Question: Work Breakdown Structure as a Skeleton for Integration Wilson Clark and Dragan Z. Milosevic Matt: I keep looking at this piece of paper and can't
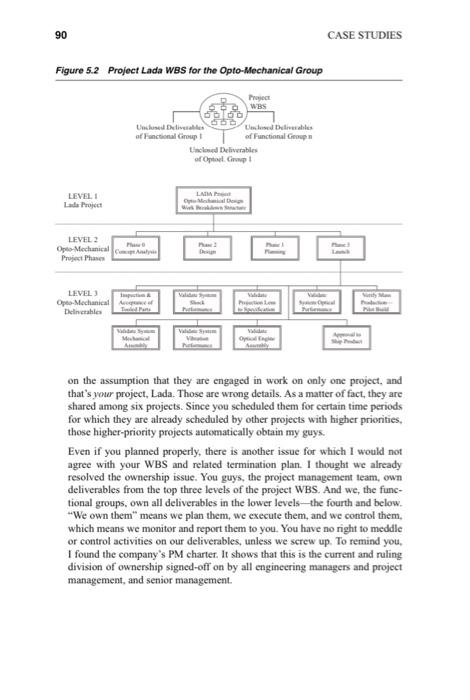
Work Breakdown Structure as a Skeleton for Integration Wilson Clark and Dragan Z. Milosevic Matt: I keep looking at this piece of paper and can't believe my eyes, or I must not understand it. Percy: What paper are you looking at? The one I brought? Matt: Yes, let me check if I understand it well. The sheet of paper I am holding shows the work breakdown structure (WBS) for the timely termination of the Opto-Mechanical group's portion of work for Project Lada (see Figure 5.2). Is that right? Percy: Yes, right. These beginning moments of the conversation between Matt Boon, the engineering manager of the Opto-Mechanical Group, and Percy Bedge, project manager of Lada, do not promise much cooperation. Rather, the atmosphere in which this conversation in Matt's office takes place smells of the open conflict and apparent tension between the meeting participants. MICROMANAGEMENT? Matt: Well, on the second page, it shows an estimate of the person-hours and needed calendar time for each of my engineers involved in Project Lada, from now until the end of it. Percy: Yes. That's the termination plan for Lada. What's wrong with it? Matt: I don't want to sound negative, but all of it is wrong from details to philosophy. Percy: Give me details. Matt: Your Lada planning indicates at what days on the calendar and how much you need each of my guys from Opto-Mechanical Group. That's based 89 90 Figure 5.2 Project Lada WBS for the Opto-Mechanical Group Project WBS Unclosed Deliverables of Functional Group I Unclosed Deliverables of Functional Group n Unclosed Deliverables of Optoel. Group 1 LADA P LEVEL I Lada Project O Mechal De Wikke Pla LEVEL 2 Opto-Mechanical Col Project Phases Phase 2 Den LEVEL 3 Pction Low SO Opto-Mechanical Ace of Deliverables Valid Sym hanical Optical Engi on the assumption that they are engaged in work on only one project, and that's your project, Lada. Those are wrong details. As a matter of fact, they are shared among six projects. Since you scheduled them for certain time periods for which they are already scheduled by other projects with higher priorities, those higher-priority projects automatically obtain my guys. Even if you planned properly, there is another issue for which I would not agree with your WBS and related termination plan. I thought we already resolved the ownership issue. You guys, the project management team, own deliverables from the top three levels of the project WBS. And we, the func- tional groups, own all deliverables in the lower levels the fourth and below. "We own them" means we plan them, we execute them, and we control them, which means we monitor and report them to you. You have no right to meddle or control activities on our deliverables, unless we screw up. To remind you, I found the company's PM charter. It shows that this is the current and ruling division of ownership signed-off on by all engineering managers and project management, and senior management. CASE STUDIES Pax Lank Project Scope Management 91 But you seem to forget or ignore the PM charter, just as you tried to ignore it during Lada's Map Day. With the termination WBS, it appears again that you would like to micromanage us. Percy: I see where you come from. Frankly, my intention was not to micro- manage you. Give me a few days to go over it, and I'll get back to you. Discussion items 1. What are the pros and cons of having many levels of WBS? 2. Do you prefer a few or many levels of WBS? Why? . . . Case Study 2: Work Breakdown Structure as a Skeleton for Integration Weight 5% of the final grade Due no later than 11:00p.m. on Sunday of Unit 4 Objectives (CLO 1, CLO 3, CLO 4] On successful completion of this assignment, students should be able to: Manage schedules, resources, and costs as it relates to the different facets of project execution, monitoring, controlling, and closing: explain specific inputs, tools, techniques, and outputs that allow project managers to execute, control, and close projects effectively: explore the entire range of key issues and fully articulate the potential pros and cons of the possible measures; and make effective project management decisions and communicate succinctly. Textbook Milosevic, D. Z., Patanakul, P., &Sriyannaboen S. (2010). Work breakdown structure as a skeleton for integration. In case studies in project, program, and organizational project management (pp. 89-91). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons Inc. This case study allows students to demonstrate their understanding of how to manage schedules, resources, and costs on a project using the work breakdown structure (WBS). Description In your analysis of this case, you must ensure that you include the following: An introductory paragraph and brief summary of what is a WBS. An explanation of how effectively the WBS was utilized in the case. Explain: a. The pros and cons of developing a detailed WBS, b. The use of the WBS to justify their choices on schedule, resource, and cost management, and How can the WBS be used as a communication tool with stakeholders during the planning and execution phases? A short paragraph as a conclusion. All submissions must be done through the online Turnitin portal in Moodle. Percentage similarity MUST NOT exceed 15%. C