Question: Use the following file: Tester.py from clock import Clock myClock = Clock() for i in range(100) : myClock.pulse() print(myClock.getHours()) print(Expected: 1) print(myClock.getMinutes()) print(Expected: 40) for
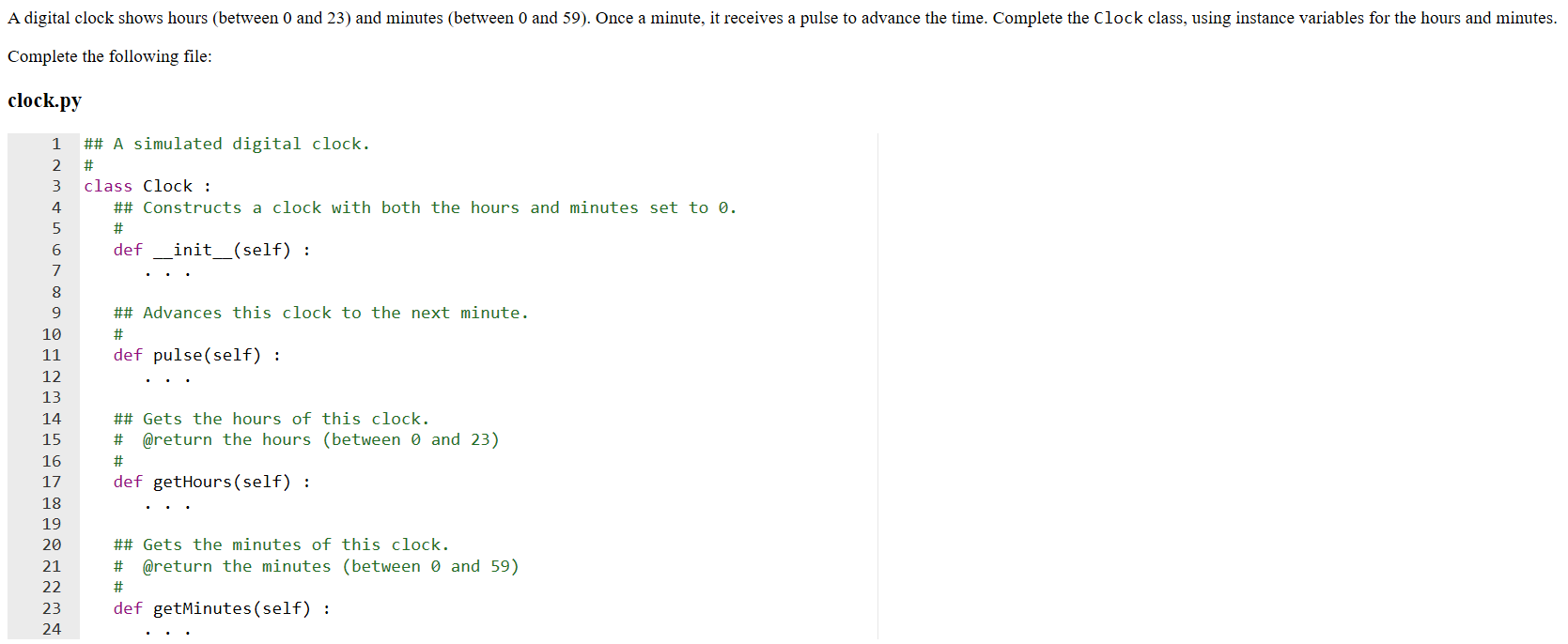
Use the following file:
Tester.py
from clock import Clock myClock = Clock() for i in range(100) : myClock.pulse() print(myClock.getHours()) print("Expected: 1") print(myClock.getMinutes()) print("Expected: 40") for i in range(70) : myClock.pulse() print(myClock.getHours()) print("Expected: 2") print(myClock.getMinutes()) print("Expected: 50") for i in range(1270) : myClock.pulse() print(myClock.getHours()) print("Expected: 0") print(myClock.getMinutes()) print("Expected: 0")A digital clock shows hours (between 0 and 23) and minutes between 0 and 59). Once a minute, it receives a pulse to advance the time. Complete the Clock class, using instance variables for the hours and minutes. Complete the following file: clock.py 1 ## A simulated digital clock. class Clock : ## Constructs a clock with both the hours and minutes set to 0. def __init__(self) : ## Advances this clock to the next minute. def pulse(self) : ## Gets the hours of this clock. # @return the hours (between 0 and 23) def getHours(self) : ## Gets the minutes of this clock. # @return the minutes (between 0 and 59) W NP def getMinutes (self)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


