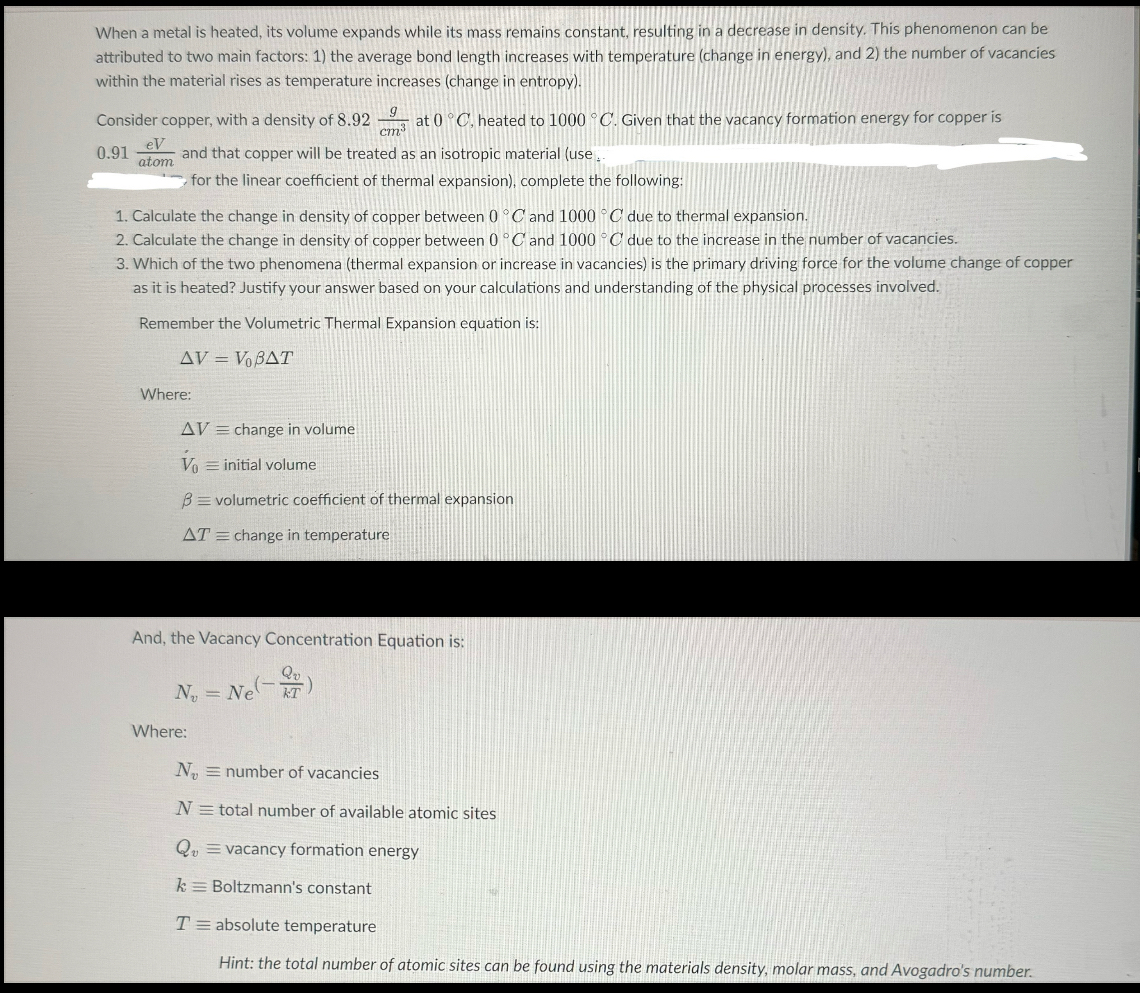
Question: When a metal is heated, its volume expands while its mass remains constant, resulting in a decrease in density. This phenomenon can be attributed to
When a metal is heated, its volume expands while its mass remains constant, resulting in a decrease in density. This phenomenon can be attributed to two main factors: the average bond length increases with temperature change in energy and the number of vacancies within the material rises as temperature increases change in entropy
Consider copper, with a density of at heated to Given that the vacancy formation energy for copper is and that copper will be treated as an isotropic material use
for the linear coefficient of thermal expansion complete the following:
Calculate the change in density of copper between and due to thermal expansion.
Calculate the change in density of copper between and due to the increase in the number of vacancies.
Which of the two phenomena thermal expansion or increase in vacancies is the primary driving force for the volume change of copper as it is heated? Justify your answer based on your calculations and understanding of the physical processes involved.
Remember the Volumetric Thermal Expansion equation is:
Where:
change volume
initial volume
volumetric coefficient thermal expansion
change temperature
And, the Vacancy Concentration Equation is:
Where:
number of vacancies
N total number of available atomic sites
vacancy formation energy
k Boltzmann's constant
T absolute temperature
Hint: the total number of atomic sites can be found using the materials density, molar mass, and Avogadro's number.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


