Question: Three-lens systems In figure stick figure O (the Object) stands on the common central axis of three thin, symmetric lenses, which are mounted in the
Three-lens systems In figure stick figure O (the Object) stands on the common central axis of three thin, symmetric lenses, which are mounted in the boxed regions. Lens 1 is mounted within the boxed region closest to O, which is at object distance pr Lens 2 is mounted within the middle boxed region, at distance d12 from lens 1. Lens 3 is mounted in the farthest boxed region, at distance d12 from lens 2. Each problem in Table 34-10 refers to a different combination of lenses and different values for distances, which are given in centimeters. The type of lens is indicated by C for converging and D for diverging; the number after C or D is the distance between a lens and either of the focal points (the proper sign of the focal distance is not indicated). Find
(a) The image distance i3 for the (final) image produced by lens 3 (the final image produced by the system) and
(b) The overall lateral magnification M for the system, including signs. Also, determine whether the final image is
(c) Real (R) or virtual (V), (d) inverted (I) from object O or non-inverted (NI), and
(e) On the same side of lens 3 as object O or on the oppositeside.
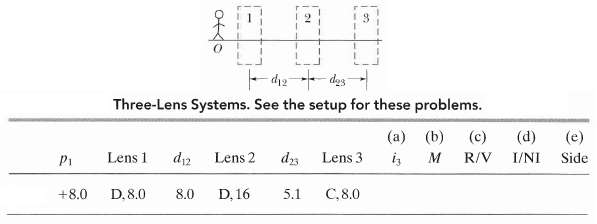
Three-Lens Systems. See the setup for these problems. (a) (c) (b) (d) (e) I/NI Side R/V Lens 1 di2 Lens 2 d3 Lens 3 is P1 +8.0 D. 8.0 D, 16 C,8.0 8.0 5.1
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
A converging lens has a positivevalued focal length and a diverging ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
2-P-L-O-I-M (117).docx
120 KBs Word File


