Question: You will implement some operations on binary trees in the template file BST . java. The file already contains methods to insert key - value
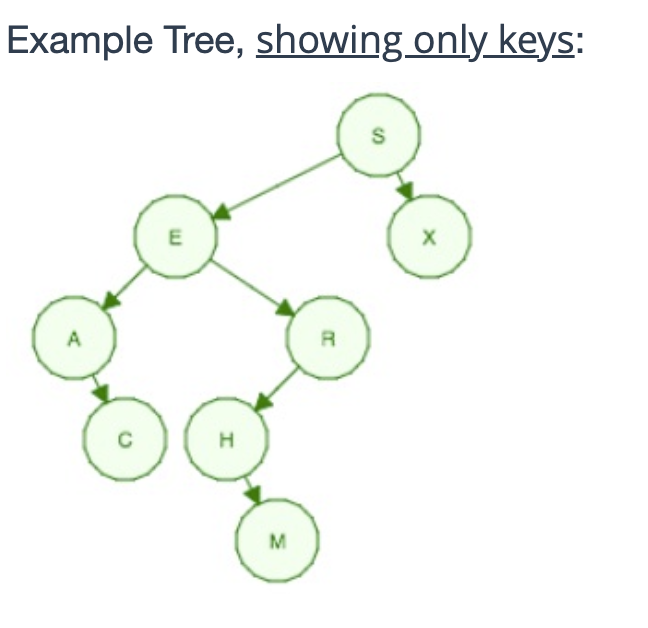
You will implement some operations on binary trees in the template file BSTjava. The file already contains methods to insert keyvalue pairs and search for a key in binary search trees. You need to Implement the following public methods recursively, adding one private recursive method for each public method: public int height: returns the height of the tree. For this method you must also write in comments the worstcase asymptotic running time of this method as a function of the number of keys N in the tree, and briefly explain it checked by showing your codecomments to demonstrators in the lab public Key median: returns the median key in the tree. if the tree is empty the method should return null. If the tree has N keys K K K KN then their median is key KNhere is integer division Note that the median is always a key, not the average of keys. If there is an even number of keys. For example if the keys in the tree are the A C U W then the median is the key at position which is key C position numbers start at zero. update: Java file instructions has a slightly different calculation because it assumes first key has index This operation needs to run in worstcase h time, where h is the height of the tree checked by showing your code in the lab Hint: To implement a h median method you need to study and understand the rank and select methods from the lectures and the book. public void deleteKey key: deletes from the tree the node containing key. Your implementation needs to be different than the Hibbard deletion from the lectures: if the node to be deleted has two child nodes, then it needs to be replaced with its predecessor not its successorchecked by showing your code in the lab The predecessor of a key in a BST is the immediately smaller key. In the book & lectures we saw the Hibbard deletion algorithm which makes use of the successor of a key the immediately larger key In the example BST at the bottom of the page, the predecessor of key E is C and the successor of E is H public String printKeysPreOrder: returns a String containing all keys but not the associated values in the tree, in preorder. This is a preorder traversal of the tree. In a preorder traversal, for every node N the key in node N is printed first, then the keys in its Left Subtree are printed, and then the keys in its Right Subtree are printed. Also: review the inorderpreorderpostorder traversals from the lectures. The keys in each subtree should be contained in a pair of parentheses. For example: When you call this method with an empty tree, it should return the empty string within paretheses without the quotes When you call it with the tree containing only a single node with key A it should return Acorrection #: Nov When you call this method on the tree in the example picture below, it should return the string SEACRHMX public String prettyPrintKeys: This method returns a multiline string representation of a tree, showing only the keys in the tree. This representation should print the key of each node in a separate line print null nodes print the left subtree before the right subtree use correct indentation to print the example below. When the method is called with an empty tree, it should return the string null
When the method is called with the example tree shown in the picture below, it should return the string: S E A null C null null R H null M null null null X null null Note that line breaks in a string are represented with the special sequence
You should have a
after every line printed, even after the last key in the tree. Hint: To implement this method you should use an inner recursive method: private String prettyPrintNode node, String prefix where the argument prefix is the string before horizontal dash In the above example, the prefix when this method is called for the node containing H is: public boolean isBSTPreOrderKey keys: This method takes an array of Key objects and determines whether the given sequence can represent the preorder traversal of a BST There are at least two algorithms of implementing this method. You only need to implement one of these. The algorithms are: Insert the keys in an empty BST from left to right. If the input array was the preorder travarsal of a BST then this will recreate the BST Then produce the preorder traversal of the resulting BST as an array. If the array is the same as the input array, then the input array was the preorder traversal of a BST the one your created If the arrays are different then the starting array was not a preorder traversa
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


