Question: The voltage equation of a dc motor is written as where e a (t) is the applied voltage; i a (t), the armature current; R
The voltage equation of a dc motor is written as
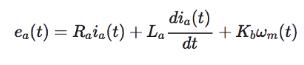
where e a (t) is the applied voltage; i a (t), the armature current; R a , the armature resistance; L a , the armature inductance; K b , the back-emf constant; ω m (t), the motor velocity; and ω (t), the reference input voltage. Taking the Laplace to transform on both sides of the voltage equation, with zero initial conditions and solving for Ωm(s), we get
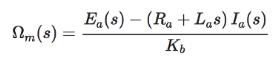
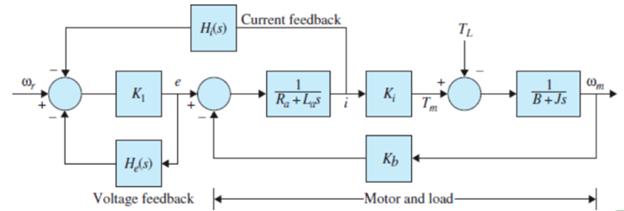
which shows that the velocity information can be generated by feeding back the armature voltage and current. The block diagram in Fig. 6P-12 shows a dc-motor system, with voltage and current feedback for speed control
a. Let K 1 be a very high gain amplifier. Show that when H i (s)/H e (s) = - (R a +L a s), the motor velocity ω m (t) is totally independent of the load-disturbance torque T L
b. Find the transfer function between Ω(s) and Ω r (s)(T L = 0) when H i (s) and H e (s) are selected as in part (a)
dia (t) dt ea(t) = Raia(t) + La- + Kiwm(t)
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (168 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To solve this problem well work through parts a and b using the given information and the block diag... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


