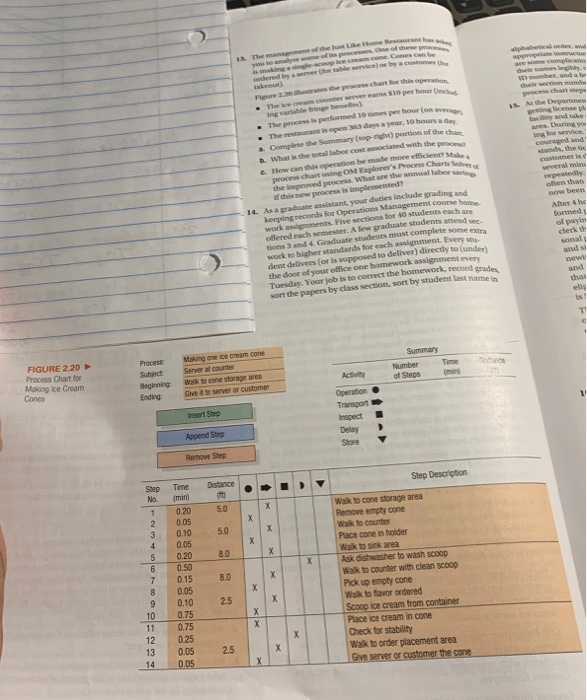
Question: yout ast, the 8. Prepare a flo ng the ely the PRO e a flowchart of the field service division process at E as described
yout ast, the 8. Prepare a flo ng the ely the PRO e a flowchart of the field service division process at E as described here. Start from the point where a call is erelved and end when a technician finishes the job was a multibillion dollar company that manufactured 10. ad distributed a wide variety of electronic, photographic, and c ographie equipment used in many engineering and system applications. The Field Service Division empled 5 field service technicians, who performed maintenance and curranty repairs on the equipment sold by DEF.Customers uld call DEF's National Service Center (NSC), which received shout 3,000 calls per day. The NSC staffed its call center with about 40 call-takers. A typical incoming service call was received at the NSC and routed to one of the call-takers, who entered Information about the machine, the caller's name, and the type of problem into DEF's mainframe computer. In some cases, the call-taker attempted to help the customer fix the problem. However, call-takers were currently only able to avoid about 10 percent of the incoming emergency maintenance service calls. If the service call could not be avoided, the call-taker usu- ally stated the following script:"Depending upon the availability of our technicians, you should expect to see a technician some- time between now and (now +X)." ("X" was the target response time based on the model number and the zone.) This informa- tion was given to the customer because many customers wanted to know when a tech would arrive on site. Call-takers entered service call information on DEF's com- puter system, which then sent the information electronically to the regional dispatch center assigned to that customer location. (DEF had four regional dispatch centers with a total of about 20 dispatchers.) Service call information was printed on a small card at the dispatch center. About every hour, cards were ripped off the printer and given to the dispatcher assigned to that customer location. The dispatcher placed each card on a magnetic board under the name of a tech that the dispatcher believed would be the most likely candidate for the service call, given the location of the machine, the cur- rent location of the tech, and the tech's training profile. After completing a service call, techs called the dispatcher in the regional dispatch center, cleared the call, and received a new call assigned by the dispatcher. After getting the service call from a dispatcher, a tech called the customer to give an ex- pected time of arrival, drove to the customer site, diagnosed the problem, repaired the machine if parts were available in the van, and then telephoned the dispatcher for the next call. if the tech did not have the right parts for a repair, the tech informed the NSC, and the part was express mailed to the customer; the repair was done the next morning. dewa s mascope con ge r e the process chart for the . The em conversio per hour Nam often than now been Atex 4 be The process is performed 10 per hour Conave . The restaurant is open 313 days a year. 10 hours Complete the Summary coop-right) portion of the chan . What is the total labor contacted with the proces How can this operation be made more efficient process chartig OM Explore Pro Charts the m oved process. What are the annual If this new process is implemented 14. As a graduate assistant your duties include grading and keeping records for Operations Management cour home work assignments. Five sections for 10 students each are Bered each semester. A few graduate students attend tions and 4. Graduate students must complete some extra work so higher standards for each assignment. Every dent delivers (or is supposed to deliver directly to under the door of your office one homework assignment every Tuesday. Your job is to the homework, recond sort the papers by class section sont by student last namen of payta sonals ands www and that Making one ice cream con Summary Time Number Process Subject FIGURE 2.20 Process Chart for Making Ice Cream Activity of Steps Walk to one storage area Give it to server or customer Cones Ending: nr Strip Operation Transport Inspect Delay Store Repend Step Removt Step Step Description Distance Step No Time min) 020 0.05 0.10 0.05 0.20 0.50 0.15 0.05 0.10 0.75 0.75 0.25 0.05 0.05 Walk to cone storage area Remove empty cone Wato counter Place cone in holder Walk to sink area Ask dishwasher to wash scoop Wak to counter with clean scoop Pick up empty cone Walk to favor ordered Scoop ice cream from container Place ice cream in cone Check for stability Wak to order placement area Give server or customer the cone 10 11 13 14 yout ast, the 8. Prepare a flo ng the ely the PRO e a flowchart of the field service division process at E as described here. Start from the point where a call is erelved and end when a technician finishes the job was a multibillion dollar company that manufactured 10. ad distributed a wide variety of electronic, photographic, and c ographie equipment used in many engineering and system applications. The Field Service Division empled 5 field service technicians, who performed maintenance and curranty repairs on the equipment sold by DEF.Customers uld call DEF's National Service Center (NSC), which received shout 3,000 calls per day. The NSC staffed its call center with about 40 call-takers. A typical incoming service call was received at the NSC and routed to one of the call-takers, who entered Information about the machine, the caller's name, and the type of problem into DEF's mainframe computer. In some cases, the call-taker attempted to help the customer fix the problem. However, call-takers were currently only able to avoid about 10 percent of the incoming emergency maintenance service calls. If the service call could not be avoided, the call-taker usu- ally stated the following script:"Depending upon the availability of our technicians, you should expect to see a technician some- time between now and (now +X)." ("X" was the target response time based on the model number and the zone.) This informa- tion was given to the customer because many customers wanted to know when a tech would arrive on site. Call-takers entered service call information on DEF's com- puter system, which then sent the information electronically to the regional dispatch center assigned to that customer location. (DEF had four regional dispatch centers with a total of about 20 dispatchers.) Service call information was printed on a small card at the dispatch center. About every hour, cards were ripped off the printer and given to the dispatcher assigned to that customer location. The dispatcher placed each card on a magnetic board under the name of a tech that the dispatcher believed would be the most likely candidate for the service call, given the location of the machine, the cur- rent location of the tech, and the tech's training profile. After completing a service call, techs called the dispatcher in the regional dispatch center, cleared the call, and received a new call assigned by the dispatcher. After getting the service call from a dispatcher, a tech called the customer to give an ex- pected time of arrival, drove to the customer site, diagnosed the problem, repaired the machine if parts were available in the van, and then telephoned the dispatcher for the next call. if the tech did not have the right parts for a repair, the tech informed the NSC, and the part was express mailed to the customer; the repair was done the next morning. dewa s mascope con ge r e the process chart for the . The em conversio per hour Nam often than now been Atex 4 be The process is performed 10 per hour Conave . The restaurant is open 313 days a year. 10 hours Complete the Summary coop-right) portion of the chan . What is the total labor contacted with the proces How can this operation be made more efficient process chartig OM Explore Pro Charts the m oved process. What are the annual If this new process is implemented 14. As a graduate assistant your duties include grading and keeping records for Operations Management cour home work assignments. Five sections for 10 students each are Bered each semester. A few graduate students attend tions and 4. Graduate students must complete some extra work so higher standards for each assignment. Every dent delivers (or is supposed to deliver directly to under the door of your office one homework assignment every Tuesday. Your job is to the homework, recond sort the papers by class section sont by student last namen of payta sonals ands www and that Making one ice cream con Summary Time Number Process Subject FIGURE 2.20 Process Chart for Making Ice Cream Activity of Steps Walk to one storage area Give it to server or customer Cones Ending: nr Strip Operation Transport Inspect Delay Store Repend Step Removt Step Step Description Distance Step No Time min) 020 0.05 0.10 0.05 0.20 0.50 0.15 0.05 0.10 0.75 0.75 0.25 0.05 0.05 Walk to cone storage area Remove empty cone Wato counter Place cone in holder Walk to sink area Ask dishwasher to wash scoop Wak to counter with clean scoop Pick up empty cone Walk to favor ordered Scoop ice cream from container Place ice cream in cone Check for stability Wak to order placement area Give server or customer the cone 10 11 13 14