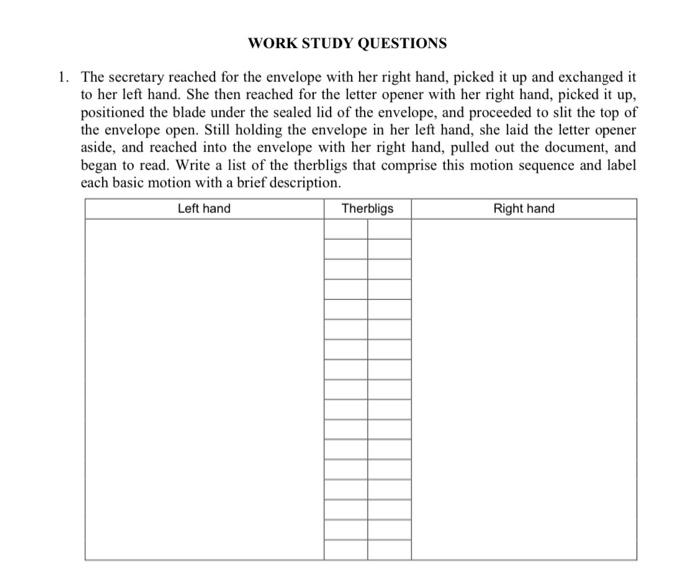
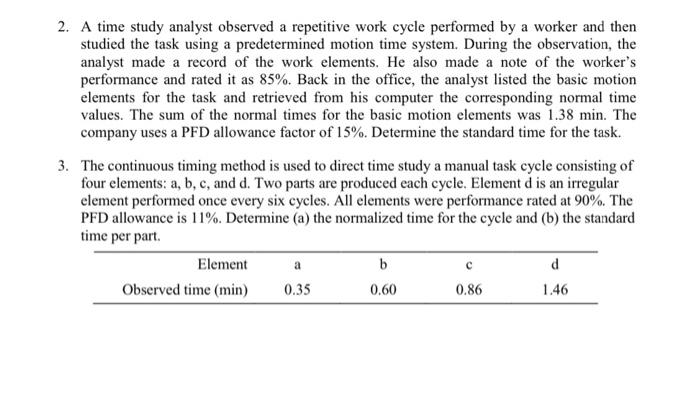
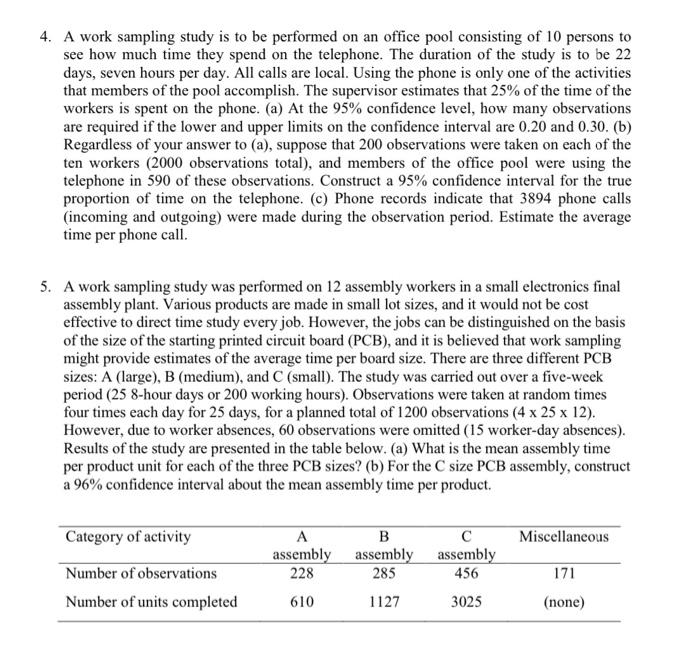
WORK STUDY QUESTIONS 1. The secretary reached for the envelope with her right hand, picked it up and exchanged it to her left hand. She then reached for the letter opener with her right hand, picked it up, positioned the blade under the sealed lid of the envelope, and proceeded to slit the top of the envelope open. Still holding the envelope in her left hand, she laid the letter opener aside, and reached into the envelope with her right hand, pulled out the document, and began to read. Write a list of the therbligs that comprise this motion sequence and label each basic motion with a brief description. Left hand Therbligs Right hand 2. A time study analyst observed a repetitive work cycle performed by a worker and then studied the task using a predetermined motion time system. During the observation, the analyst made a record of the work elements. He also made a note of the worker's performance and rated it as 85%. Back in the office, the analyst listed the basic motion elements for the task and retrieved from his computer the corresponding normal time values. The sum of the normal times for the basic motion elements was 1.38 min. The company uses a PFD allowance factor of 15%. Determine the standard time for the task. 3. The continuous timing method is used to direct time study a manual task cycle consisting of four elements: a, b, c, and d. Two parts are produced each cycle. Element d is an irregular element performed once every six cycles. All elements were performance rated at 90%. The PFD allowance is 11%. Determine (a) the normalized time for the cycle and (b) the standard time per part Element b d Observed time (min) 0.35 0.60 0.86 1.46 a 4. A work sampling study is to be performed on an office pool consisting of 10 persons to see how much time they spend on the telephone. The duration of the study is to be 22 days, seven hours per day. All calls are local. Using the phone is only one of the activities that members of the pool accomplish. The supervisor estimates that 25% of the time of the workers is spent on the phone. (a) At the 95% confidence level, how many observations are required if the lower and upper limits on the confidence interval are 0.20 and 0.30. (b) Regardless of your answer to (a), suppose that 200 observations were taken on each of the ten workers (2000 observations total), and members of the office pool were using the telephone in 590 of these observations. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the true proportion of time on the telephone. (C) Phone records indicate that 3894 phone calls (incoming and outgoing) were made during the observation period. Estimate the average time per phone call. 5. A work sampling study was performed on 12 assembly workers in a small electronics final assembly plant. Various products are made in small lot sizes, and it would not be cost effective to direct time study every job. However, the jobs can be distinguished on the basis of the size of the starting printed circuit board (PCB), and it is believed that work sampling might provide estimates of the average time per board size. There are three different PCB sizes: A (large), B (medium), and C (small). The study was carried out over a five-week period (25 8-hour days or 200 working hours). Observations were taken at random times four times each day for 25 days, for a planned total of 1200 observations (4 x 25 x 12). However, due to worker absences, 60 observations were omitted (15 worker-day absences). Results of the study are presented in the table below. (a) What is the mean assembly time per product unit for each of the three PCB sizes? (b) For the C size PCB assembly, construct a 96% confidence interval about the mean assembly time per product. Category of activity Miscellaneous Number of observations Number of units completed A B assembly assembly assembly 228 285 456 610 1127 3025 171 (none)