Question: Use the standard reduction potentials located in the 'Tables' linked above to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for the reaction: Cu2+(aq)+2Cr2+(aq)Cu(s)+2Cr3+(aq) Answer:

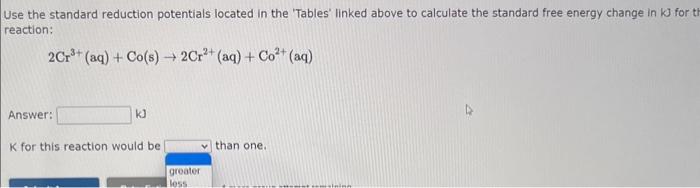

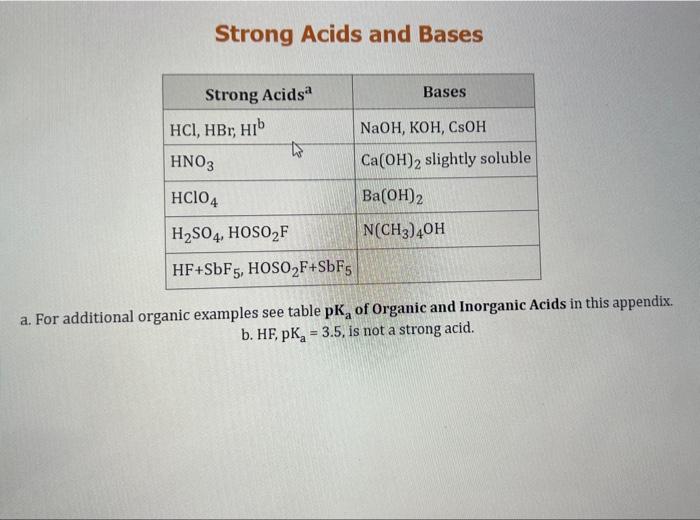
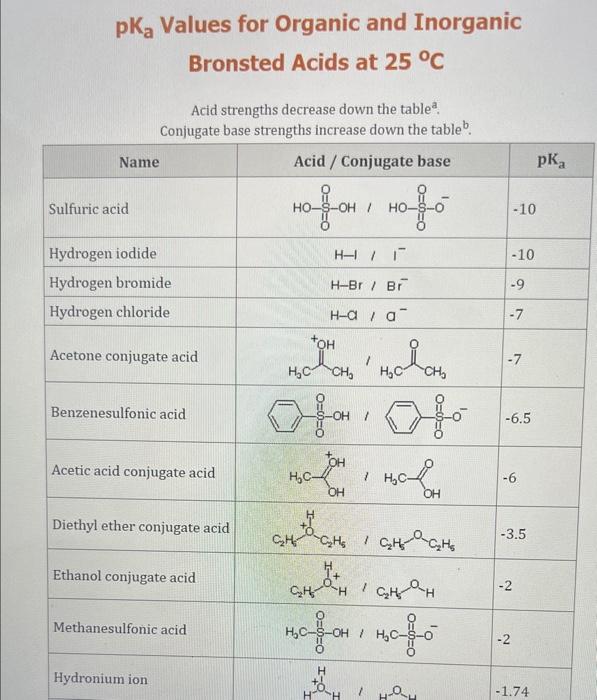
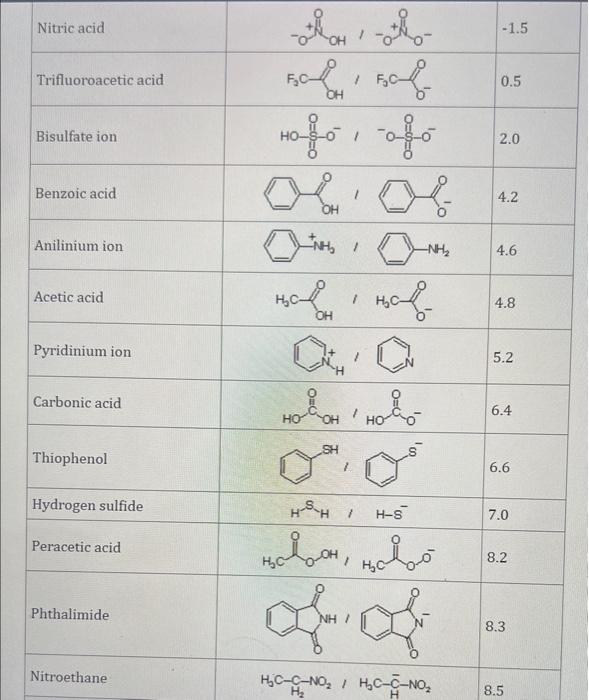
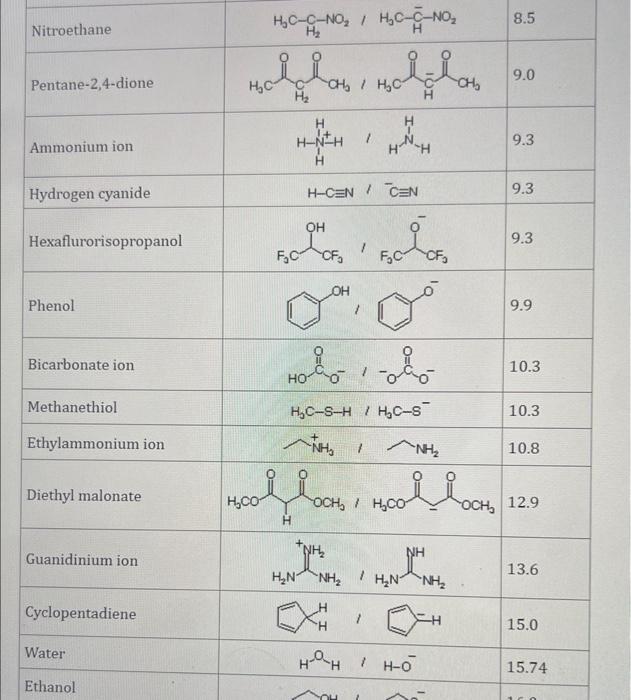
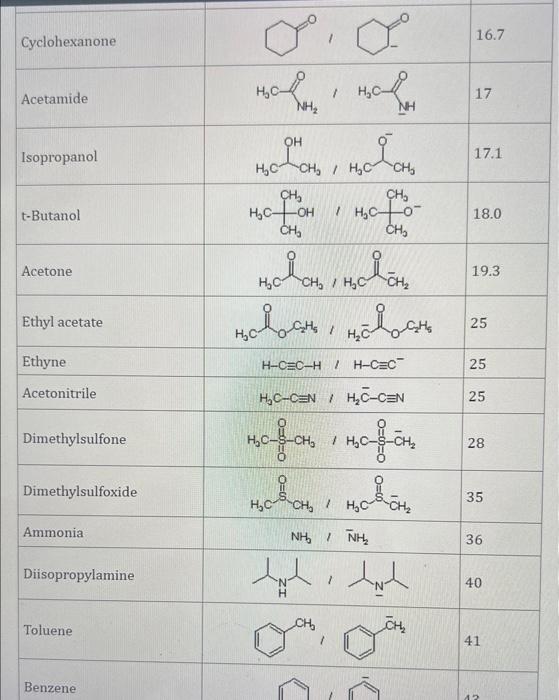
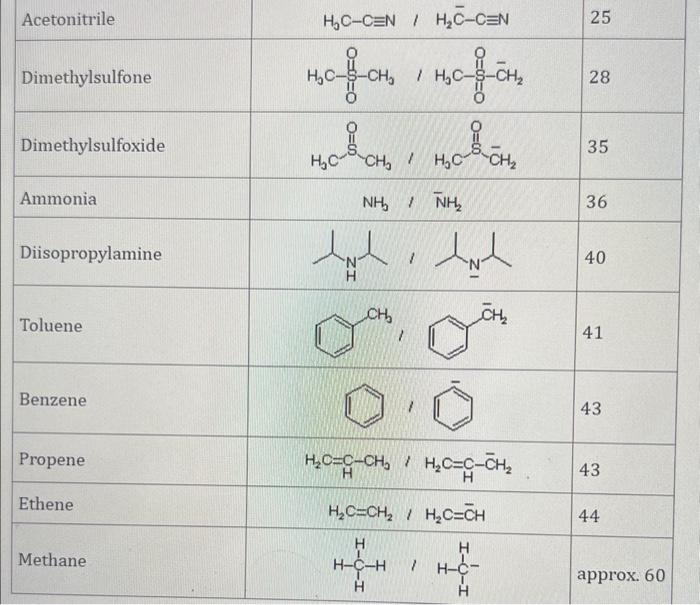
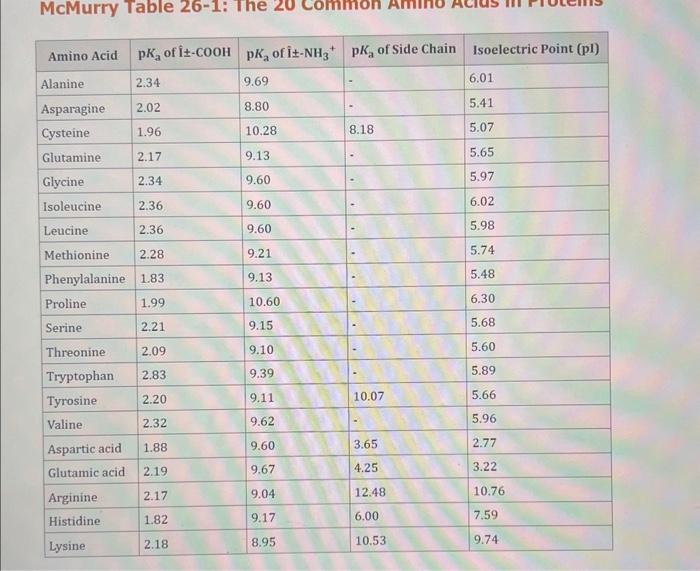
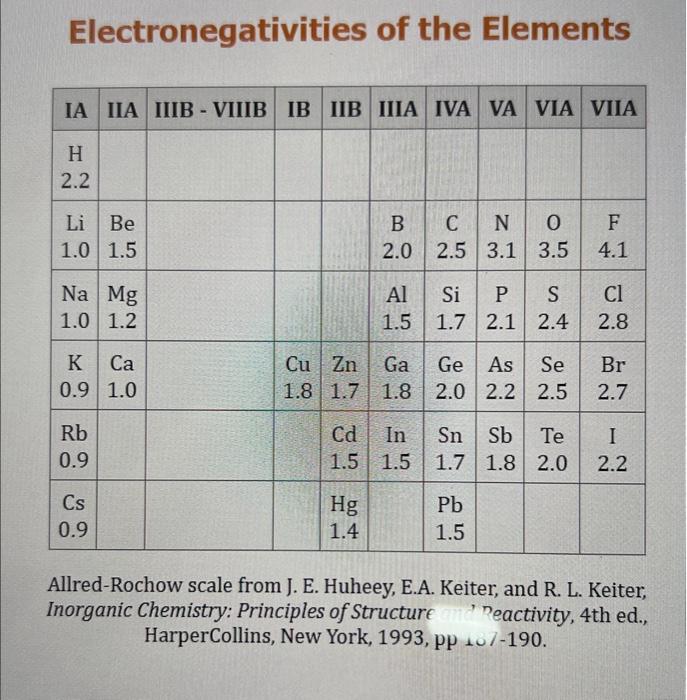
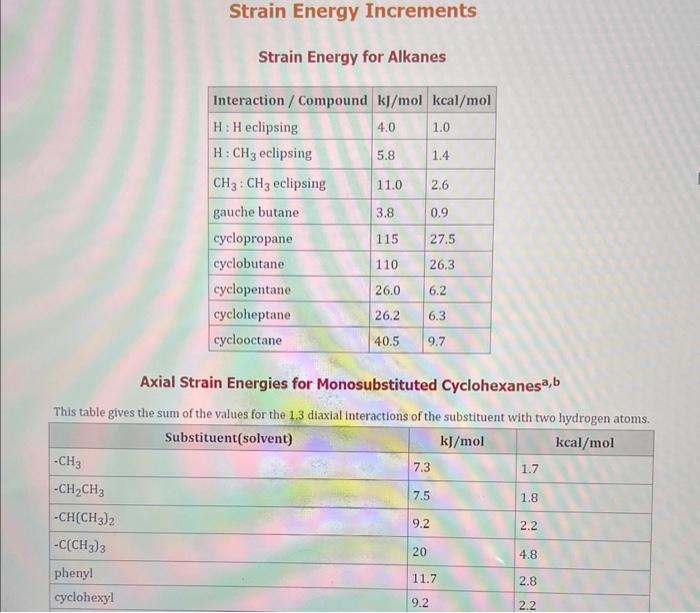
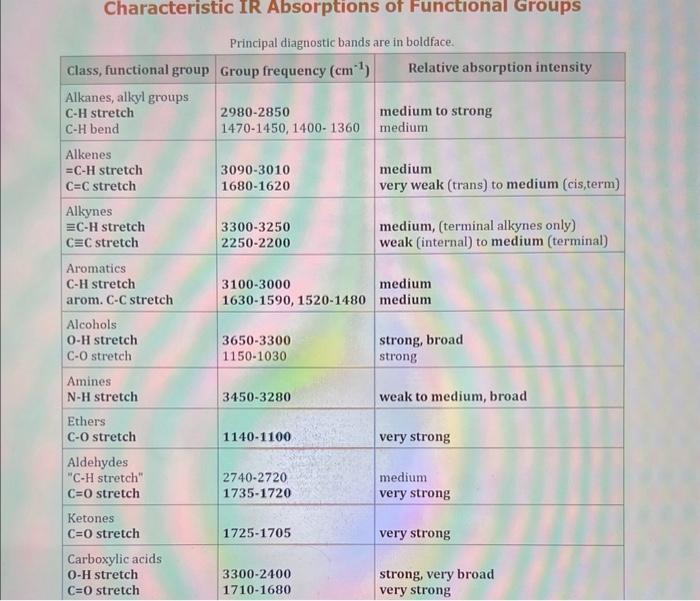
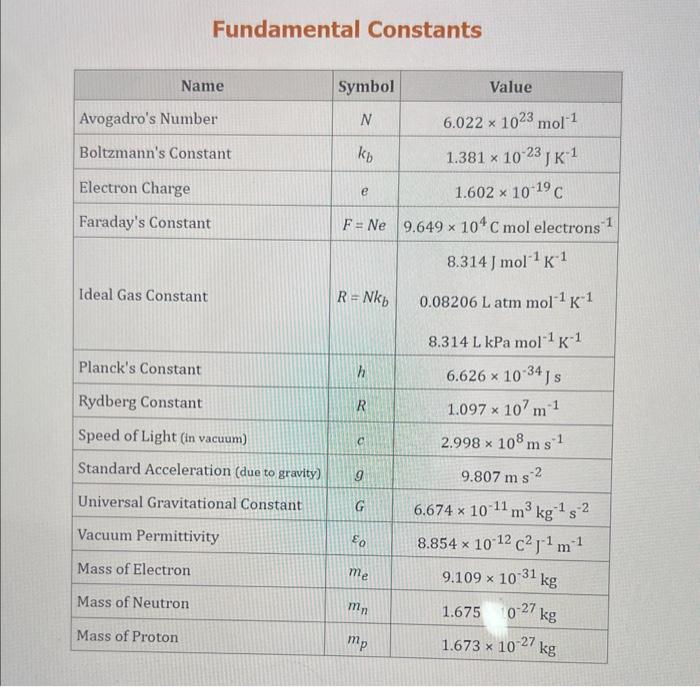
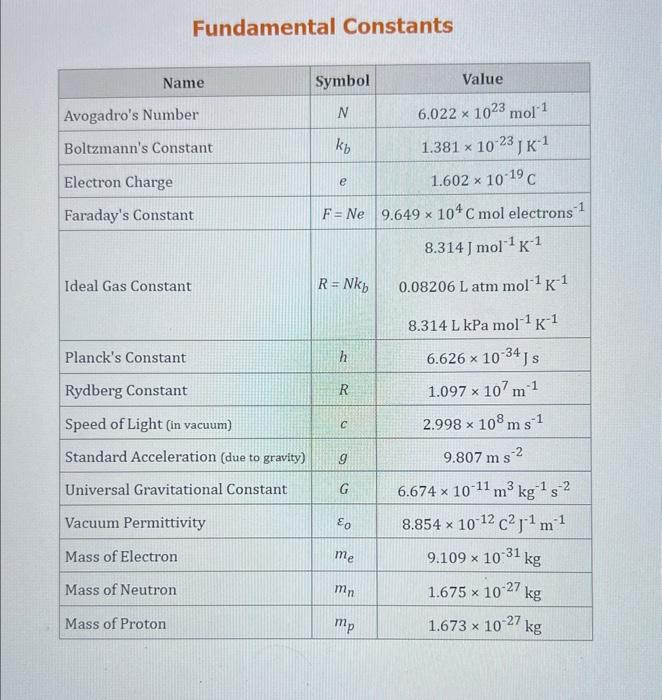
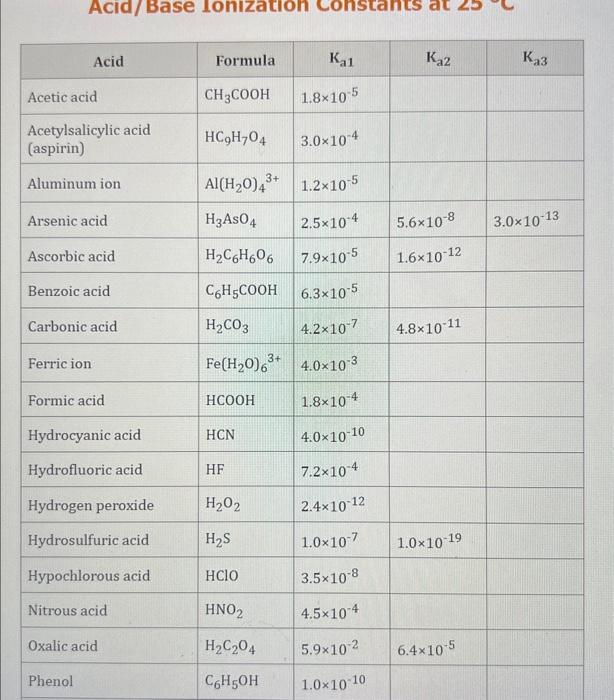
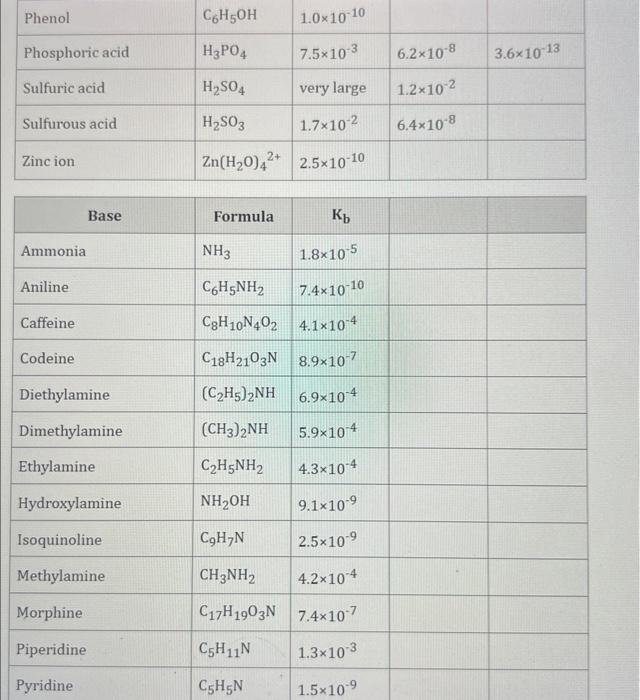
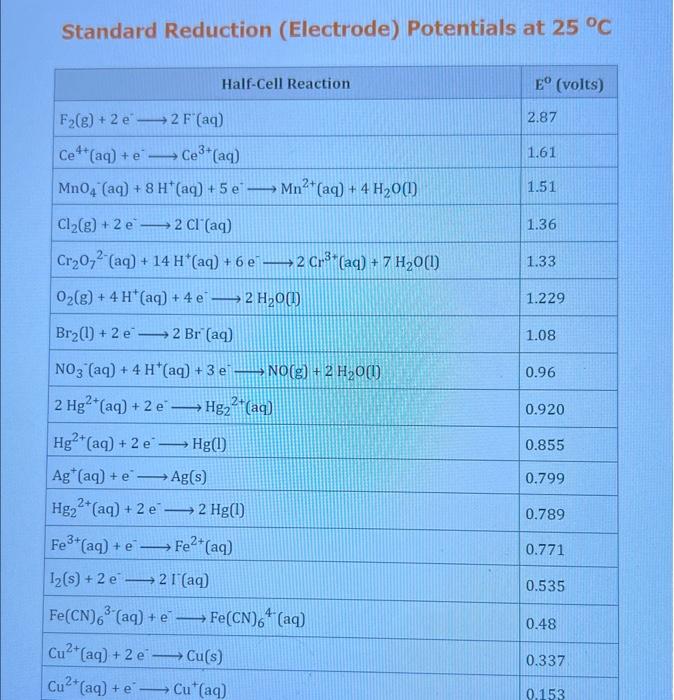

Use the standard reduction potentials located in the 'Tables' linked above to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for the reaction: Cu2+(aq)+2Cr2+(aq)Cu(s)+2Cr3+(aq) Answer: K for this reaction would be than one. 1 more group attenpt remaining Use the standard reduction potentials located in the 'Tables' linked above to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for t reaction: 2Cr3+(aq)+Co(s)2Cr2+(aq)+Co2+(aq) Answer: kJ K for this reaction would be than one. Use the standard reduction potentials located in the 'Tables' linked above to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for the reaction: 2Cr3+(aq)+2I(aq)2Cr2+(aq)+I2(s) Answer: kJ K for this reaction would be than one. Strong Acids and Bases a. For additional organic examples see table pKa of Organic and Inorganic Acids in this appendix. b. HF,pKa=3.5, is not a strong acid. Acid strengths decrease down the table a. Coniugate base strengths increase down the table . Nitroethane 8.5 Pentane-2,4-dione 9.0 Ammonium ion 9.3 Hydrogen cyanide 9.3 Hexaflurorisopropanol Phenol 9.9 Bicarbonate ion 1a00 10.3 Methanethiol H3CSH 3H3Cs 10.3 Ethylammonium ion 10.8 Diethyl malonate 12.9 Guanidinium ion 13.6 Cyclopentadiene 15.0 Water Ethanol Cyclohexanone 16.7 Acetamide Isopropanol t-Butanol 17.1 Acetone Dimethylsulfone 19.3 Ethyl acetate Ethyne HCCH H2CCN O H2COOCH3 O 25 Acetonitrile 25 Diisopropylamine 1 28 Toluene 35 36 40 41 Benzene Electronegativities of the Elements Allred-Rochow scale from J. E. Huheey, E.A. Keiter, and R. L. Keiter, Inorganic Chemistry: Principles of Structure 'Deactivity, 4th ed., HarperCollins, New York, 1993, pp to/-190. Strain Energy Increments Strain Energy for Alkanes Axial Strain Energies for Monosubstituted Cyclohexanes a,b Characteristic IR Absorptions of Functional Groups Principal diagnostic bands are in boldface. Eindamontal Conctante Fundamental Constants \begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|} \hline \multicolumn{1}{|c|}{ Base } & \multicolumn{1}{|c|}{ Formula } & \multicolumn{1}{c|}{Kb} \\ \hline Ammonia & NH3 & 1.8105 \\ \hline Aniline & C6H5NH2 & 7.41010 \\ \hline Caffeine & C8H10N4O2 & 4.1104 \\ \hline Codeine & C18H21O3N & 8.9107 \\ \hline Diethylamine & (C2H5)2NH & 6.9104 \\ \hline Dimethylamine & (CH3)2NH & 5.9104 \\ \hline Ethylamine & C2H5NH2 & 4.3104 \\ \hline Hydroxylamine & NH2OH & 9.1109 \\ \hline Isoquinoline & C9H7N & 2.5109 \\ \hline Methylamine & CH3NH2 & 4.2104 \\ \hline Morphine & C17H19O3N & 7.4107 \\ \hline Piperidine & C5H11N & 1.3103 \\ \hline Pyridine & C5H5N & 1.5109 \\ \hline \end{tabular} Standard Reduction (Electrode) Potentials at 25C
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


