Question: Ion exclusion is a process that uses ion-exchange resins to separate nonionic organic compounds from ionic species contained in a polar solvent, usually water. The
Ion exclusion is a process that uses ion-exchange resins to separate nonionic organic compounds from ionic species contained in a polar solvent, usually water. The resin is presaturated with the same ions as in the solution, thus eliminating ion exchange. However, in the presence of the polar solvent, resins undergo considerable swelling by absorbing the solvent. Experiments have shown that a nonionic solute will distribute between the bulk solution and solution within the resin, while ions only exchange.
A feed solution of 1,000 kg contains 6 wt% NaCl, 35 wt% glycerol, and 47 wt% water. It is to be treated with Dowex-50 ionexchange resin in the sodium form, after prewetting with water, to recover 75% of the glycerol. The data for the glycerol distribution coefficient,
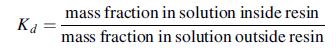
are from Asher and Simpson [J. Phys. Chem., 60, 518–521 (1956)]:
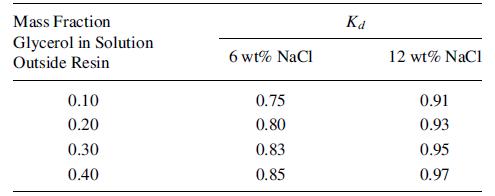
If the prewetted resin contains 40 wt% water, determine the kg of resin (dry basis) required.
Ka mass fraction in solution inside resin mass fraction in solution outside resin
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To determine the amount of resin required we need to calculate the volume of resin needed to absorb ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


