Question: Write a function interleaved_sum, which takes in a number n and two one-argument functions: odd_term and even_term. It applies odd_term to every odd number
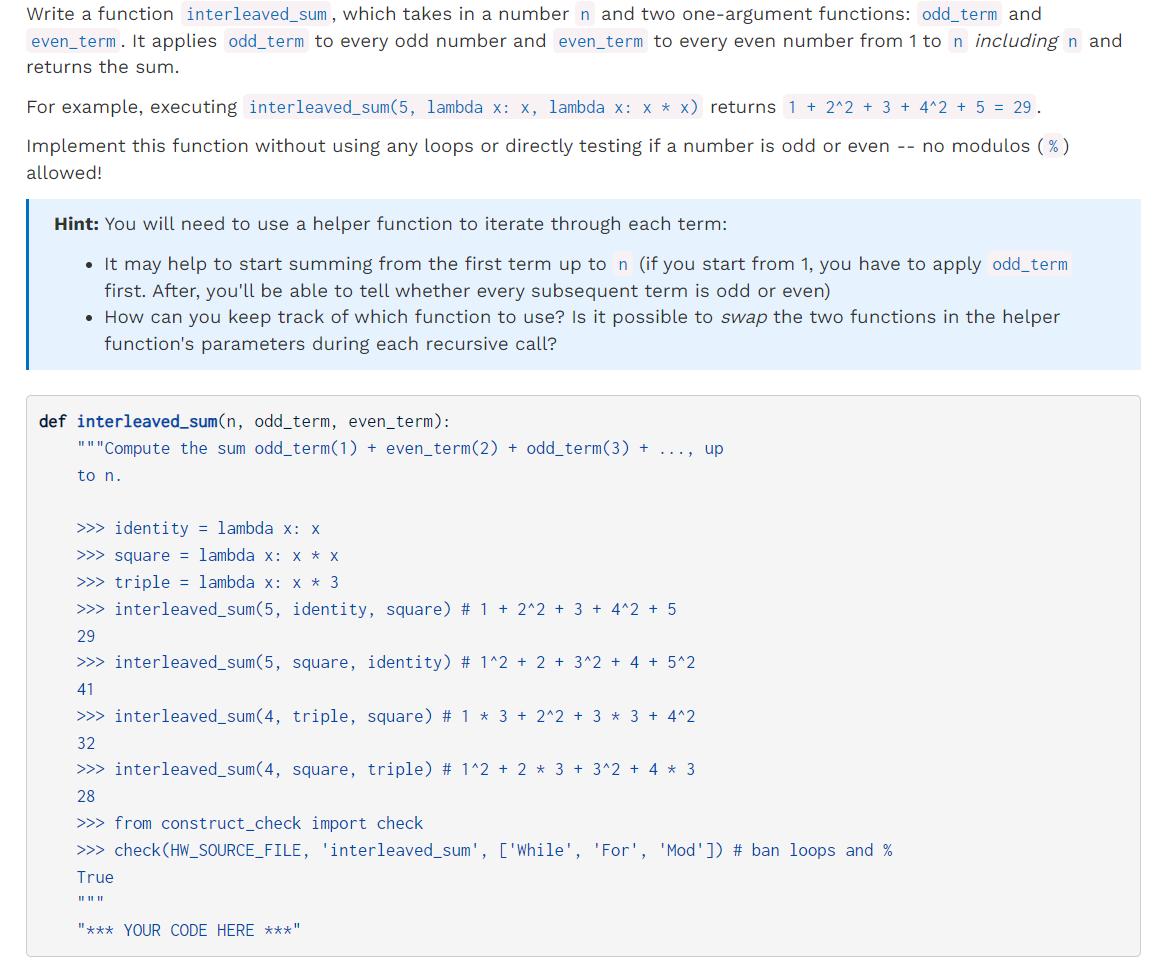
Write a function interleaved_sum, which takes in a number n and two one-argument functions: odd_term and even_term. It applies odd_term to every odd number and even_term to every even number from 1 to n including n and returns the sum. For example, executing interleaved_sum (5, lambda x: x, lambda x: x x x) returns 1 + 2^2 + 3 + 4^2 + 5 = 29. Implement this function without using any loops or directly testing if a number is odd or even -- no modulos ( % ) allowed! Hint: You will need to use a helper function to iterate through each term: It may help to start summing from the first term up to n (if you start from 1, you have to apply odd_term first. After, you'll be able to tell whether every subsequent term is odd or even) How can you keep track of which function to use? Is it possible to swap the two functions in the helper function's parameters during each recursive call? def interleaved_sum(n, odd_term, even_term): """Compute the sum odd_term(1) + even_term(2) + odd_term(3) + to n. >>> identity = lambda x: x >>> square = lambda x: x * X >>> triple = lambda x: x * 3 >>> interleaved_sum (5, identity, square) # 1 + 2^2 + 3 + 4^2 + 5 29 >>> interleaved_sum (5, square, identity) # 1^2 + 2 + 3^2 + 4 + 5^2 41 >>> interleaved_sum (4, triple, square) # 1 * 3 + 2^2 + 3 * 3 + 4^2 32 >>> interleaved_sum (4, square, triple) # 1^2 + 2 * 3 + 3^2 + 4 * 3 28 ..., up >>> from construct_check import check >>> check (HW_SOURCE_FILE, 'interleaved_sum', ['While', 'For', 'Mod']) # ban loops and % True |||||| "*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To implement the interleavedsum function without using loops or modules you can create a h... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


