Question: When a solution contains a weak acid and its conjugate base What is the pH of a buffer prepared by adding 0.708mol of the weak
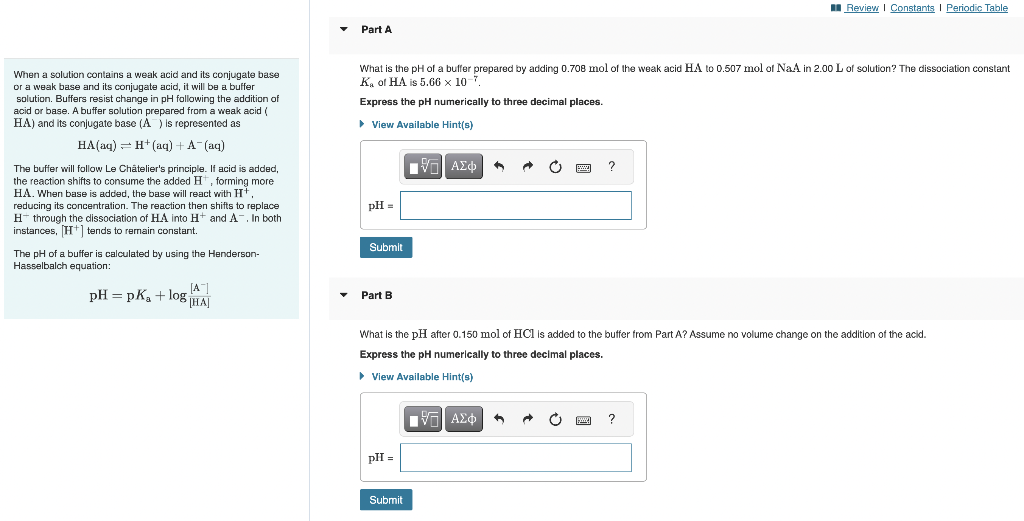
When a solution contains a weak acid and its conjugate base What is the pH of a buffer prepared by adding 0.708mol of the weak acid HA to 0.507mol of Na A in 2.00L of solution? The dissociation constant or a weak base and its conjugate acid, it will be a buffer Ka of HA is 5.66107. solution. Bulfers resist change in pH following the addition of Express the pH numerically to three decimal places. acid or base. A buffer solution prepared from a weak acid ( HA) and its conjugate base (A)is represented as HA(aq)H+(aq)+A(aq) The buffer will follow Le Chtelier's principle. If acid is added, the reaction shifts to consume the added H+, forming more HA. When base is added, the base will react with H+. reducing its concentration. The reaction then shifts to replace Hthrough the dissociation of HA into H+and A, In both instances, [H+]tends to remain constant. The pH of a buffer is calculated by using the Henderson- Hasselbalch equation: pH=pKa+log[HA][A]PartB What is the pH after 0.150mol of HCl is added to the butfer from Part A? Assume no volume change on the addition of the acid. Express the pH numerically to three decimal places
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


