Essilor is the result of the merger in 1972 of two French ophthalmological companies: Essel, a specialist
Question:
Essilor is the result of the merger in 1972 of two French ophthalmological companies: Essel, a specialist in corrective glass lenses, and Silor, a specialist in plastic lenses. Its products used to be exported through an international network of local distributors but, in 1979, the company embarked on a global strategy with the opening of its first international factory in the Philippines and the progressive acquisition of local distributors. Global development has occurred through a mixture of greenfield investments, acquisitions and alliances. Between 2008 and 2010 it acquired or allied with 83 companies worldwide, and since 2011 an additional 45 partnerships have been completed.
By 2019 Essilor was the number one player for corrective optical lenses with a global market share of around 25 per cent, a turnover of €7.5 billion with a profit of €757 million and 64,000 employees worldwide.
In January 2017, Essilor announced a merger with the Italian Luxottica Group, a global player in the design, manufacture and distribution of eyewear, creating a new entity with combined sales in excess of €17 billion, more than 140,000 employees and sales in more than 150 countries.
The Essilor corrective lenses business process is built around five elements:
● Retail optical shops (opticians) providing customer contact, with ophthalmologists determining the type of lens required. Essilor relies on 300,000 independent optical shops around the world.
● Prescription laboratories which deliver lenses to professional customers (opticians, independent optometrists, wholesalers and optical chain stores) as quickly as possible. Essilor’s network includes 449 prescription laboratories and numerous independent laboratories which distribute its lenses.
● Factories that manufacture the lenses either in a semi-finished or finished form. Finished lenses are mass produced, with both sides prepared in the plant. For semi-finished lenses, only the front of the lenses is prepared in the plant. The back and coatings are applied later by prescription laboratories, before the lenses are delivered to stores. Essilor has 33 factories worldwide.
● Distribution centres (14 in total) cover every stage in the distribution process: from the delivery of raw materials to plants to the delivery of finished products to optician customers. Essilor ships lenses from 14 production sites to 332 finishing laboratories, before they are distributed to 300,000 opticians around the world.
● Technology and innovation centres undertake R&D for the development of new lenses as well as the anticipation of future needs. Essilor employs more than 600 researchers, in ten R&D centres and laboratories, some of which are its own and others in the form of joint ventures or joint partnerships.
The interaction of these components is represented in Figure 5.16.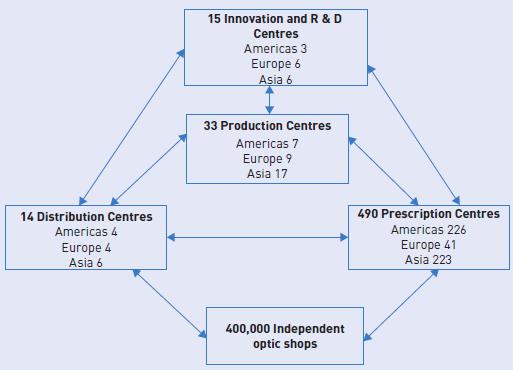
Essilor’s strategy is based on four pillars:
● Innovation in products, services and marketing as well as the quality of its relationships with opticians all over the world.
● The growth and development of middle markets in emerging countries. Figure 5.17 represents the company’s views about the perspective of market development.
● The pursuit of acquisitions and partnerships.
● Offering check-ups and supplying lenses in regions where access to optical care is difficult, in order to develop new markets.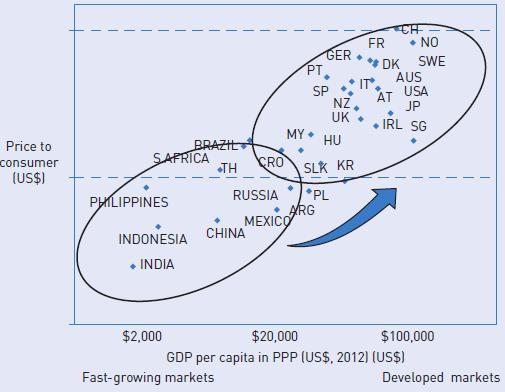
By December 2018, EssilorLuxottica, resulting from the merger of Essilor and Luxottica, claimed that it had formed a global leader in the design, manufacture and distribution of ophthalmic lenses, frames and sunglasses, combining complementary expertise in advanced lens technologies and in eyewear, creating a vertically integrated business positioned to serve the global market of eyecare and eyewear industry. EssilorLuxottica directly operates 7,700 stores (50 per cent in North America, 14 per cent in Europe, 20 per cent in Asia, Oceania, Africa and 16 per cent in Latin America) plus 3,200 franchises. The sales of the group amounted to €17.4 billion with a net profit of 11.8 per cent.
Questions:
1 Based on the description of the business system and Figure 5.16, what are the strategic and organizational challenges for Essilor’s global management?
2 From Figure 5.17 it appears that the most potentially attractive markets are in emerging countries.
Do you think that Essilor’s strategic pillars are compatible with these market prospects?
3 What issues would be involved in developing the business in China, India, Indonesia and Russia?
4 Can EssilorLuxottica as an integrated group become a dominant global player in eyewear and lens products? What are the benefits of vertical integration?
Step by Step Answer:

Global Strategic Management
ISBN: 9781350932968
5th Edition
Authors: Philippe Lasserre, Felipe Monteiro





