isentropic turbine efficiency (Iturbine) and include Nturbine in your calculation for cycle efficiency. ii) You should include the plotting function as a method of the rankine class. And, iii) You should modify your test_rankine.py and call it EX2_3.py with the following main function: def main(): A test program for rankine power cycles. R1 is a rankine cycle object that is instantiated for turbine inlet of saturated vapor. R2 is a rankine cycle object that is instantiated for turbine inlet of superheated vapor. :return: none Rl=rankine (p high=8000, Blow=8, name='Rankine Cycle - Saturated at Turbine Inlet') Rl.calc_efficiency) Rl.plot_cycle_TS() R2=rankine ( high=8000, Blow=8, thigh=500, name='Rankine Cycle - Superheated at Turbine Inlet') R2.calc efficiency ( ) R2.plot cycle_TS()
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


