Question: use the graphs below to answer question 1 6. a) Explain the role of demand, variable cost, and perceived benefits/value in pricing. Be sure to

 use the graphs below to answer question 1
use the graphs below to answer question 1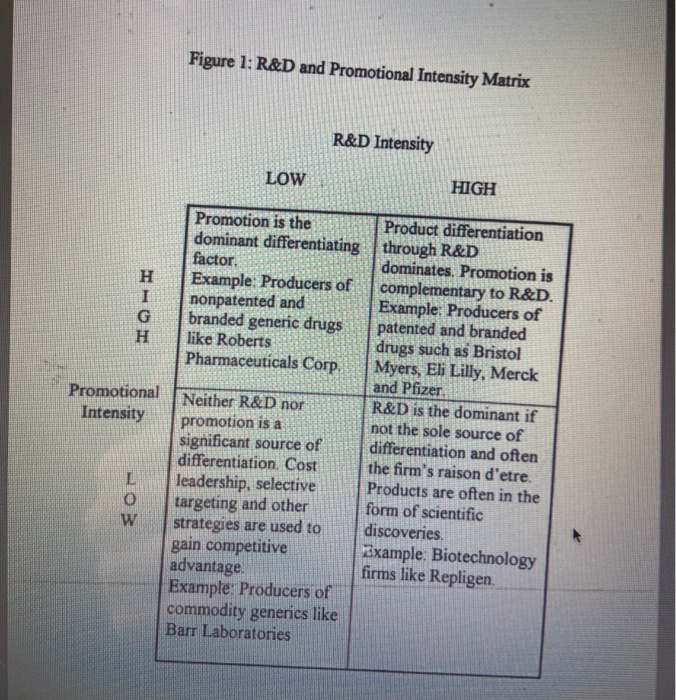
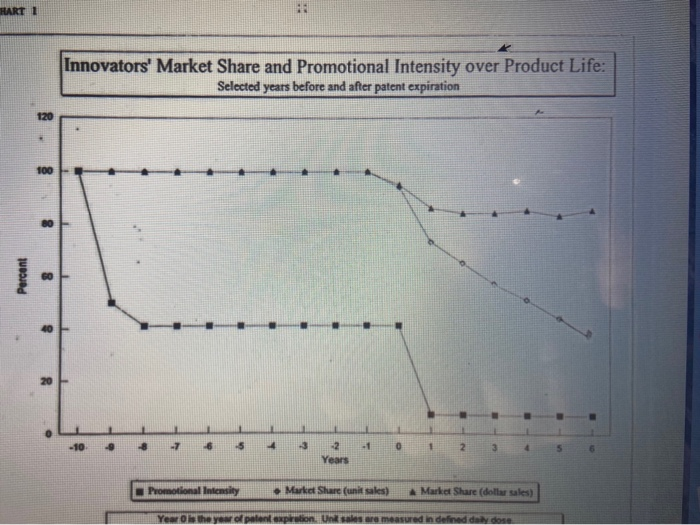
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


