Unlike most other commonly used engineering materials, concrete experiences a characteristic marked increase in creep when it
Question:
Unlike most other commonly used engineering materials, concrete experiences a characteristic marked increase in “creep” when it is heated for the first time under load. To investigate this phenomenon, a study of the thermal strain behavior of concrete was conducted (Magazine of Concrete Research, Dec. 1985). Concrete specimens were prepared and a constant load applied to each. The test specimens were then heated to a specified temperature at a rate of 1°C per minute, with the specimens randomly assigned to one of five temperature settings (100°, 200°, 300°, 400°, and 500°C). For each specimen, the difference between the free (unloaded) thermal strain and load-induced thermal strain, called the total thermal strain, was calculated. The sample size, mean, and standard deviation of the total thermal strain values for each temperature setting are given in the table on p. 758. Thermal strain is recorded in units × 106.
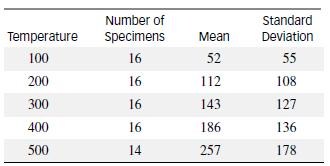
a. Find the totals for each temperature and the total for all 78 strain measurements. Then compute CM and SST.
b. Since we do not know the value of Σi=1n yi2, calculate SSE using the pooled method:
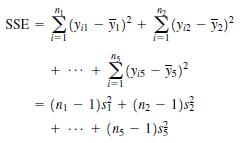
c. Find SS(Total).
d. Construct an analysis of variance table for the data.
e. Is there sufficient evidence to indicate that heating temperature affects the mean total thermal strain of concrete? Test using α = .01.
Step by Step Answer:

Statistics For Engineering And The Sciences
ISBN: 9781498728850
6th Edition
Authors: William M. Mendenhall, Terry L. Sincich





