Zoning is defined as the distribution of vacant land to residential and nonresidential uses via policy set
Question:
”Zoning” is defined as the distribution of vacant land to residential and nonresidential uses via policy set by local governments. Although the negative effects of zoning have been studied (e.g., distorting urban property markets, creating barriers to residential mobility, and impeding economic and social integration), little empirical evidence exists identifying the factors that encourage restrictive zoning practices. A study, reported in the Journal of Urban Economics (Vol. 21, 1987), developed a series of multiple regression models that hypothesize several determinants of zoning. One of the models studied took the form
E(y) = βo + β1x1 + β2x12 + β3x2
where
y = Percentage of vacant land zoned for residential use
x1 = Proportion of existing land in nonresidential use
x2 = Proportion of total tax base derived from nonresidential property
The model was fit to data collected for n = 185 municipal communities in northeastern New Jersey, with the following results:
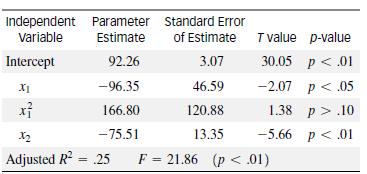
a. Construct a 95% confidence interval for β3. Interpret the result.
b. Test the hypothesis that a curvilinear relationship exists between percentage (y) of land zoned for residential use and proportion (x1) of existing land in nonresidential use.
c. Is the overall model statistically useful for predicting y?
d. Interpret the adjusted R2 value.
Step by Step Answer:

Statistics For Engineering And The Sciences
ISBN: 9781498728850
6th Edition
Authors: William M. Mendenhall, Terry L. Sincich





