Question: Ocean thermal energy conversion is a process that uses the temperature difference between the warm surface water of tropical oceans and the cold deep ocean
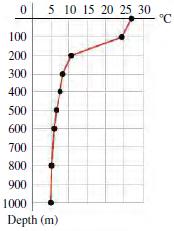
5 10 15 20 25 30 C 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Depth (m)
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
IDENTIFY and SET UP For a cycle Q H W Q C and e WQ H EXECUTE For this engine W... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


