Question: Useful equations, formulae, physical constants and properties ( i ) Energy equation for the total flow in a pipeline running from point 1 to point
Useful equations, formulae, physical constants and properties
i Energy equation for the total flow in a pipeline running from point to point :
where is the velocity of the flow expressed in
is the hydraulic pressure expressed in
is the elevation of the pipe expressed in above datum
is the head loss expressed in
ii DarcyWeisbach Formula:
where is a friction factor
is the length of the pipe
is the internal diameter of the pipe
iii Colebrook and White Formula:
where is the linear measurement of surface roughness of the pipe
is Reynolds number
is the kinematic viscosity of the fluid
iv Values to be used for design purpose: ;;
v For simplicity, the nominal diameter DN of the pipe can be taken as for design
purpose. Common pipe sizes include DN DN DN and DN
vi Friction factor calculated in an iterative process using and different
combinations of and values are shown in the table below. You may use the nearest
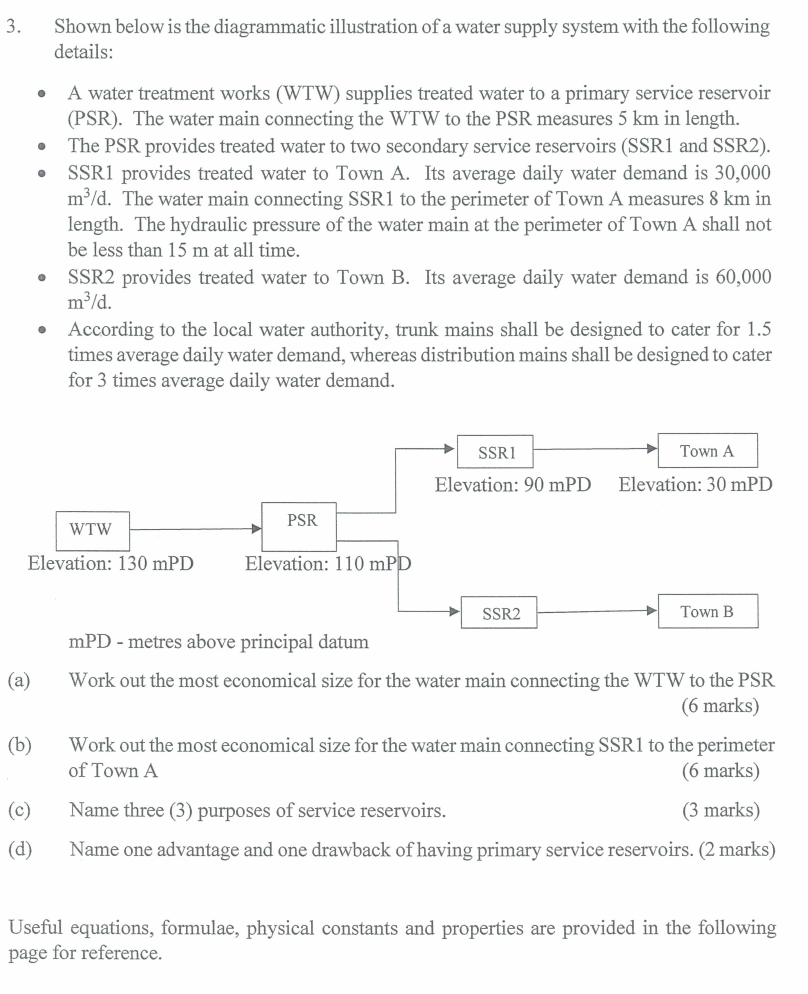
Re value to obtain Shown below is the diagrammatic illustration of a water supply system with the following
details:
A water treatment works WTW supplies treated water to a primary service reservoir
PSR The water main connecting the WTW to the PSR measures in length.
The PSR provides treated water to two secondary service reservoirs SSR and SSR
SSR provides treated water to Town A Its average daily water demand is
The water main connecting SSR to the perimeter of Town A measures in
length. The hydraulic pressure of the water main at the perimeter of Town A shall not
be less than at all time.
SSR provides treated water to Town B Its average daily water demand is
According to the local water authority, trunk mains shall be designed to cater for
times average daily water demand, whereas distribution mains shall be designed to cater
for times average daily water demand.
a Work out the most economical size for the water main connecting the WTW to the PSR
marks
b Work out the most economical size for the water main connecting SSR to the perimeter
of Town A
marks
c Name three purposes of service reservoirs.
marks
d Name one advantage and one drawback of having primary service reservoirs. marks
Useful equations, formulae, physical constants and properties are provided in the following
page for reference.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


