Question: Use the given graph of the function f to answer the following questions. 110 -1 1. 1. Find the open interval(s) on which f is
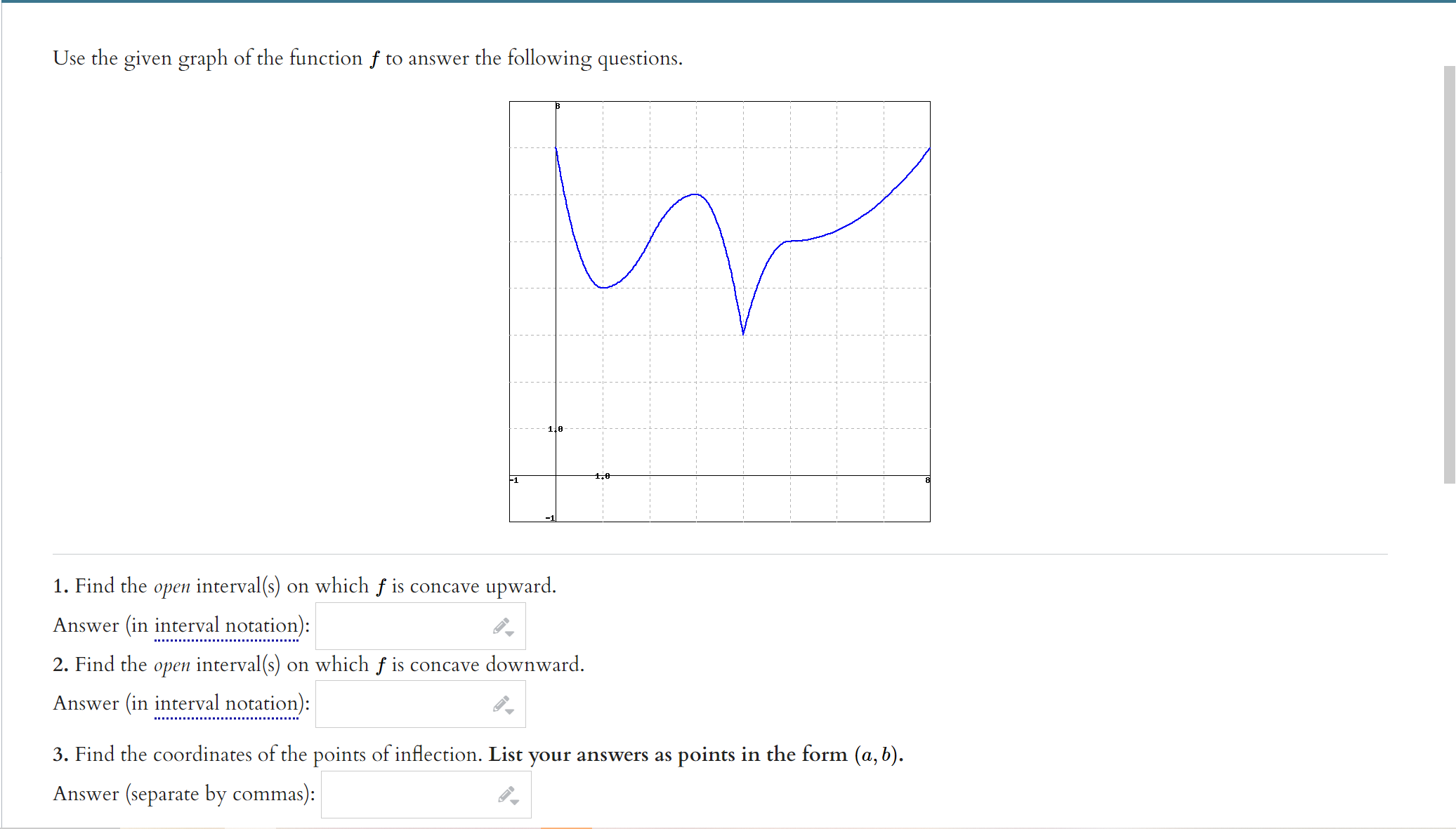
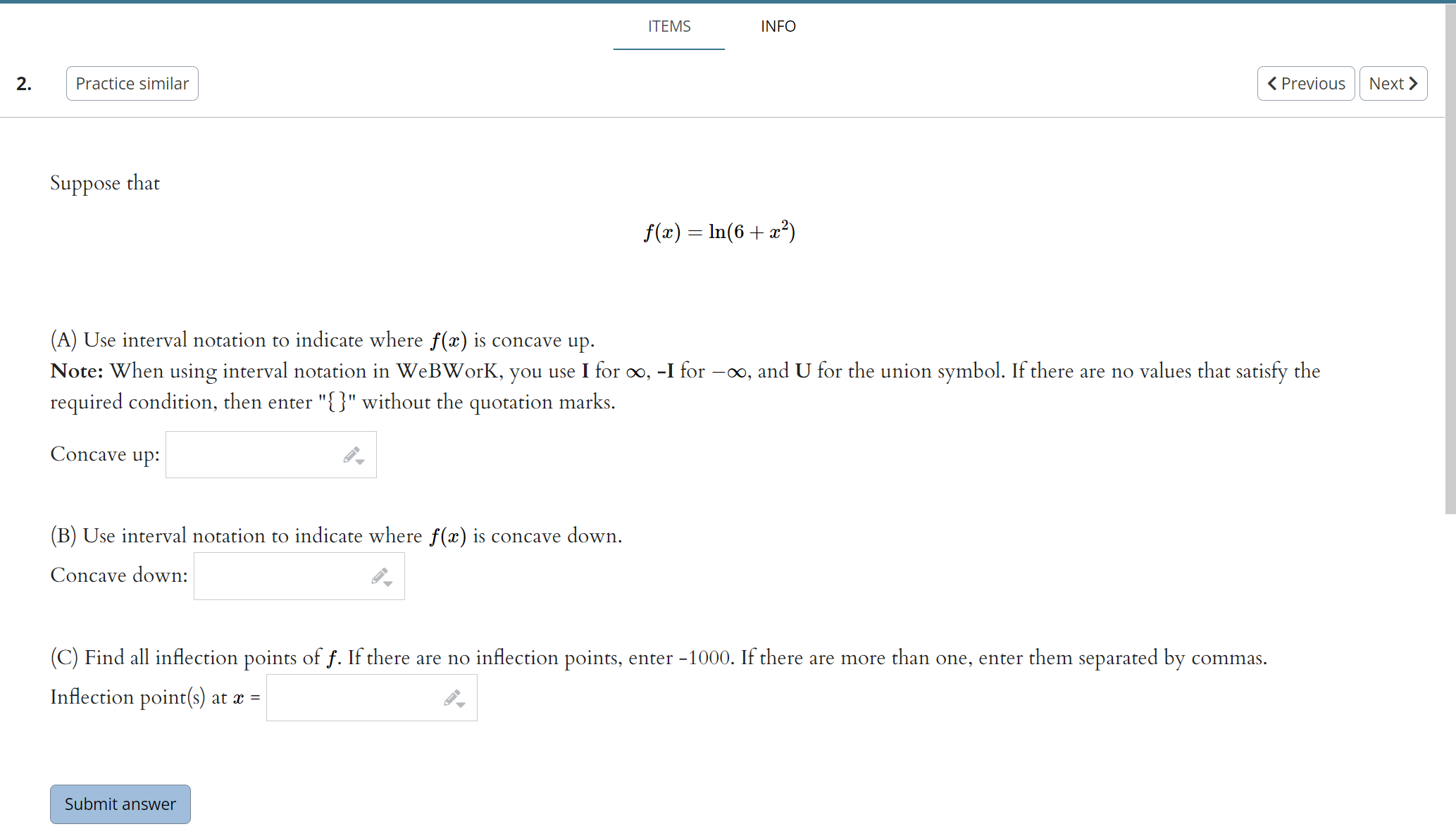
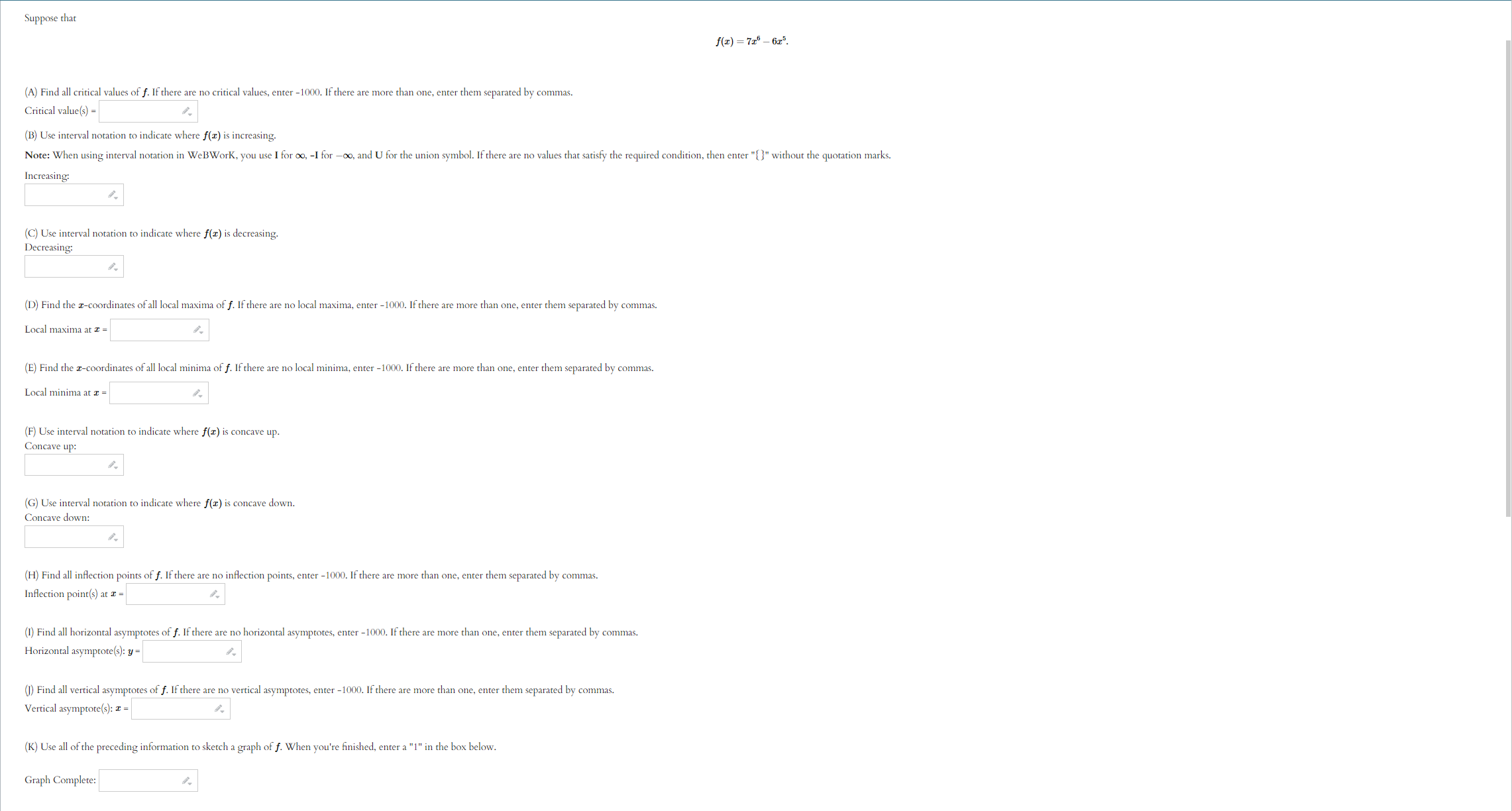
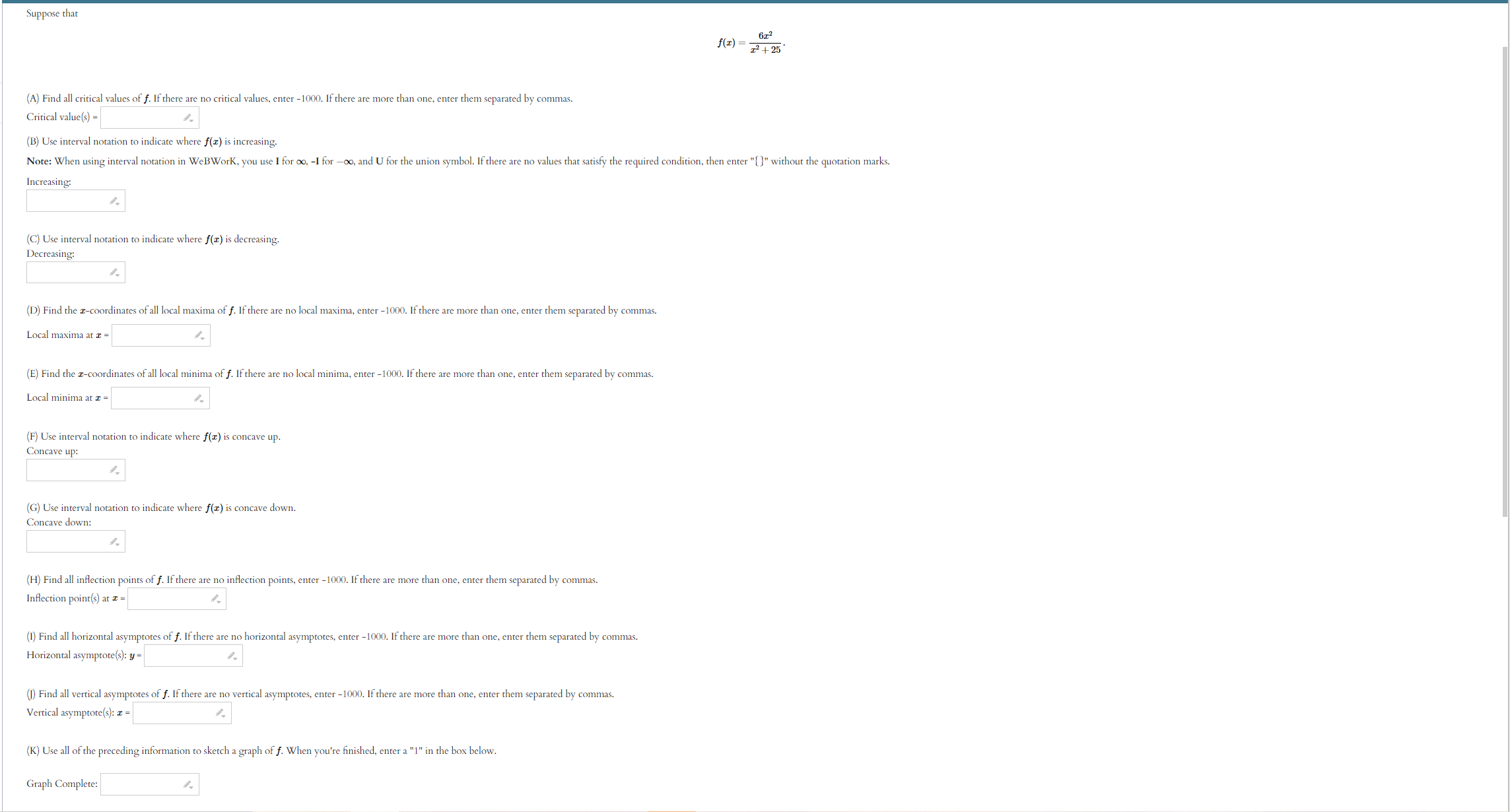
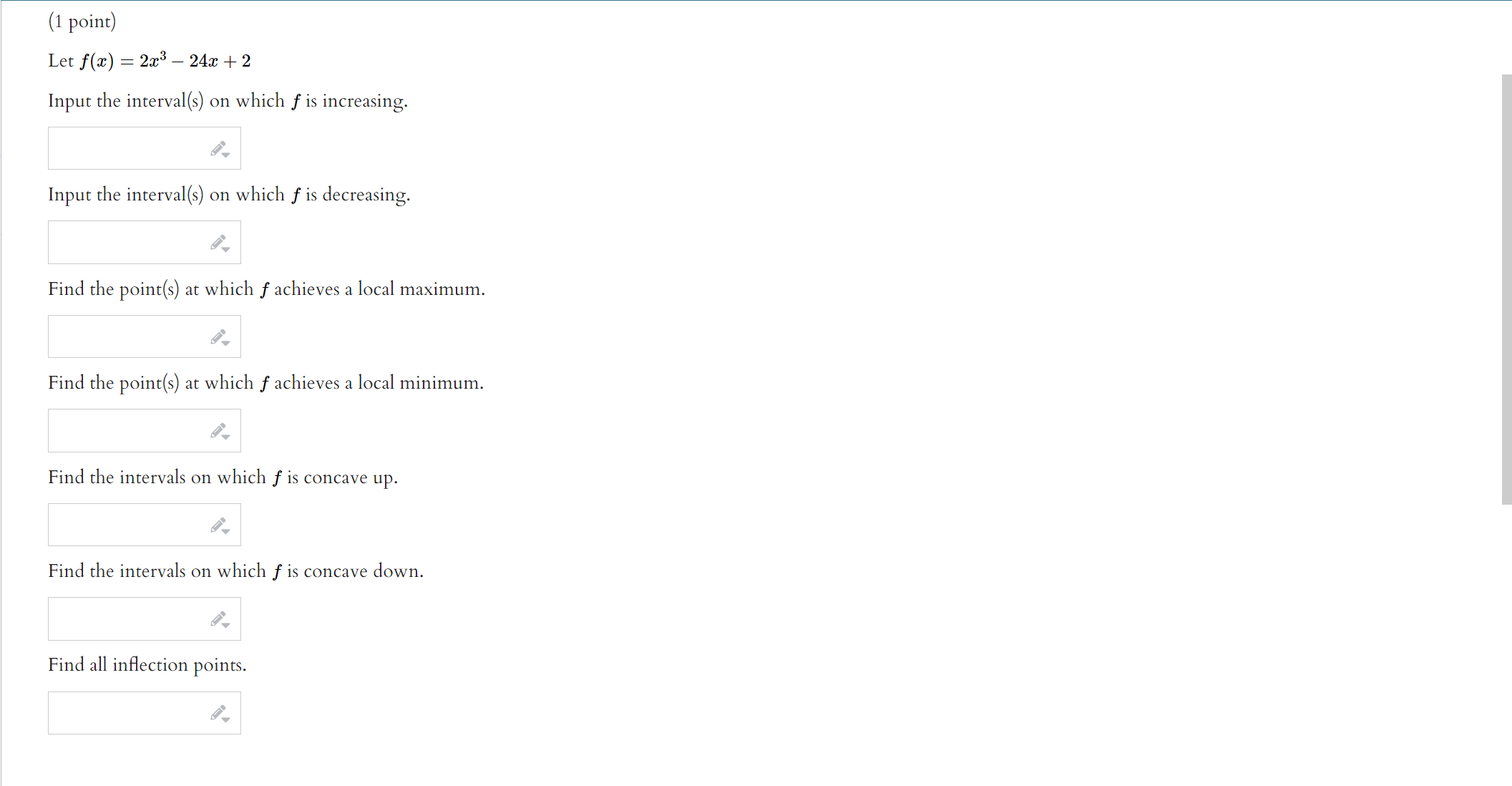
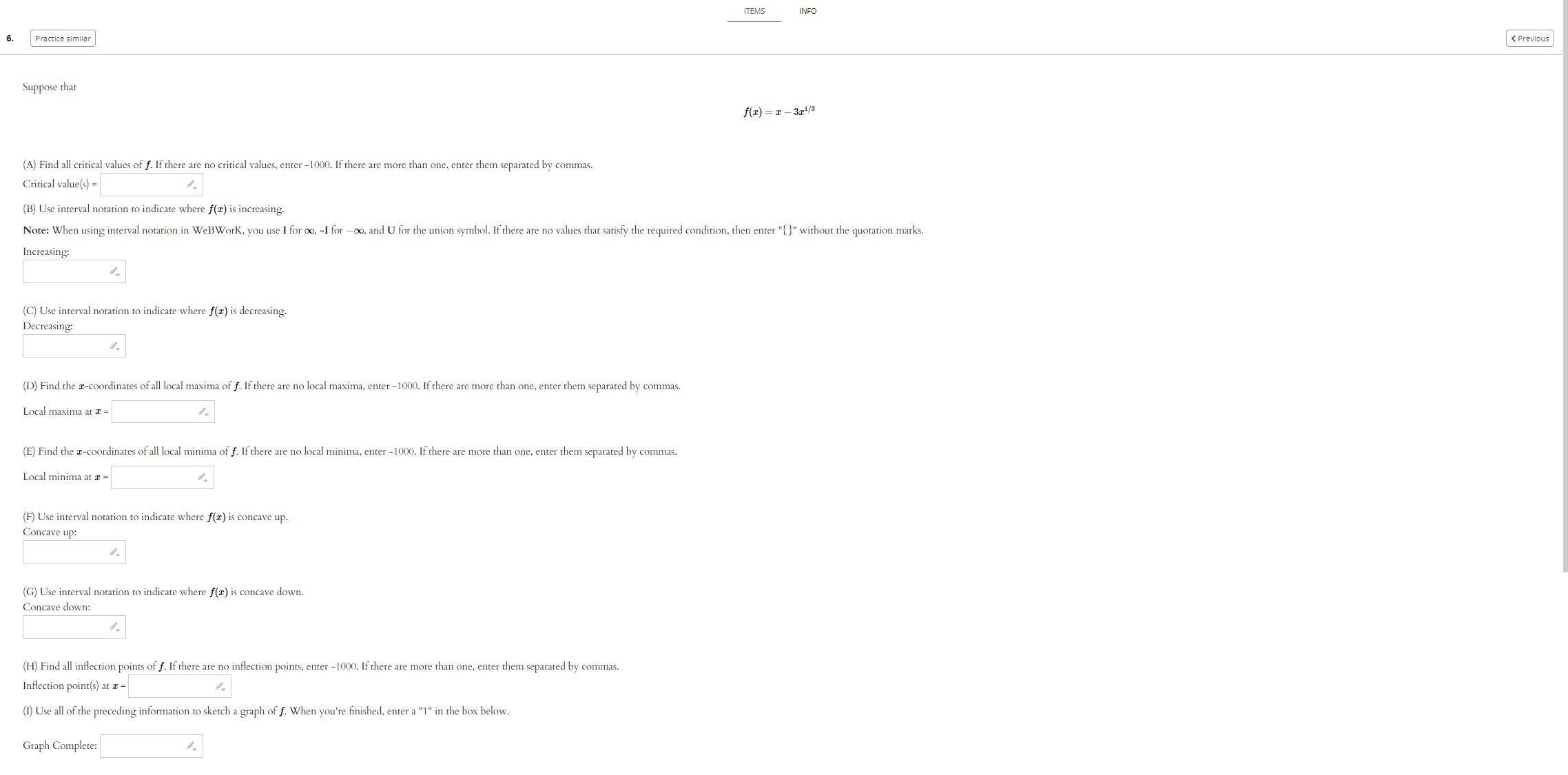
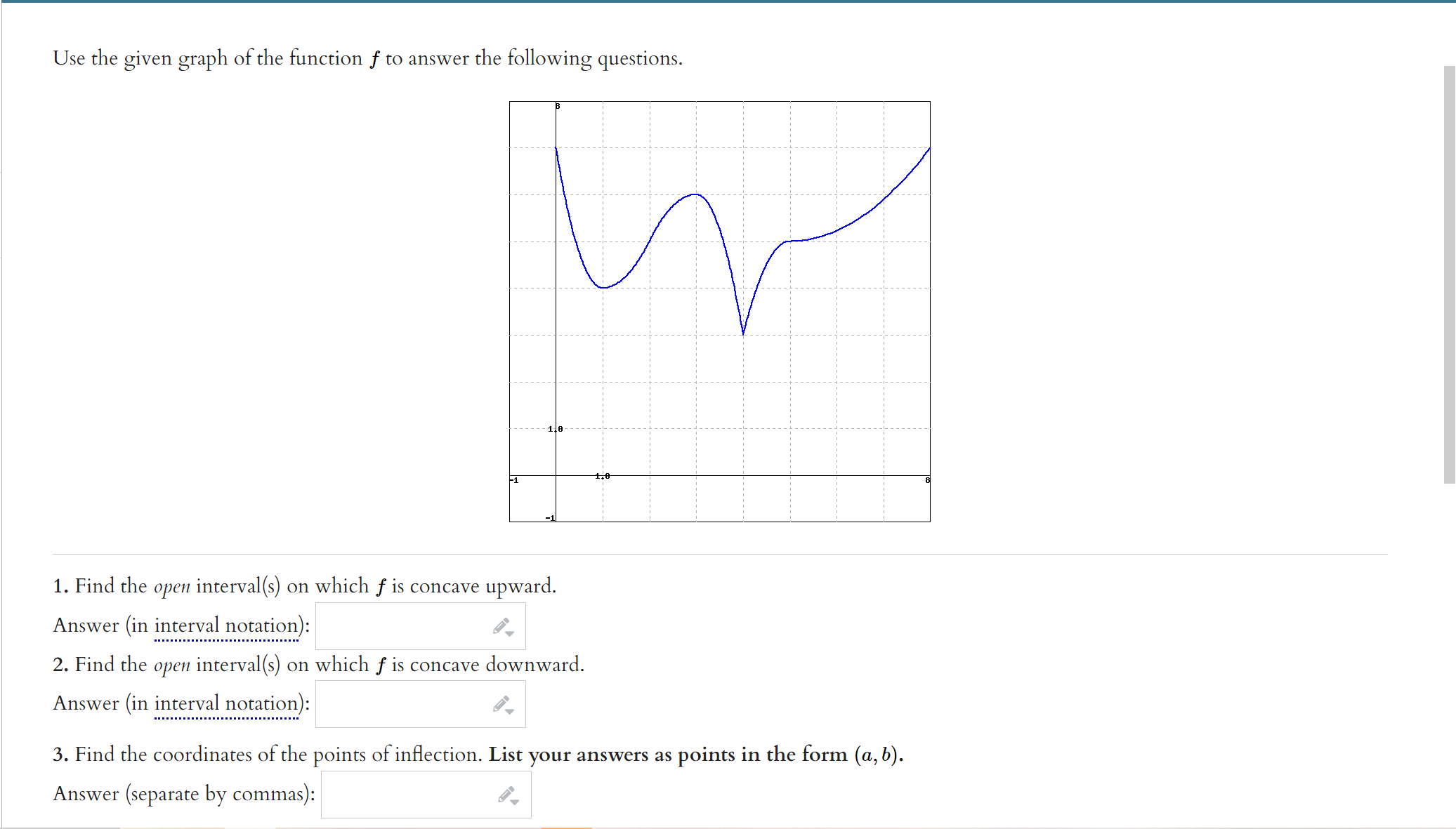
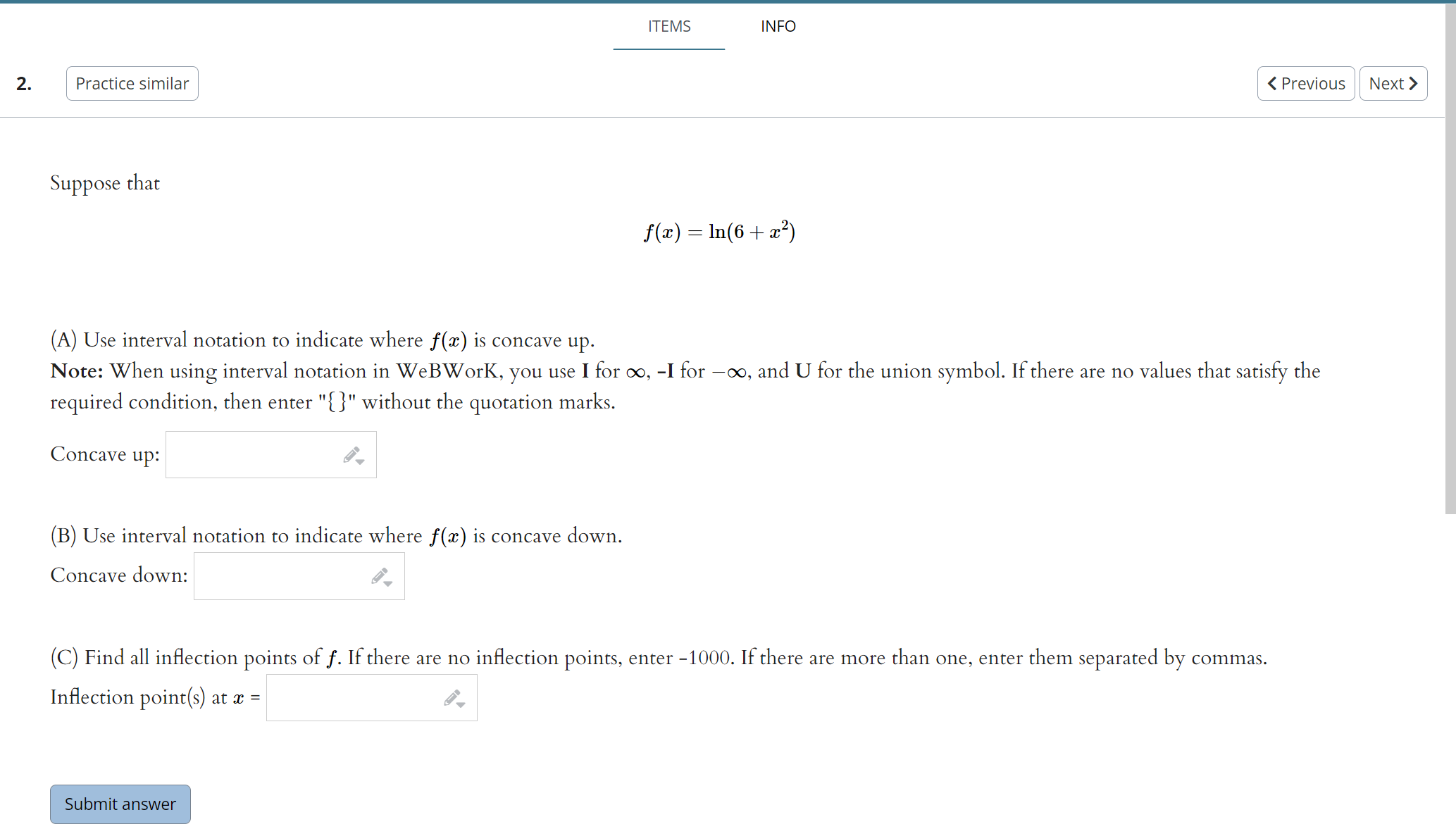
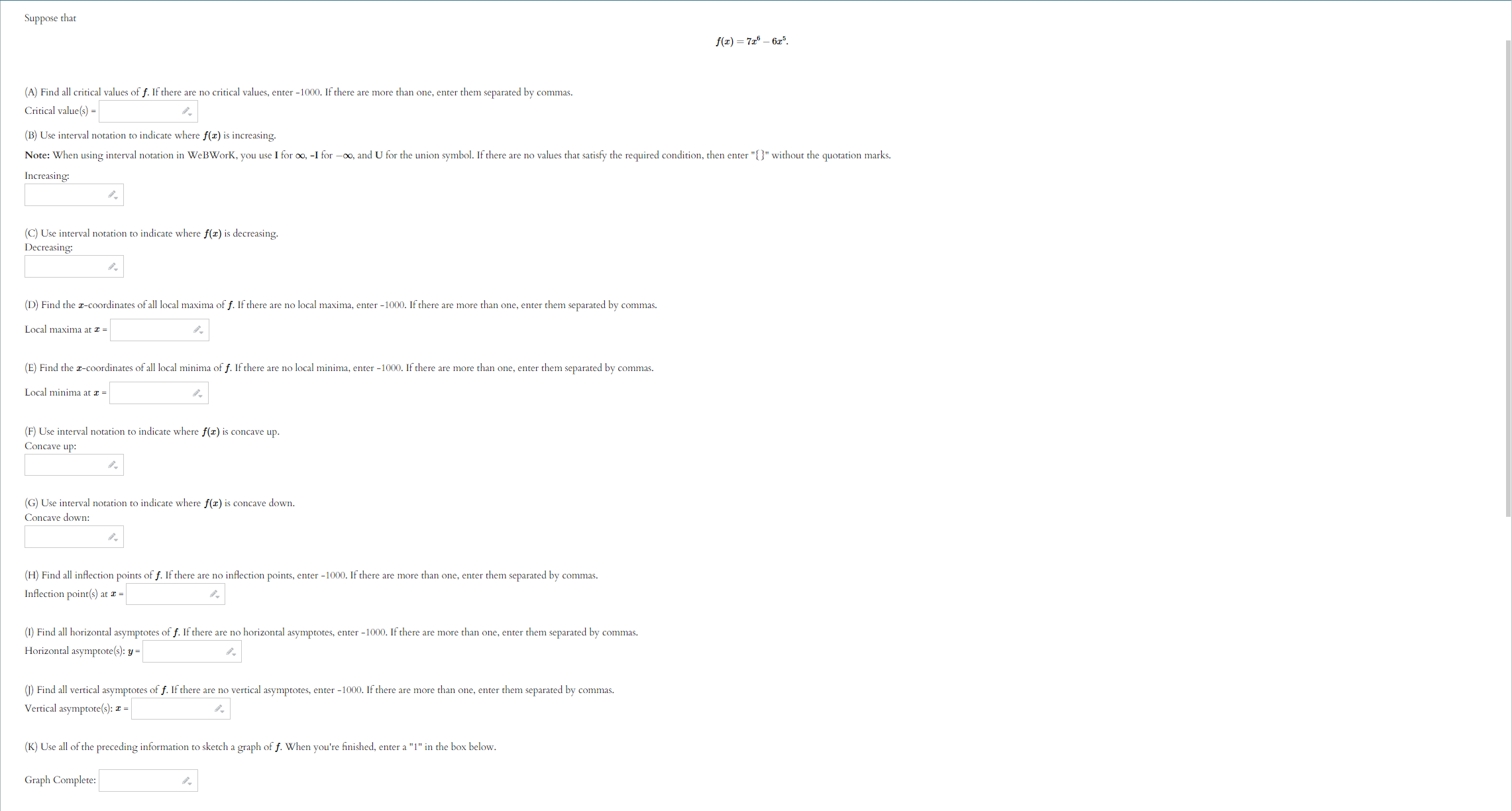
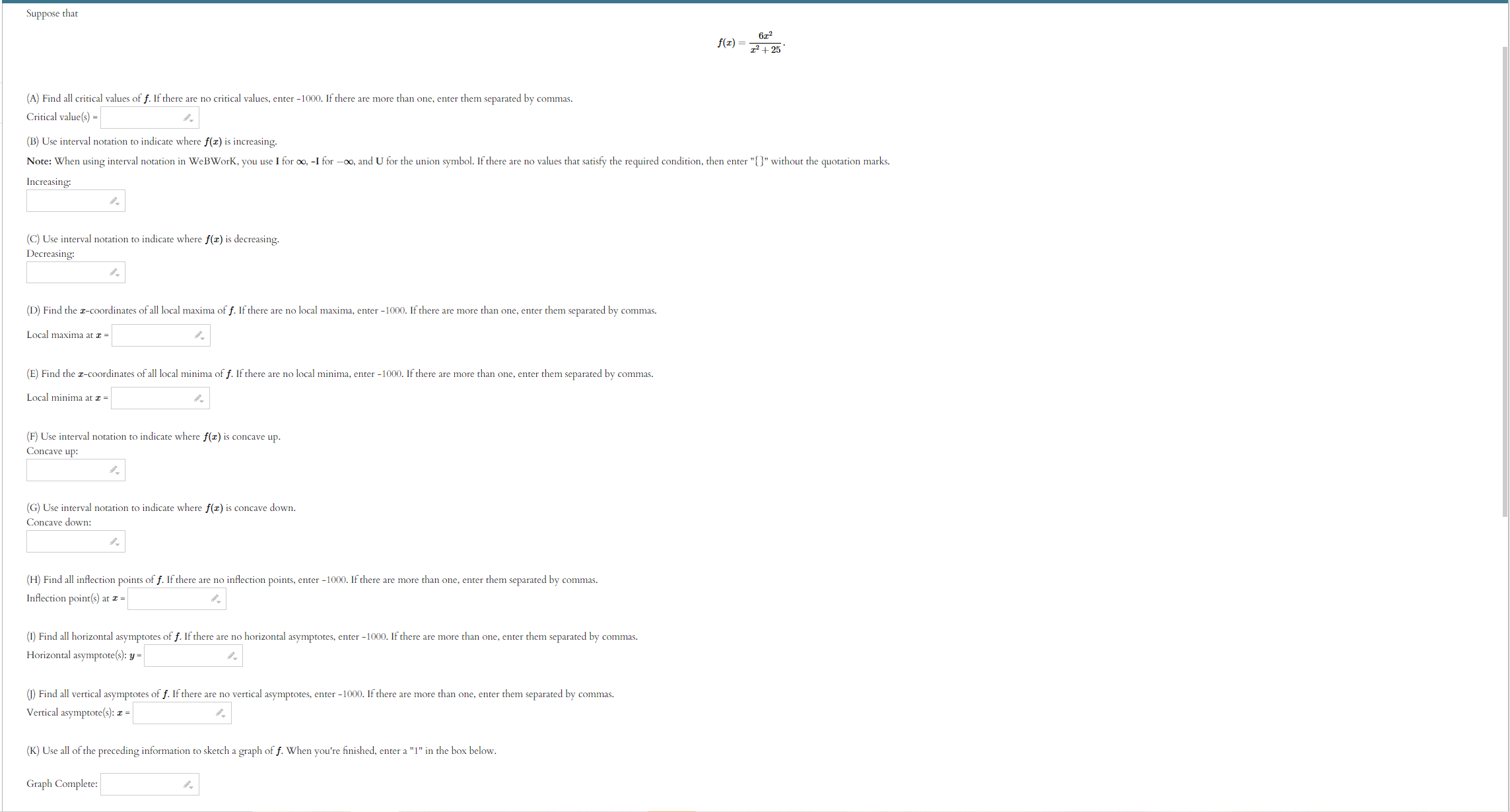
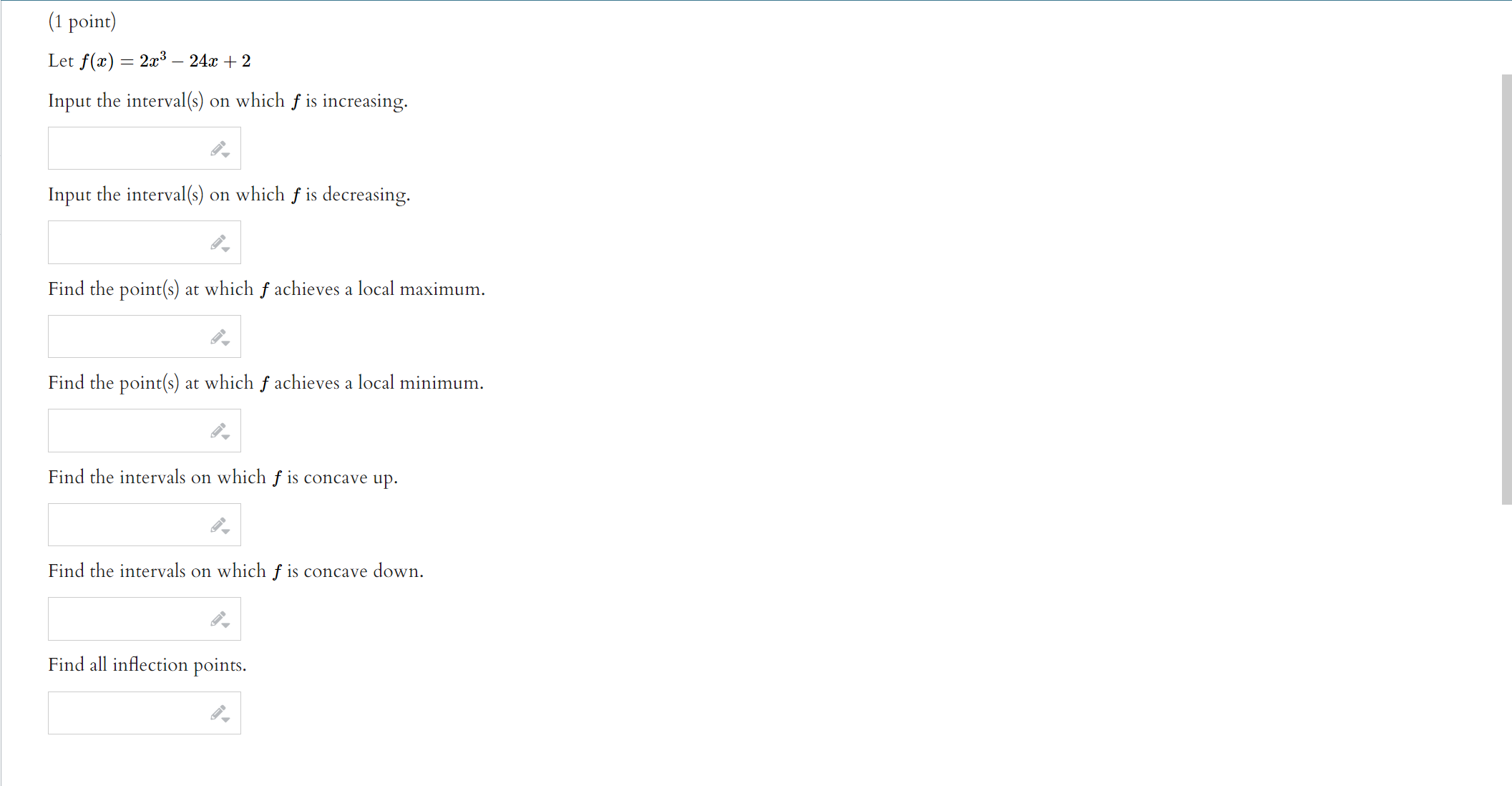
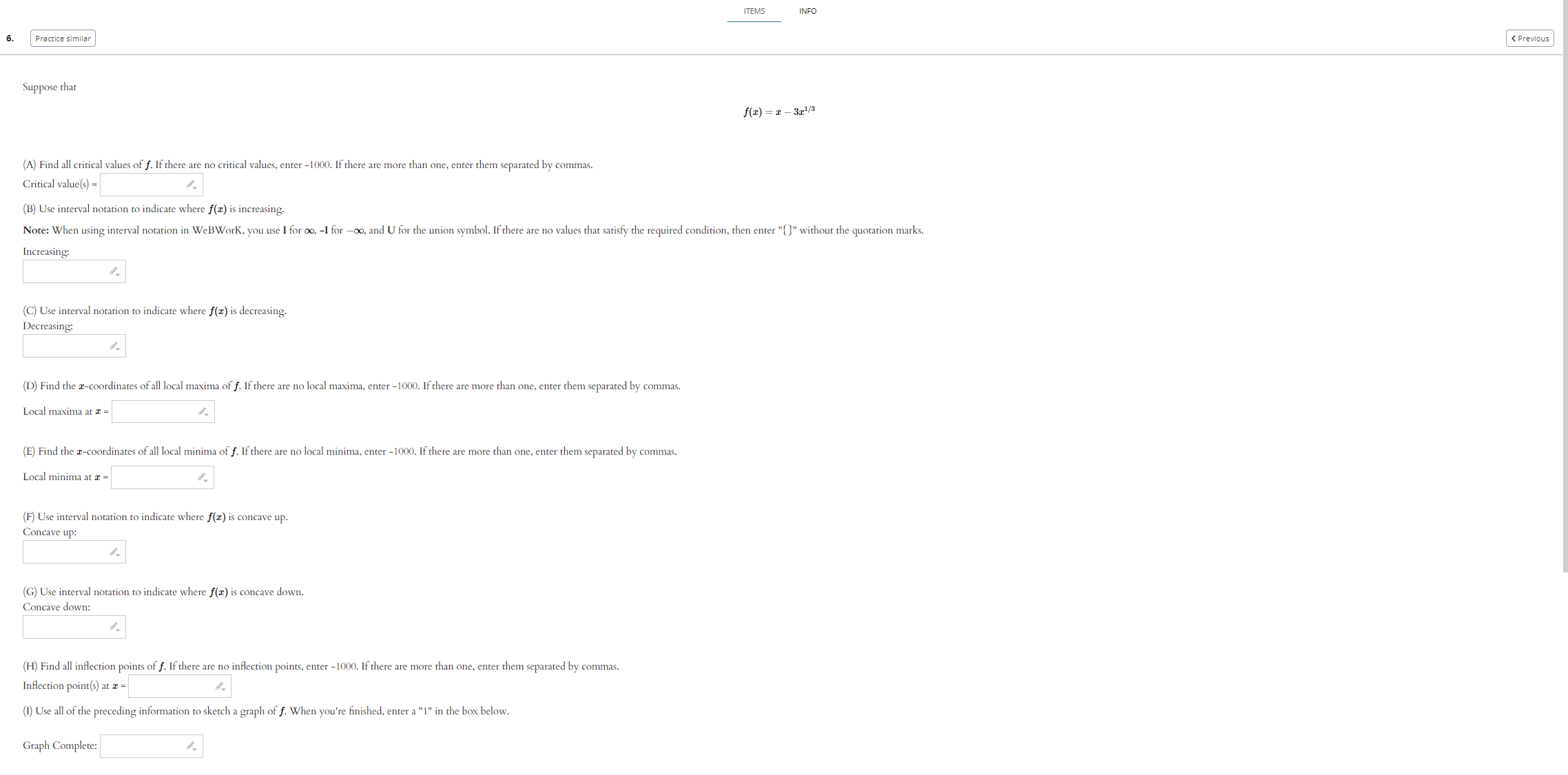
Use the given graph of the function f to answer the following questions. 110 -1 1. 1. Find the open interval(s) on which f is concave upward. Answer (in interval notation): 2. Find the open interval(s) on which f is concave downward. Answer (in interval notation): 3. Find the coordinates of the points of inflection. List your answers as points in the form (a, b). Answer (separate by commas):ITEMS INFO 2. Practice similar Suppose that f(ac) = In(6 + ac2) (A) Use interval notation to indicate where f(x) is concave up. Note: When using interval notation in WeBWork, you use I for co, -I for -co, and U for the union symbol. If there are no values that satisfy the required condition, then enter "{}" without the quotation marks. Concave up: (B) Use interval notation to indicate where f(x) is concave down. Concave down: (C) Find all inflection points of f. If there are no inflection points, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Inflection point(s) at a = Submit answerSuppose that f(x) =725 - 625. (A) Find all critical values of f. If there are no critical values, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Critical value(s) = (B) Use interval notation to indicate where f(I) is increasing. Note: When using interval notation in WeBWork, you use I for co, -I for -oo, and U for the union symbol. If there are no values that satisfy the required condition, then enter "[" without the quotation marks. Increasing: (C) Use interval notation to indicate where f(x) is decreasing. Decreasing: (D) Find the r-coordinates of all local maxima of f. If there are no local maxima, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Local maxima at I = (E) Find the z-coordinates of all local minima of f. If there are no local minima, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Local minima at I = (F) Use interval notation to indicate where f(x) is concave up. Concave up: (G) Use interval notation to indicate where f(I) is concave down. Concave down: (H) Find all inflection points of f. If there are no inflection points, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Inflection point(s) at a = (1) Find all horizontal asymptotes of f. If there are no horizontal asymptotes, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Horizontal asymptote(s): y = (1) Find all vertical asymptotes of f. If there are no vertical asymptotes, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Vertical asymptote(s): I = (K) Use all of the preceding information to sketch a graph of f. When you're finished, enter a "1" in the box below. Graph Complete:Suppose that 672 f ( I) = - 12 + 25 (A) Find all critical values of f. If there are no critical values, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Critical value(s) = (B) Use interval notation to indicate where f(I) is increasing. Note: When using interval notation in WeBWork, you use I for oo, -I for -oo, and U for the union symbol. If there are no values that satisfy the required condition, then enter "" without the quotation marks. Increasing: (C) Use interval notation to indicate where f(x) is decreasing. Decreasing: (D) Find the r-coordinates of all local maxima of f. If there are no local maxima, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Local maxima at I = (E) Find the r-coordinates of all local minima of f. If there are no local minima, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Local minima at a = (F) Use interval notation to indicate where f(I) is concave up. Concave up: (G) Use interval notation to indicate where f(z) is concave down. Concave down: (H) Find all inflection points of f. If there are no inflection points, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Inflection point(s) at z = (1) Find all horizontal asymptotes of f. If there are no horizontal asymptotes, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Horizontal asymptote(s): y = (1) Find all vertical asymptotes of f. If there are no vertical asymptotes, enter -1000. If there are more than one, enter them separated by commas. Vertical asymptote(s): I = (K) Use all of the preceding information to sketch a graph of f. When you're finished, enter a "1" in the box below. Graph Complete:(1 point) Let f(ac) = 2x3 - 24x + 2 Input the interval(s) on which f is increasing. Input the interval(s) on which f is decreasing. Find the point(s) at which f achieves a local maximum. Find the point(s) at which f achieves a local minimum. Find the intervals on which f is concave up. Find the intervals on which f is concave down. Find all inflection points.ITEMS INFO 6. Practice similar
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


