Question: Write these functions in MatLab: Your task is to implement a function d -get displacements(f, ...) that computes the inverse of this transformation: given the
Write these functions in MatLab:
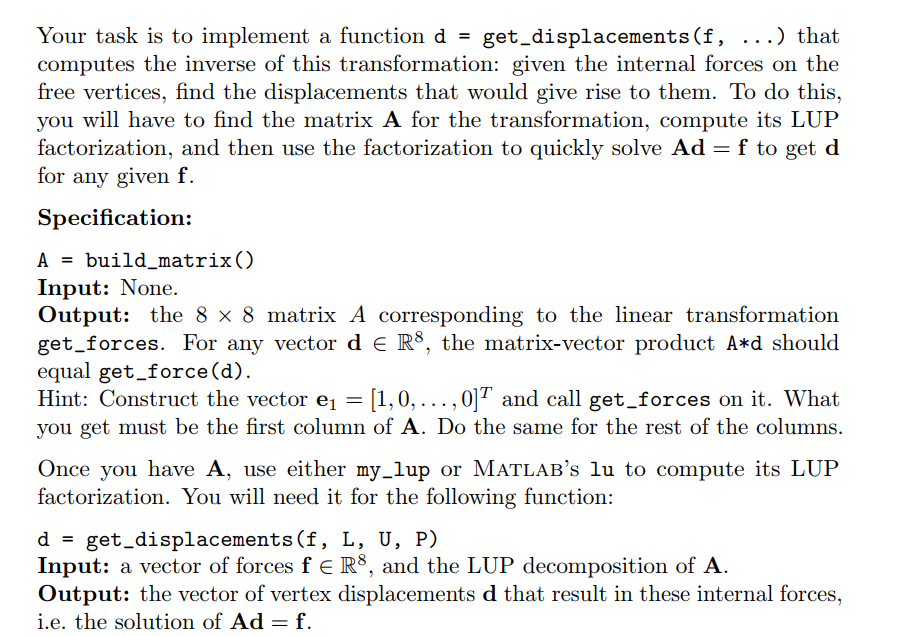
Your task is to implement a function d -get displacements(f, ...) that computes the inverse of this transformation: given the internal forces on the free vertices, find the displacements that would give rise to them. To do this, you will have to find the matrix A for the transformation, compute its LUP factorization, and then use the factorization to quickly solve Ad - f to get d for any given f. Specification: A build-matrix() Input: None. Output: the 8 8 matrix A corresponding to the linear transformation get forces. For any vector d E R8, the matrix-vector product A*d should equal get force(d). Hint: Construct the vector e [1,0,...,0] and call get_forces on it. What you get must be the first column of A. Do the same for the rest of the columns. Once you have A, use either my_lup or MATLAB's lu to compute its LUP factorization. You will need it for the following function: d get-displacement s (f, L, U, P) Input: a vector of forces feR8, and the LUP decomposition of A Output: the vector of vertex displacements d that result in these internal forces, 1.e. the solution of Ad f. the solution of Ad Your task is to implement a function d -get displacements(f, ...) that computes the inverse of this transformation: given the internal forces on the free vertices, find the displacements that would give rise to them. To do this, you will have to find the matrix A for the transformation, compute its LUP factorization, and then use the factorization to quickly solve Ad - f to get d for any given f. Specification: A build-matrix() Input: None. Output: the 8 8 matrix A corresponding to the linear transformation get forces. For any vector d E R8, the matrix-vector product A*d should equal get force(d). Hint: Construct the vector e [1,0,...,0] and call get_forces on it. What you get must be the first column of A. Do the same for the rest of the columns. Once you have A, use either my_lup or MATLAB's lu to compute its LUP factorization. You will need it for the following function: d get-displacement s (f, L, U, P) Input: a vector of forces feR8, and the LUP decomposition of A Output: the vector of vertex displacements d that result in these internal forces, 1.e. the solution of Ad f. the solution of Ad
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


