Question: When the blood sugar increases, excess glucose will covalently bind to hemoglobin resulting in glycosylated hemoglobin. Hemoglobin with bound glucose is called Hemoglobin A1c (HbA
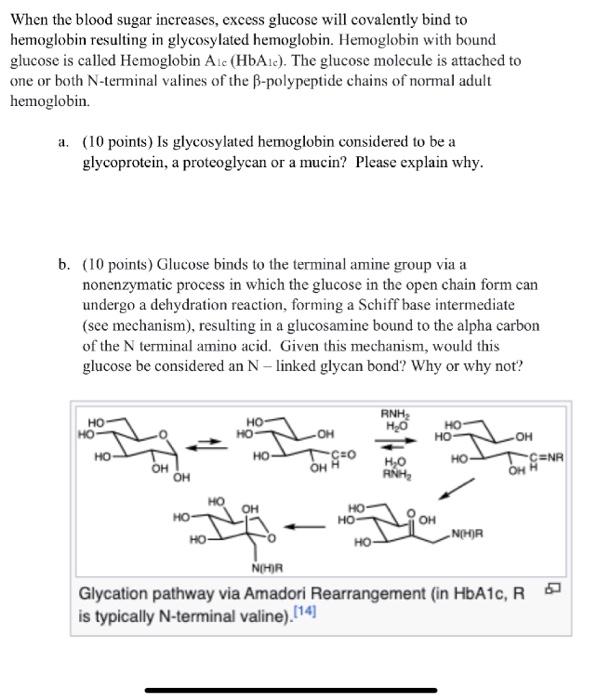
When the blood sugar increases, excess glucose will covalently bind to hemoglobin resulting in glycosylated hemoglobin. Hemoglobin with bound glucose is called Hemoglobin A1c (HbA H1c ). The glucose molecule is attached to one or both N-terminal valines of the -polypeptide chains of normal adult hemoglobin. a. (10 points) Is glycosylated hemoglobin considered to be a glycoprotein, a proteoglycan or a mucin? Please explain why. b. (10 points) Glucose binds to the terminal amine group via a nonenzymatic process in which the glucose in the open chain form can undergo a dehydration reaction, forming a Schiff base intermediate (see mechanism), resulting in a glucosamine bound to the alpha carbon of the N terminal amino acid. Given this mechanism, would this glucose be considered an N - linked glycan bond? Why or why not? is typically N-terminal valine)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


