Question: You are to use the parse function from the previous lab to parse an input delimited text string to tokens in a vector. Additional vector


You are to use the parse function from the previous lab to parse an input delimited text string to tokens in a vector. Additional vector programming examples can be found in cplusplus.com (Links to an external site.)Links to an external site..
The Starter:
Use the quicksort_starter.cpp from github.
The user is expected to enter the entire collection (of test data) within one single line of delimited data.
quicksort.cpp and appropriate validations.
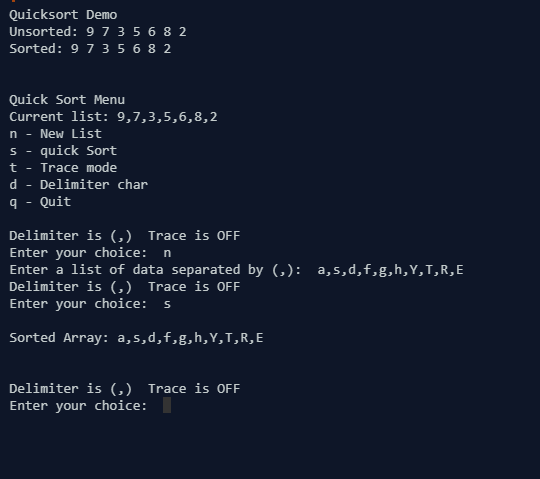
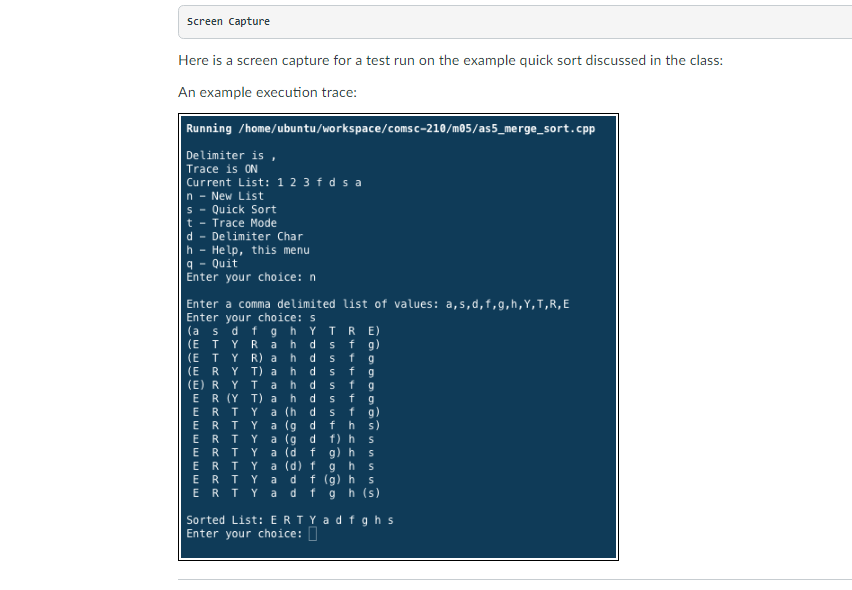
As an example, the program should be able to produce the trace output when the TRACE option is enabled. Here is an example output:
Enter your choice> s (9 7 3 5 6 8 2) (2 7 3 5 6 8 9) (2 3)5 8 6 7 9 2 3 5 (8 6 7 9) 2 3 5 (6 8 7 9) 2 3 5 (6 7)8 9 2 3 5 6 7 8 (9) Sorted Array: 2,3,5,6,7,8,9
quick_sort.cpp
| #include #include #include #include #include
#define under "\33[4m" #define over "\33[0m"
// example cout
using namespace std;
static const int MIN_SIZE = 2; //smaller use swap char delimiter = ','; bool trace = false;
void showTrace(vector void show(vector int comp(const void *one, const void *two); void order(vector void sortFirstMiddleLast(vector int partition(vector void quickSort(vector
int main() { cout vector
cout for(auto item:a) cout cout
// Try lambda for local meaning auto acomp = [] (const void* a, const void* b) {return ( (a > b)?1:( (a==b)?0:-1) );};
vector qsort(&demo[0], demo.size(), sizeof(int), acomp); cout for(auto item:demo) { cout } cout
vector
auto menu = [&] () { cout
show(ar); cout
menu( ); char choice; // user choice of command do { cout
cin >> choice; cin.ignore(1000, ' '); choice = tolower(choice); string input, token; vector stringstream ss; switch(choice) { // main menu switch starts case 'n': // new cout getline (cin, input); ss ar.clear(); while(getline(ss, token, delimiter)) ar.push_back(token); break; case 't': trace = !trace; break; case 'd': // delimiter cout cin >> delimiter; break; case 's': // quickSort(test, 0, test.size() - 1); cout show(test); cout break; case 'm': menu(); break; case 'q': break; default: cout } } while (choice!='q'); }
// void quickSort(vector // { // }
void sortFirstMiddleLast(vector int middle = (first + last)/2; order(arr, first, middle); order(arr, middle, last); order(arr, first, middle); }
// int partition(vector // }
int comp(const void *one, const void *two) { int a = *((int*)one); int b = *((int*)two); if (a if (a == b) return 0; return 1; }
void show(vector string output; // how does this one work? for(auto item:arr) { if (!output.empty()) output += ","; output += item; } cout }
void showTrace(vector for(int i=0; i cout } cout } void order(vector if (arr[i] > arr[j]) std::swap(arr[i], arr[j]); } | |
| Current output:
|
This assignment is to write a quicksort.cpp program based on the Pseudo Code Example on chapter 11.2.2, p.318- 324. You are to implement a Quick Sort program based on the textbook example. This program have to trace the sorting of a random array in progress and its trace output needs to Show all items of the array on a single trace line Each data exchange needs to be on a separate trace line, and . Show the active sorting range by placing an opening and a closing parenthesis around it. Your program needs to run the quick sort only, i,e. sort the data using quick sort all the way through, from the begining to the end, Do not swtich to Insertion Sort as described in the textbook Although the Quick sort pivot selection is costly especially when the item numbers to sort is small. Therefore, the textbook example switch to selection sort when the item numbers in the segment to sort is less than 10. In this assignment, our main objective is to learn how this sort works, hence we are not going to fine tune the performance by switching to another basic sort, cheaper to setup when the item numbers in the segment to sort is below a certain threshold Here are the features need to be in your quick sort program: Write C++ program based on this pseudo code in the textbook; .A the program start, show a predefined list (of your own) than before; Use the median-of-three (fist middle last) pivot selection. Do NOT switch to a basic (selection) sort when the item numbers in the segment to sort is smaller than the threshold! Stop the Quick Sort when the terminal case is reached, i.e. the segment to be sorted is less or equal to 2 items. If the number is 2, perform a simple swap if out of order. Otherwise, just return. Display (prompt) the menu, defined in the User Interface below, after the start test and after the completion of a menu command Explain what and why for the worst case and average case of quick sort efficiency in Big O notation on the header of the quicksort.cpp
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts