Question: Using C++ Implement the linked list using the UML diagram. You can use the private access specifier for the data members and you do not
Using C++ Implement the linked list using the UML diagram. You can use the private access specifier for the data members and you do not need to develop the linkedList Iterator functions.
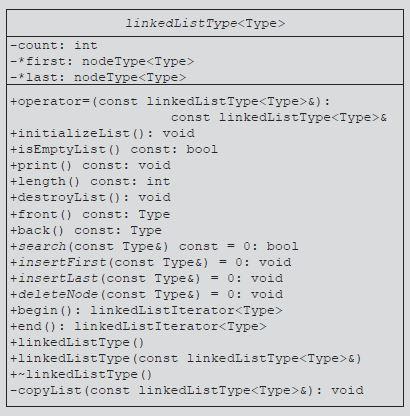
| // This class specifies the members to implement the basic |
| // properties of a linked list. This is an abstract class. |
| // We cannot instantiate an object of this class. |
| //*********************************************************** |
| template |
| class linkedListType |
| { |
| public: |
| const linkedListType |
| (const linkedListType |
| //Overload the assignment operator. |
| void initializeList(); |
| //Initialize the list to an empty state. |
| //Postcondition: first = NULL, last = NULL, count = 0; |
| bool isEmptyList() const; |
| //Function to determine whether the list is empty. |
| //Postcondition: Returns true if the list is empty, otherwise |
| // it returns false. |
| void print() const; |
| //Function to output the data contained in each node. |
| //Postcondition: none |
| int length() const; |
| //Function to return the number of nodes in the list. |
| //Postcondition: The value of count is returned. |
| void destroyList(); |
| //Function to delete all the nodes from the list. |
| //Postcondition: first = NULL, last = NULL, count = 0; |
| Type front() const; |
| //Function to return the first element of the list. |
| //Precondition: The list must exist and must not be empty. |
| //Postcondition: If the list is empty, the program terminates; |
| // otherwise, the first element of the list is returned. |
| Type back() const; |
| //Function to return the last element of the list. |
| //Precondition: The list must exist and must not be empty. |
| //Postcondition: If the list is empty, the program |
| // terminates; otherwise, the last |
| // element of the list is returned. |
| virtual bool search(const Type& searchItem) const = 0; |
| //Function to determine whether searchItem is in the list. |
| //Postcondition: Returns true if searchItem is in the list, |
| // otherwise the value false is returned. |
| virtual void insertFirst(const Type& newItem) = 0; |
| //Function to insert newItem at the beginning of the list. |
| //Postcondition: first points to the new list, newItem is |
| // inserted at the beginning of the list, last points to |
| // the last node in the list, and count is incremented by |
| // 1. |
| virtual void insertLast(const Type& newItem) = 0; |
| //Function to insert newItem at the end of the list. |
| //Postcondition: first points to the new list, newItem is |
| // inserted at the end of the list, last points to the |
| // last node in the list, and count is incremented by 1. |
| virtual void deleteNode(const Type& deleteItem) = 0; |
| //Function to delete deleteItem from the list. |
| //Postcondition: If found, the node containing deleteItem is |
| // deleted from the list. first points to the first node, |
| // last points to the last node of the updated list, and |
| // count is decremented by 1. |
| linkedListIterator |
| //Function to return an iterator at the beginning of the |
| //linked list. |
| //Postcondition: Returns an iterator such that current is set |
| // to first. |
| linkedListIterator |
| //Function to return an iterator one element past the |
| //last element of the linked list. |
| //Postcondition: Returns an iterator such that current is set |
| // to NULL. |
| linkedListType(); |
| //default constructor |
| //Initializes the list to an empty state. |
| //Postcondition: first = NULL, last = NULL, count = 0; |
| linkedListType(const linkedListType |
| //copy constructor |
| ~linkedListType(); |
| //destructor |
| //Deletes all the nodes from the list. |
| //Postcondition: The list object is destroyed. |
| protected: |
| int count; //variable to store the number of list elements |
| // |
| nodeType |
| nodeType |
| private: |
| void copyList(const linkedListType |
| //Function to make a copy of otherList. |
| //Postcondition: A copy of otherList is created and assigned |
| // to this list. |
};
linkedListType
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


