Question: You are working with a friend on a presentation for your principal level economics course. Both of you can either work hard or free
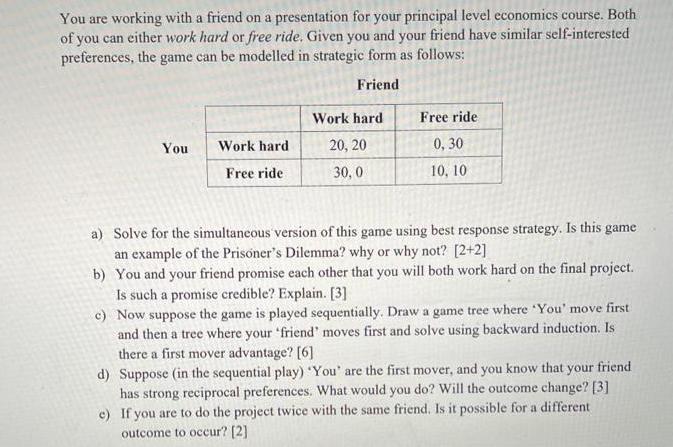
You are working with a friend on a presentation for your principal level economics course. Both of you can either work hard or free ride. Given you and your friend have similar self-interested preferences, the game can be modelled in strategic form as follows: Friend You Work hard Free ride Work hard 20, 20 30,0 Free ride 0,30 10, 10 a) Solve for the simultaneous version of this game using best response strategy. Is this game an example of the Prisoner's Dilemma? why or why not? [2+2] b) You and your friend promise each other that you will both work hard on the final project. Is such a promise credible? Explain. [3] c) Now suppose the game is played sequentially. Draw a game tree where 'You' move first and then a tree where your friend' moves first and solve using backward induction. Is there a first mover advantage? [6] d) Suppose (in the sequential play) 'You' are the first mover, and you know that your friend has strong reciprocal preferences. What would you do? Will the outcome change? [3] If you are to do the project twice with the same friend. Is it possible for a different outcome to occur? [2] e)
Step by Step Solution
3.35 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a The simultaneous version of this game can be solved using a best response strategy The Nash equili... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


