Question: A heat conduction problem is modeled using four onedimensional heat conduction elements, as shown in figure 4.6. All elements are of the same length, (L=1
A heat conduction problem is modeled using four onedimensional heat conduction elements, as shown in figure 4.6. All elements are of the same length, \(L=1 \mathrm{~m}\), cross sectional area of \(A=1 \mathrm{~m}^{2}\), and thermal conductivity of \(k=10 \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m} \cdot{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). The boundary conditions are given such that the temperature at node 1 is prescribed as \(T_{1}=20{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\), while there is no heat flux at node 5, that is, \(Q_{5}=0\). In addition, heat enters at nodes 2 with \(Q_{2}=500\) watts, and heat leaves from node 4 with \(Q_{4}=-200\) watts. Determine all nodal temperatures and the heat input at node 1 in order to maintain the temperature distribution.
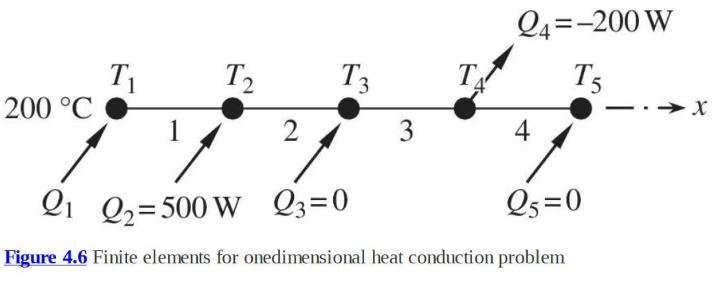
Q4=-200 W T5 200 C T 1 T2 T3 T 2 3 4 Q1 Q2=500 W 23=0 25=0 Figure 4.6 Finite elements for onedimensional heat conduction problem X
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


