Question: You are given an implementation of a Vector class, representing the coordinates of a vector in a multidimensional space. For example, in a three-dimensional

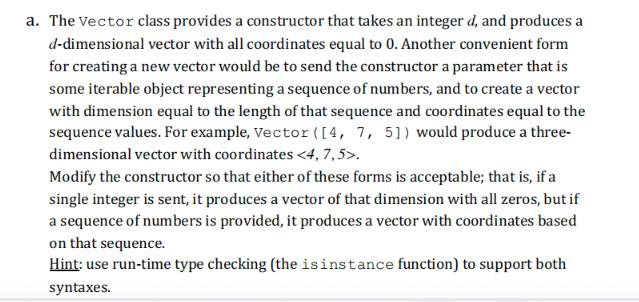
You are given an implementation of a Vector class, representing the coordinates of a vector in a multidimensional space. For example, in a three-dimensional space, we might wish to represent a vector with coordinates . For a detailed explanation of this implementation as well as of the syntax of operator overloading that is used here, please read sections 2.3.2 and 2.3.3 in the textbook (pages 74-78). class Vector: def def _len__(self): def def def def _init__(self, d): self.coords = [0] *d def return len (self.coords) getitem_(self, j): return self.coords[j] setitem_(self, j, val): self.coords [j] = val add_(self, other) : if (len (self) !len (other)): raise ValueError("dimensions must agree") result Vector (len (self)) for j in range (len (self)): result [j] = self[j] + other [j] return result: eq (self, other): return self.coords == other.coords: ne (self, other): return not (self other) def _str_(self): return + str (self.coords) [1:-1] + *> def repr_(self): return str (self)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To modify the constructor of the Vector class to accept either a single integer o... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


