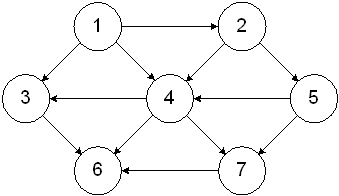
Question: Write or draw an adjacency (edge) list (NOT adjacency matrix) for the following graph. Using the Graph.java methods, and assuming the variable called graph has
Write or draw an adjacency (edge) list (NOT adjacency matrix) for the following graph.
Using the Graph.java methods, and assuming the variable called graph has been assigned an instance of a Graph, write statements to add EDGES/vertices which represent the following graph (use 0 for the weight when adding). See GraphTester.java in the Graph Code Files folder in Catalyst for examples.
Graph.java:
import java.util.*; import java.util.Map.Entry; interface Visitor
// --- assumes definition of simple class Pair
// --- Vertex class ------------------------------------------------------ class Vertex
public Vertex( E x ) { data = x; dist = INFINITY; nextInPath = null; } public Vertex() { this(null); }
public void addToAdjList(Vertex
return (data.equals(other.data));
} public int hashCode() { return (data.hashCode()); }
public void showAdjList() { Iterator
System.out.print( "Adj List for " + data + ": "); iter = adjList.entrySet().iterator(); while( iter.hasNext() ) { entry = iter.next(); pair = entry.getValue(); System.out.print( pair.first.data + "(" + String.format("%3.1f", pair.second) + ") " ); } System.out.println(); }
}
public class Graph
// public graph methods -------------------------------- public Graph () { vertexSet = new HashMap
for (k = 0; k src, dst;
// put both source and dest into vertex list(s) if not already there src = addToVertexSet(source); dst = addToVertexSet(dest);
// add dest to source's adjacency list src.addToAdjList(dst, cost); //dst.addToAdjList(src, cost); // ADD THIS IF UNDIRECTED GRAPH } public void addEdge(E source, E dest, int cost) { addEdge(source, dest, (double)cost); } // adds vertex with x in it, and always returns ref to it public Vertex
// find if Vertex already in the list: foundVertex = vertexSet.get(x); if ( foundVertex != null ) // found it, so return it { return foundVertex; }
// the vertex not there, so create one retVal = new Vertex
return retVal; // should never happen } public boolean remove(E start, E end) { Vertex
return removedOK; } public void showAdjTable() { Iterator
System.out.println( "------------------------ "); iter = vertexSet.entrySet().iterator(); while( iter.hasNext() ) { (iter.next().getValue()).showAdjList(); } System.out.println(); }
public void clear() { vertexSet.clear(); } /** Breadth-first traversal from the parameter startElement*/ public void breadthFirstTraversal(E startElement, Visitor
/** Postorder traversal from the parameter startElement */ public void depthFirstTraversal(E startElement, Visitor
}
GraphTester.java:
import java.util.*; import java.text.*;
//------------------------------------------------------ public class GraphTester { // ------- main -------------- public static void main(String[] args) { // build graph Graph
myGraph1.showAdjTable();
}
}
5 2 7 6 3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


