Question: The VAX/VMS operating system makes use of four processor access modes to facilitate the protection and sharing of system resources among processes. The access mode
The VAX/VMS operating system makes use of four processor access modes to facilitate the protection and sharing of system resources among processes. The access mode determines
• Instruction execution privileges: What instructions the processor may execute
• Memory access privileges: Which locations in virtual memory the current instruction may access
The four modes are as follows:
• Kernel: Executes the kernel of the VMS operating system, which includes memory management, interrupt handling, and I/O operations
• Executive: Executes many of the OS service calls, including file and record (disk and tape) management routines
• Supervisor: Executes other OS services, such as responses to user commands
• User: Executes user programs, plus utilities such as compilers, editors, linkers, and debuggers
A process executing in a less privileged mode often needs to call a procedure that executes in a more privileged mode; for example, a user program requires an operating system service. This call is achieved by using a change-mode (CHM) instruction, which causes an interrupt that transfers control to a routine at the new access mode. A return is made by executing the REI (return from exception or interrupt) instruction.
a. A number of operating systems have two modes, kernel and user. What are the advantages and disadvantages of providing four modes instead of two?
b. Can you make a case for even more than four modes?
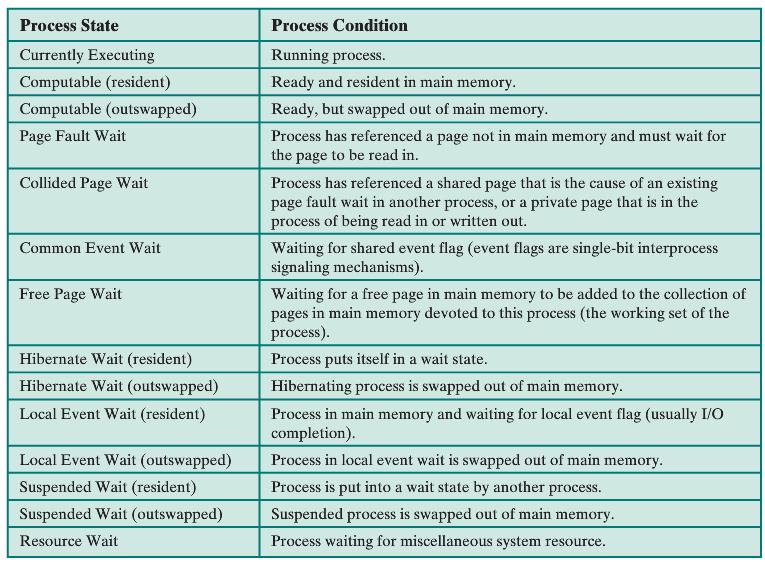
Process State Currently Executing Computable (resident) Computable (outswapped) Page Fault Wait Process Condition Running process Ready and resident in main memory Ready, but swapped out of main memory Process has referenced a page not in main memory and must wait for the page to be read in. Collided Page Wait Process has referenced a shared page that is the cause of an existing page fault wait in another process, or a private page that is in the process of being read in or written out. Waiting for shared event flag (event flags are single-bit interprocess signaling mechanisms) Common Event Wait Free Page Wait Waiting for a free page in main memory to be added to the collection of pages in main memory devoted to this process (the working set of the process. Process puts itself in a wait state Hibernate Wait (resident) Hibernate Wait (outswapped) Local Event Wait (resident) Hibernating process is swapped out of main memory Process in main memory and waiting for local event flag (usually IO completion) Local Event Wait (outswapped) Process in local event wait is swapped out of main memory Suspended Wait (resident) Suspended Wait (outswapped) Suspended process is swapped out of main memory. Resource Wait Process is put into a wait state by another process. Process waiting for miscellaneous system resource
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a The advantage of four modes is that there is more flexibility to control access ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
451-C-S-D-B-O-S (44).docx
120 KBs Word File


