Question: For the five bus system from Example 6.9, assume the transmission lines and transformers are modeled with just their per unit reactance (e.g., neglect their
For the five bus system from Example 6.9, assume the transmission lines and transformers are modeled with just their per unit reactance (e.g., neglect their resistance and B shunt values). If bus one is assumed to be an infinite bus, what is the equivalent (Thévenin) reactance looking into the system from the bus three terminal? Neglect any impedances associated with the loads.
Example 6.9
The synchronous generator in Figure 11.4 is initially operating in the steady-state condition given in Example 11.3 when a permanent three-phase-to-ground bolted short circuit occurs on line 1-3 at bus 3 . The fault is cleared by opening the circuit breakers at the ends of line \(1-3\) and line \(2-3\). These circuit breakers then remain open. Calculate the critical clearing angle. As in previous examples, \(\mathrm{H}=\) 3.0 p.u.-s, \(p_{m}=1.0\) per unit and \(\omega_{\text {p.u. }}=1.0\) in the swing equation.
Figure 11.4
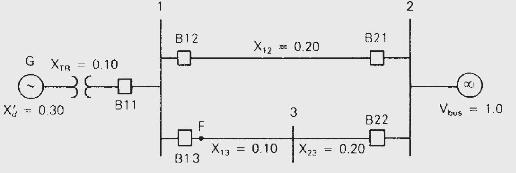
G XTA = 0.10 038 X = 0.30 B11 B12 F B13 X3 = 0.10 0.20 3 B21 X23 = 0.20 B22 2 XI Vous = 1.0
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


