Question: with the given procedure, please help with the incomplete data: Data Collection Cell Configuration Anode Metal Anode Electrolyte Cathode Metal Cathode Electrolyte Experimental Voltage Theoretical
with the given procedure, please help with the incomplete data:
Data Collection
| Cell Configuration | Anode Metal | Anode Electrolyte | Cathode Metal | Cathode Electrolyte | Experimental Voltage | Theoretical Voltage | % error |
| 1 | Fe |
| Cu |
| 0.660 | 0.78 | 15.38% |
| 2 | X |
| Cu |
| 0.906 | XXXX | XXXX |
| 3 | X |
| Fe |
| 0.251 | XXXX | XXXX |
| 4 | Cu | 0.001M CuSO4 | Cu | 1.00M CuSO4 | 0.026 |
|
|
Unknown supposed to be Zn (experimental error with salt bridge in cell configuration 1)
|
| Standard Cell Notation |
| Configuration 1 |
|
| Configuration 2 |
|
| Configuration 3 |
|
| Configuration 4 | |
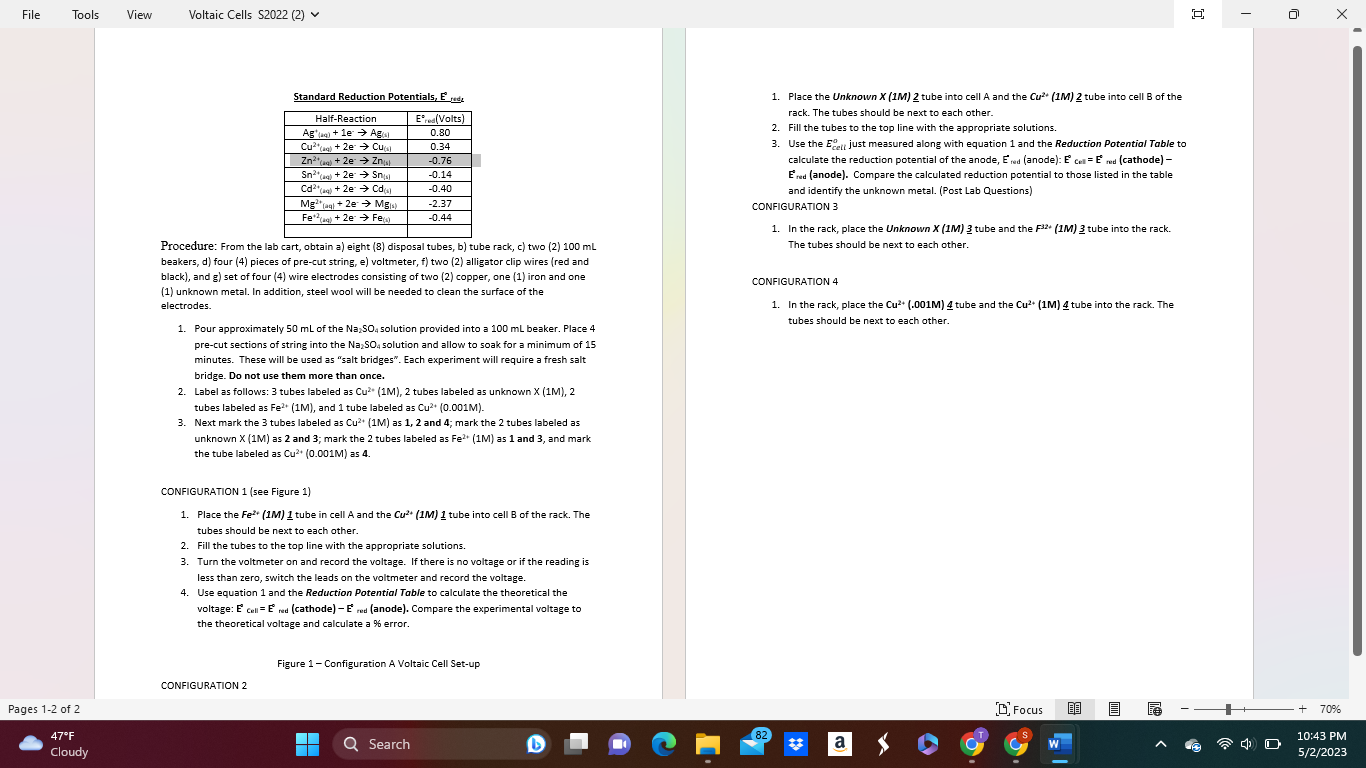
Standard Reduction Potentials. Ered. 1. Place the Unknown X(1M)2 tube into cell A and the Cu2+(1M)2 tube into cell B of the rack. The tubes should be next to each other. 2. Fill the tubes to the top line with the appropriate solutions. 3. Use the Ecalljustmeasuredalongwithequation1andtheReductionPotentialTabletoo calculate the reduction potential of the anode, Ered (anode): E cell =E (cathode) Ered (anode). Compare the calculated reduction potential to those listed in the table and identify the unknown metal. (Post Lab Questions) CONFIGURATION 3 1. In the rack, place the Unknown X(1M)3 tube and the F32+ (1M) 3 tube into the rack. Procedure: From the lab cart, obtain a) eight (8) disposal tubes, b) tube rack, c) two (2) 100mL The tubes should be next to each other. beakers, d) four (4) pieces of pre-cut string, e) voltmeter, f) two (2) alligator clip wires (red and black), and g) set of four (4) wire electrodes consisting of two (2) copper, one (1) iron and one CONFIGURATION 4 (1) unknown metal. In addition, steel wool will be needed to clean the surface of the electrodes. 1. In the rack, place the Cu2+(.001M) tube and the Cu2+(1M) tube into the rack. The 1. Pour approximately 50mL of the Na2SO4 solution provided into a 100mL beaker. Place 4 tubes should be next to each other. pre-cut sections of string into the Na2SO4 solution and allow to soak for a minimum of 15 minutes. These will be used as "salt bridges". Each experiment will require a fresh salt bridge. Do not use them more than once. 2. Label as follows: 3 tubes labeled as Cu2(1M),2 tubes labeled as unknown X (1M), 2 tubes labeled as Fe2+(1M), and 1 tube labeled as Cu2+(0.001M). 3. Next mark the 3 tubes labeled as Cu2+(1M) as 1,2 and 4 ; mark the 2 tubes labeled as unknown X(1M) as 2 and 3; mark the 2 tubes labeled as Fe2+(1M) as 1 and 3 , and mark the tube labeled as Cu2+(0.001M) as 4. CONFIGURATION 1 (see Figure 1) 1. Place the F2+(1M)1 tube in cell A and the Cu2+(1M)1 tube into cell B of the rack. The tubes should be next to each other. 2. Fill the tubes to the top line with the appropriate solutions. 3. Turn the voltmeter on and record the voltage. If there is no voltage or if the reading is less than zero, switch the leads on the voltmeter and record the voltage. 4. Use equation 1 and the Reduction Potential Table to calculate the theoretical the voltage: Ea cell =Ered(cathode)E red (anode). Compare the experimental voltage to the theoretical voltage and calculate a % error. Standard Reduction Potentials. Ered. 1. Place the Unknown X(1M)2 tube into cell A and the Cu2+(1M)2 tube into cell B of the rack. The tubes should be next to each other. 2. Fill the tubes to the top line with the appropriate solutions. 3. Use the Ecalljustmeasuredalongwithequation1andtheReductionPotentialTabletoo calculate the reduction potential of the anode, Ered (anode): E cell =E (cathode) Ered (anode). Compare the calculated reduction potential to those listed in the table and identify the unknown metal. (Post Lab Questions) CONFIGURATION 3 1. In the rack, place the Unknown X(1M)3 tube and the F32+ (1M) 3 tube into the rack. Procedure: From the lab cart, obtain a) eight (8) disposal tubes, b) tube rack, c) two (2) 100mL The tubes should be next to each other. beakers, d) four (4) pieces of pre-cut string, e) voltmeter, f) two (2) alligator clip wires (red and black), and g) set of four (4) wire electrodes consisting of two (2) copper, one (1) iron and one CONFIGURATION 4 (1) unknown metal. In addition, steel wool will be needed to clean the surface of the electrodes. 1. In the rack, place the Cu2+(.001M) tube and the Cu2+(1M) tube into the rack. The 1. Pour approximately 50mL of the Na2SO4 solution provided into a 100mL beaker. Place 4 tubes should be next to each other. pre-cut sections of string into the Na2SO4 solution and allow to soak for a minimum of 15 minutes. These will be used as "salt bridges". Each experiment will require a fresh salt bridge. Do not use them more than once. 2. Label as follows: 3 tubes labeled as Cu2(1M),2 tubes labeled as unknown X (1M), 2 tubes labeled as Fe2+(1M), and 1 tube labeled as Cu2+(0.001M). 3. Next mark the 3 tubes labeled as Cu2+(1M) as 1,2 and 4 ; mark the 2 tubes labeled as unknown X(1M) as 2 and 3; mark the 2 tubes labeled as Fe2+(1M) as 1 and 3 , and mark the tube labeled as Cu2+(0.001M) as 4. CONFIGURATION 1 (see Figure 1) 1. Place the F2+(1M)1 tube in cell A and the Cu2+(1M)1 tube into cell B of the rack. The tubes should be next to each other. 2. Fill the tubes to the top line with the appropriate solutions. 3. Turn the voltmeter on and record the voltage. If there is no voltage or if the reading is less than zero, switch the leads on the voltmeter and record the voltage. 4. Use equation 1 and the Reduction Potential Table to calculate the theoretical the voltage: Ea cell =Ered(cathode)E red (anode). Compare the experimental voltage to the theoretical voltage and calculate a % error
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts