Question: A summary of the balance sheet of Travelers Inn Inc. (TII), a company which was formed by merging a number of regional motel chains and
A summary of the balance sheet of Travelers Inn Inc. (TII), a company which was formed by merging a number of regional motel chains and which hopes to rival Holiday Inn on the national scene, is shown in the table: Travelers Inn: December 31, 2004 (Millions of Dollars)
These facts are also given for TII:
(1) Short-term debt consists of bank loans that currently cost 10 percent, with interest payable quarterly. These loans are used to finance receivables and inventories on a seasonal basis, so in the off-season, bank loans are zero.
(2) The long-term debt consists of 20-year, semiannual payment mortgage bonds with a coupon rate of 8 percent. Currently, these bonds provide a yield to investors of rd _ 12%. If new bonds were sold, they would yield investors 12 percent.
(3) TII's perpetual preferred stock has a $100 par value, pays a quarterly dividend of $2, and has a yield to investors of 11 percent. New perpetual preferred would have to provide the same yield to investors, and the company would incur a 5 percent flotation cost to sell it.
(4) The company has 4 million shares of common stock outstanding. P0 = $20, but the stock has recently traded in a range of $17 to $23. D0 = $1 and EPS0 _ $2. ROE based on average equity was 24 percent in 2004, but management expects to increase this return on equity to 30 percent; however, security analysts are not aware of management's optimism in this regard.
(5) Betas, as reported by security analysts, range from 1.3 to 1.7; the T-bond rate is 10 percent; and RPM is estimated by various brokerage houses to be in the range of 4.5 to 5.5 percent. Brokerage house reports forecast growth rates in the range of 10 to 15 percent over the foreseeable future. However, some analysts do not explicitly forecast growth rates, but they indicate to their clients that they expect TII's historical trends as shown in the table below to continue.
(6) At a recent conference, TII's financial vice president polled some pension fund investment managers on the minimum rate of return they would have to expect on TII's common to make them willing to buy the common rather than TII bonds, when the bonds yielded 12 percent. The responses suggested a risk premium over TII bonds of 4 to 6 percentage points.
(7) TII is in the 40 percent federal-plus-state tax bracket.
(8) TII's principal investment banker, Henry, Kaufman & Company, predicts a decline in interest rates, with rd falling to 10 percent and the T-bond rate to 8 percent, although Henry, Kaufman & Company acknowledges that an increase in the expected inflation rate could lead to an increase rather than a decrease in rates.
(9) Here is the historical record of EPS and DPS:
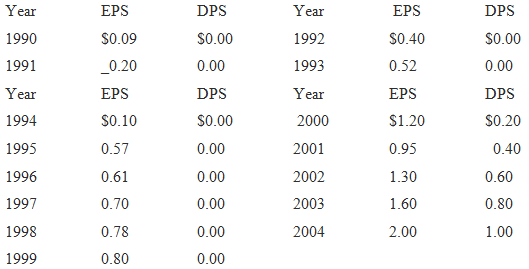
Assume that you are a recently hired financial analyst, and your boss, the treasurer, has asked you to estimate the company's WACC; assume no new equity will be issued. Your cost of capital should be appropriate for use in evaluating projects which are in the same risk class as the firm's average assets now on books.
Cash $ 10 Accounts payable $ 10 Accounts receivable 20 Accruals 10 Inventories 20 Short-term debt Current assets $ 50 Current liabilities $ 25 Net fixed assets Long-term debt Preferred stock 50 30 Common equity Common stock $ 10 Retained carnings 30 Total common equity 40 Total assets $100 Total liabilities and equity $100
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Several steps are involved in the solution of this problem Our solution follows Step 1 Establish a set of market value capital structure weights In this case AP and accruals and also shortterm debt ma... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
9-B-F-F-M (160).docx
120 KBs Word File



.PNG)