Question: We consider the initial value problem 10xy 17xy' + 5y = 0, y(1) = 3, y'(1) = -1 By looking for solutions in the form
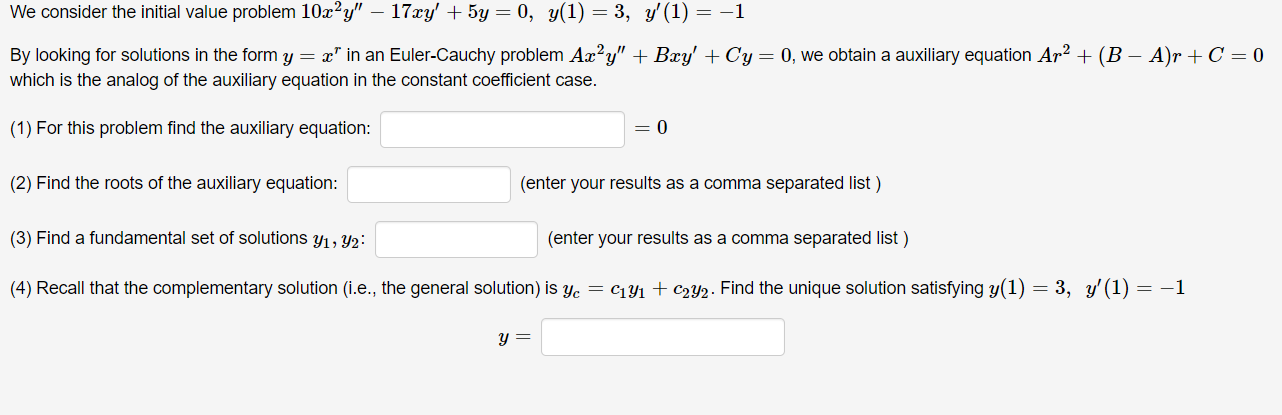
We consider the initial value problem 10xy" 17xy' + 5y = 0, y(1) = 3, y'(1) = -1 By looking for solutions in the form y = x" in an Euler-Cauchy problem Axy" + Bxy' + Cy= 0, we obtain a auxiliary equation Ar2 + (B A)r +C = 0 which is the analog of the auxiliary equation in the constant coefficient case. (1) For this problem find the auxiliary equation: 0 (2) Find the roots of the auxiliary equation: (enter your results as a comma separated list) (3) Find a fundamental set of solutions yi, y2: (enter your results as a comma separated list ) (4) Recall that the complementary solution (i.e., the general solution) is yc = C141 + c2y2. Find the unique solution satisfying y(1) = 3, y' (1) = -1 y =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


