Question: Worked Solution (Formula Solution) The IRR is the discount rate that equates the NPV of an investment opportunity with $0 (because the present value of
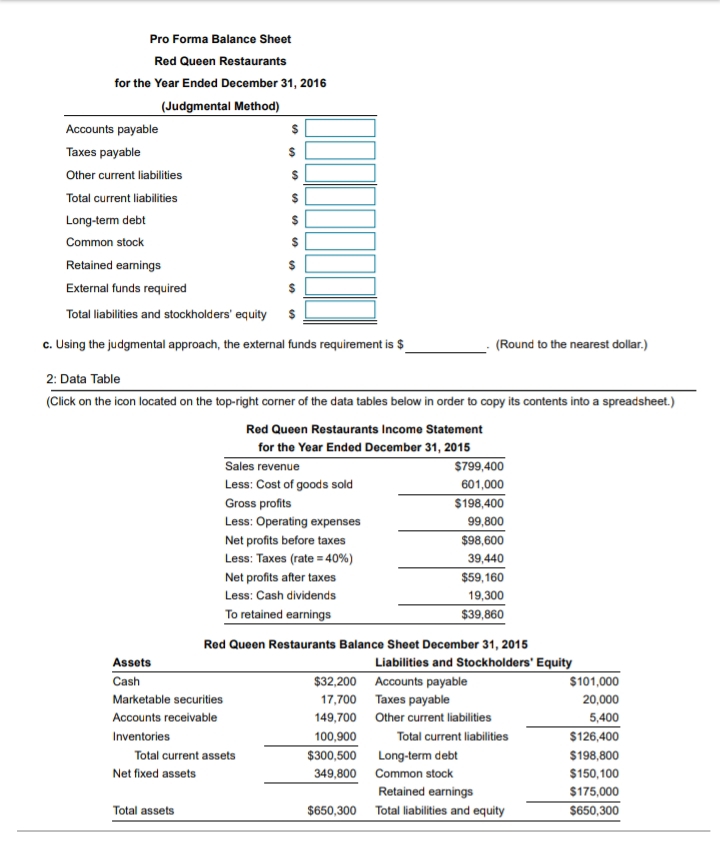
Worked Solution (Formula Solution) The IRR is the discount rate that equates the NPV of an investment opportunity with $0 (because the present value of cash Inflows equals the initial investment). It is the rate of return that the firm will earn if it invests in the project and receives the given cash inflows. Mathematically, the IRR is the value of / that causes NPV to equal $0: CF 1=1 (1 + IRR) = CFO Thus, the IRR of project Terra is 13.39% and the IRR of project Firma is 10.25%. The IRR is very difficult to calculate by hand, but can easily be found using a financial calculator or an Excel spreadsheet. The net present value (NPV) of a project is found by subtracting a project's initial investment (CF) from the present value of its cash inflows (CF,) discounted at a rate equal to the firm's cost of capital (r). If the discount rate is 0%, the NPV of project Terra can be computed as follows: NPV = S CF 1=1 (1 + r) - CFO $8,000 $8,000 $8,000 $8,000 (1 + 0.00)1 (1 +0.00) (1 +0.00)3 (1 + 0.00)4 - $26,000, = 10,000.00. The NPV of project Terra is found to be $10,000.00. The net present value (NPV) of a project is found by subtracting a project's initial investment (CF) from the present value of its cash inflows (CF,) discounted at a rate equal to the firm's cost of capital (r). If the discount rate is 0%, the NPV of project Terra can be computed as follows: NPV = $10,000 $6,000 $7,000 $10,000 (1 + 0.00) (1 +0.00)2 (1 + 0.00) (1 + 0.00) - $26,000 = $7,000.00. If the discount rate is 0%, the NPV of project Firma is found to be $7,000.00. The net present value (NPV) of a project is found by subtracting a project's initial investment (CF) from the present value of its cash inflows (CF,) discounted at a rate equal to the firm's cost of capital (r). If the discount rate is 8%, the NPV of project Terra can be computed as follows: NPV = $8,000 $6,000 $12,000 $10,000 (1 + 0.08)1 (1+0.08)2 (1 + 0.08)3 (1 +0.08) - $26,000 = $3,427.73. If the discount rate is 8%, the NPV of project Terra is found to be $3,427.73. The net present value (NPV) of a project is found by subtracting a project's initial investment (CF) from the present value of its cash inflows (CF ) discounted at a rate equal to the firm's cost of capital (r). If the discount rate is 8%, the NPV of project Terra can be computed as follows: NPV = $10,000 $6,000 $7,000 $10,000 (1 + 0.08) (1 +0.08) (1 + 0.08) (1 +0.08)" - $26,000 = $1,310.42. If the discount rate is 8%, the NPV of project Firma is found to be $1,310.42. If the discount rate is the project's IRR, the NPV of any project should be $0 because the IRR is the discount rate that equates the NPV of an investment opportunity with $0 (because the present value of cash inflows equals the initial Investment). Projects can be compared graphically by constructing net present value profiles that depict the projects' NPVs for various discount rates. The following graph shows the NPV profiles of the two projects: 14000- 12000- Project Terra Project Firma 10000- 8000- NPV (5) 6000- 4000- 2000- 10 20 -2000- 4000- Discount Rate (%) According to the NPV mehtod, the project with the highest positive NPV is preferred. According to the IRR method, the project with the highest IRR is preferred. However, when there is a conflict between the NPV and IRR methods, the decision should be based on NPV. Project Terra should be selected because its NPV is higher at any discount rate that produces a positive NPV. The results can also be seen from the NPV profiles.3. Integrative-Pro forma statements Red Queen Restaurants wishes to prepare financial plans. Use the financial statements and the other information provided here . to prepare the financial plans. The following financial data are also available: (1) The firm has estimated that its sales for 2016 will be $900,800. (2) The firm expects to pay $34,800 in cash dividends in 2016. (3) The firm wishes to maintain a minimum cash balance of $30,800. (4) Accounts receivable represent approximately 18% of annual sales. (5) The firm's ending inventory will change directly with changes in sales in 2016. (6) A new machine costing $42,600 will be purchased in 2016. Total depreciation for 2016 will be $15,700. (7) Accounts payable will change directly in response to changes in sales in 2016. (8) Taxes payable will equal one-fourth of the tax liability on the pro forma income statement. (9) Marketable securities, other current liabilities, long-term debt, and common stock will remain unchanged. a. Prepare a pro forma income statement for the year ended December 31, 2016, using the percent-of-sales method. b. Prepare a pro forma balance sheet dated December 31, 2016, using the judgmental approach. C. Analyze these statements, and discuss the resulting external financing required. Click the icon to see the Worked Solution (Formula Solution). a. Prepare a pro forma income statement for the year ended December 31, 2016, using the percent-of-sales method. Complete the pro forma income statement for the year ended December 31, 2016 below: (Round to the nearest dollar. Round the percentage of sales to four decimal places.) Pro Forma Income Statement Red Queen Restaurants for the Year Ended December 31, 2016 (percent-of-sales method) Sales Less: Cost of goods sold Gross profits Less: Operating expenses Net profits before taxes Less: Taxes (rate = 40%) Net profits after taxes Less: Cash dividends To Retained earnings b. Prepare a pro forma balance sheet dated December 31, 2016, using the judgmental approach. Complete assets part of the pro forma balance sheet as of December 31, 2016 below: (Round to the nearest dollar.) Pro Forma Balance Sheet Red Queen Restaurants for the Year Ended December 31, 2016 (Judgmental Method) Cash Marketable securities Accounts receivable Inventories Total current assets Net fixed assets Total assets Complete liabilities and stockholders' equity part of the pro forma balance sheet as of December 31, 2016 below: (Round to the nearest dollar.)Pro Forma Balance Sheet Red Queen Restaurants for the Year Ended December 31, 2016 (Judgmental Method) Accounts payable Taxes payable Other current liabilities Total current liabilities Long-term debt Common stock Retained earnings External funds required Total liabilities and stockholders' equity c. Using the judgmental approach, the external funds requirement is $ (Round to the nearest dollar.) 2: Data Table (Click on the icon located on the top-right corner of the data tables below in order to copy its contents into a spreadsheet.) Red Queen Restaurants Income Statement for the Year Ended December 31, 2015 Sales revenue $799,400 Less: Cost of goods sold 601,000 Gross profits $198,400 Less: Operating expenses 99.800 Net profits before taxes $98,600 Less: Taxes (rate = 40%) 39,440 Net profits after taxes $59, 160 Less: Cash dividends 19,300 To retained earnings $39,860 Red Queen Restaurants Balance Sheet December 31, 2015 Assets Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Cash $32,200 Accounts payable $ 101,000 Marketable securities 17,700 Taxes payable 20,000 Accounts receivable 149,700 Other current liabilities 5.400 Inventories 100.900 Total current liabilities $126,400 Total current assets $300,500 Long-term debt $ 198,800 Net fixed assets 349,800 Common stock $150,100 Retained earnings $175,000 Total assets $650,300 Total liabilities and equity $650,30010. Rate of return and investment choice Clare Jaccard has $4,000 to invest. Because she is only 25 years old, she is not concerned about the length of the investment's life. What she is sensitive to is the rate of return she will earn on the investment. With the help of her financial advisor, Clare has isolated four equally risky investments, each providing a single amount at the end of its life, as shown in the following table, *. All of the investments require an initial $4,000 payment. a. Calculate, to the nearest 1%, the rate of return on each of the four investments available to Clare. b. Which investment would you recommend to Clare, given her goal of maximizing the rate of return? Review Only Click the icon to see the Worked Solution (Formula Solution). Click the icon to see the Worked Solution (Financial Calculator Solution). Click the icon to see the Worked Solution (Spreadsheet Solution). a. The annual rate of return, r, on Investment A is %. (Round to two decimal places.) The annual rate of return, r, on Investment B is %. (Round to two decimal places.) The annual rate of return, r, on Investment C is %. (Round to two decimal places.) The annual rate of return, r, on Investment D is %. (Round to two decimal places.) b. Which of the investments should Clare Jaccard choose to reach her goal of maximizing the rate of return? (Select the best answer below.) A. Investment A O B. Investment B O C. Investment C O D. Investment D 4: Data Table (Click on the icon located on the top-right corner of the data table below in order to copy its contents into a spreadsheet.) Investment Single amount Investment life (years) $6,100 6 $12,800 15 $6,400 $10,500 108. Rate of return and investment choice Clare Jaccard has $5,000 to invest. Because she is only 25 years old, she is not concerned about the length of the investment's life. What she is sensitive to is the rate of return she will earn on the investment. With the help of her financial advisor, Clare has isolated four equally risky investments, each providing a single amount at the end of its life, as shown in the following table, ". All of the investments require an initial $5,000 payment. a. Calculate, to the nearest 1%, the rate of return on each of the four investments available to Clare. b. Which investment would you recommend to Clare, given her goal of maximizing the rate of return? Click the icon to see the Worked Solution (Formula Solution). Click the icon to see the Worked Solution (Financial Calculator Solution). Click the icon to see the Worked Solution (Spreadsheet Solution). a. The annual rate of return, r, on Investment A is %. (Round to two decimal places.) The annual rate of return, r, on Investment B is %. (Round to two decimal places.) The annual rate of return, r, on Investment C is %. (Round to two decimal places.) The annual rate of return, r, on Investment D is %. (Round to two decimal places.) b. Which of the investments should Clare Jaccard choose to reach her goal of maximizing the rate of return? (Select the best answer below.) A. Investment A O B. Investment B O C. Investment C O D. Investment D 3: Data Table Click on the icon located on the top-right corner of the data table below in order to copy its contents into a spreadsheet.) Investment Single amount Investment life (years) $8,400 6 $15,900 15 $7,600 $13,000 10